

CA SiteMinder® Federation Standalone Guide › User Directory Connections for Authentication › Create a Common View of the Same User Information Across Directories › Establish Connections to User Directories › Constant Use Case
Constant Use Case
This use case represents a scenario in which one user directory stores only customers, while another user directory stores only employees.
Note: Review the advanced user attribute mapping examples, which detail how to use different attribute mapping types to identify the same user attribute across different directory types.
The following illustration details how two constant attribute mappings can represent different values for different user directories.
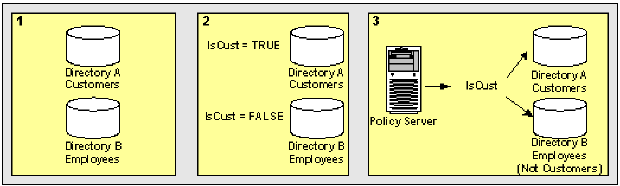
- Directory A only stores customers. Directory B only stores employees.
- IsCust is the common name that is mapped to different values in different directories:
- IsCust is mapped to TRUE in Directory A.
- IsCust is mapped to FALSE in Directory B.
- Reference IsCust when defining assertion attributes or NameID attributes. The common name lets the system determine whether a user is a customer, without regard to the particular directory in which the user is stored. The mapping indicates that every user in Directory A is a customer, while every user in Directory B is not a customer.
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


