

This use case shows how you can use an expression attribute mapping to simplify references to multiple user attributes in one directory. A protected resource needs the sort name of each user (last name,first name). The user directory does not uniquely reference this attribute. Instead, the directory does store the last name of each user as surname and the first name of each user as givenname.
The following illustration details how an expression attribute mapping can create a common view of the same user information.
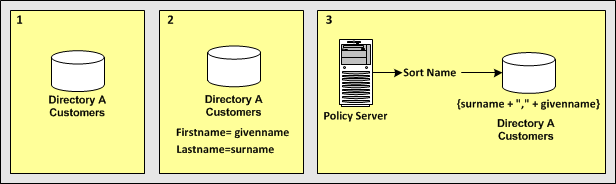
In the single user directory, a common name is mapped to an expression that creates the sort name using the user attribute names in the directory.
{surname + "," + givenname}
Note: The expression conforms to the syntax rules of a CA SiteMinder® expression. For complete syntax information, see the Attributes and Expression Reference appendix in the SiteMinder Policy Server Configuration Guide in the SiteMinder bookshelf.
Reference SortName when defining assertion attributes or NameID attributes that require the sort name of users without concern for the directory-specific schema.
The following examples show more complex user attribute mapping configurations.
The example deployment is a retail clothing company that uses two user directories of different types:
An internal LDAP user directory for employees only.
An ODBC user directory for customers only.
Each user attribute mapping is specific to the user directory for which it is defined.
The following table details how Directory A and Directory B identify the same user information. The accompanying use cases explain how to use different attribute mappings to define a common view of the same user information. The common view serves as a universal schema, which makes the directories operationally identical.
|
Attribute Description |
Directory A Attributes (LDAP) |
Directory B Attributes (ODBC) |
|
First name of each user |
givenname |
u_first_name |
|
Last name of each user |
surname |
u_last_name |
|
Sort name of each user (last name, first name) |
The user directory does not uniquely store the user attribute. |
sort_name |
|
User as a customer |
group:cn=customer,ou=groups,o=acme.com |
Users are always customers. |
|
Status of a user account |
AccountStatus attribute (a set of flags). Second bit is a disabled account. |
u_disabled |
Use two alias attribute mappings to represent the first name user attribute in Directory A and Directory B.
Deployment
User Directory A identifies the first name of users with givenname. Directory B identifies the first name of users with u_first_name.
Solution
FirstName
Alias
givenname
FirstName
Alias
u_first_name
When referencing users in Directory A, the FirstName is mapped to givenname. When referencing users in Directory B, the FirstName maps to u_first_name.
Use two alias attribute mappings to represent the last name user attribute in Directory A and Directory B.
Deployment
User Directory A identifies the last name of users with surname. Directory B identifies the last name of users with u_last_name.
Solution
LastName
Alias
surname
LastName
Alias
u_last_name
When referencing users in Directory A, the common view determines that the last name of users is identified by surname. When referencing users in Directory B, the common view determines that the last name is identified by u_last_name.
Use an expression attribute mapping and an alias attribute mapping to represent the sort name of a user in Directory A and Directory B.
Deployment
Solution
SortName
Expression
(surname + "," + givenname)
Note: The expression must conform to the syntax rules of an expression.
SortName
Alias
sort_name
When referencing users in Directory A, the sort name is calculated based on the specified expression. When referencing users in Directory B, the sort name is represented by the attribute sort_name.
Use a group and a constant attribute mapping to identify customers in Directory A and Directory B.
Deployment
cn=Customers,ou=Groups,o=acme.com
Solution
IsCustomer
Group
cn=Customers,ou=Groups,o=acme.com
IsCustomer
Constant
TRUE
When referencing Directory A, a user is considered a customer if they belong to cn=Customers,ou=Groups,o=acme.com. When referencing Directory B, every user is a customer.
Use a mask attribute mapping and an expression attribute mapping to identify user accounts that are disabled in Directory A and Directory B.
Deployment
Solution
IsDisabled
Mask
AccountStatus:2
The definition indicates that the bit pattern is stored in AccountStatus, and the bit mask is 2 (decimal).
IsDisabled
Expression
(u_disabled = "y")
u_disabled is a Boolean expression.
When referencing Directory A, the bit pattern determines if a user is disabled. When referencing Directory B, the expression determines if a user is disabled.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|