

Administer Triggers › How to Configure and Use Triggers
How to Configure and Use Triggers
For external applications that cannot issue SOAP calls to start CA Process Automation processes, CA Process Automation provides four predefined triggers. You can configure triggers to enable the initiation of processes from any of the following:
- An event from a Catalyst connector
- A received file
- An email
- An SNMP trap
After you configure a file trigger or a mail trigger, you can create XML contents. The XML contents start configured CA Process Automation processes with parameters from the external applications. The XML content can be put in a file and placed in the configured directory or sent as an email to the configured account. The trigger invokes the process specified in the XML content when specified criteria are met. The process instance invoked by the trigger also populates process datasets with the values specified in the XML content.
After you configure an SNMP trap trigger in CA Process Automation, external applications can send SNMP traps to CA Process Automation. When CA Process Automation receives an SNMP trap that matches object IDs (OIDs) and the payload values filter, the configured process starts. The dataset of the triggered process receives the trap information.
After you configure a Catalyst event subscription, external Catalyst Connectors can send events to CA Process Automation. When CA Process Automation receives a Catalyst event that matches the filter, the configured process starts with the event properties available in the process dataset.
Unlike settings that the environment inherits from the Domain by default, triggers are disabled at both the environment level and Orchestrator levels by default. To enable CA Process Automation triggers that are set at Domain level, set inheritance from the Domain at the environment level. Then, set inheritance from the environment at the Orchestrator level. Alternatively, you can override inherited values and configure trigger values at the environment and Orchestrator levels.
Use the following approach to implement triggers:
- Configure triggers at the Domain level. These configurations are not inherited by default. Configure triggers only if you plan to accept process initiation from external applications and only for the trigger types you plan to receive.
- At the environment level, where the trigger status is Disabled, take one of the following actions:
- Leave disabled for trigger types that are not applicable.
- Change the status to Inherit from the Domain for Environments where Domain configuration is applicable.
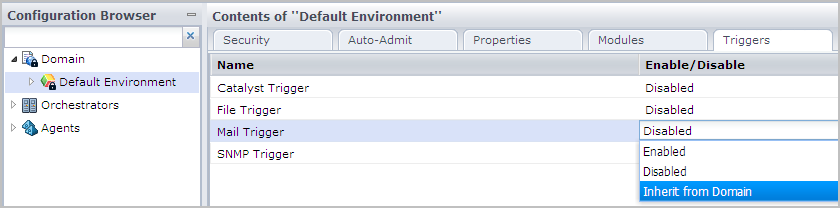
- Change the status to Enabled and configure the triggers at this level, where needed.
- At the Orchestrator level, where the trigger status is Disabled, take one of the following actions:
- Leave disabled for trigger types that are not applicable.
- Change the status to Inherit from Environment. If you select this option, values are picked up from the environment at runtime if the triggers are defined at the environment level. Otherwise, the values defined at the Domain level are used.
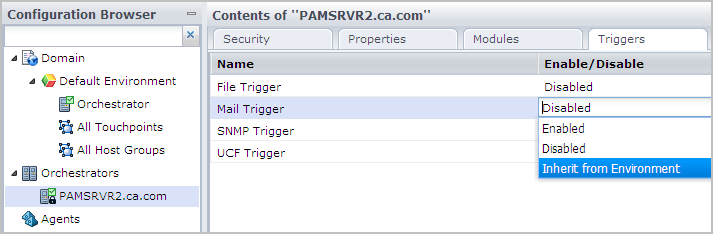
- Change the status to Enabled and edit the properties.
- CA Process Automation searches the configured directory, the configured email account, and the configured port for content that matches the corresponding trigger criteria.
- External applications create the input for configured triggers:
- For a file trigger or mail trigger, they create valid XML content. XML content specifies the path to the starting process, the credentials, the time to start, and the initialization parameter values.
- For an SNMP trap trigger, they send a valid SNMP trap to port 162 with values that match the configured criteria.
- External applications send triggers to CA Process Automation as part of automation processing.
- CA Process Automation processes new content and starts the configured CA Process Automation process with the values passed by the external application.
- Monitor the process instance invoked by the trigger sent from the external process. You can monitor the running process through process watch. You can view the values passed by the trigger in the page containing dataset variables for the associated trigger type.
More information:
Configure File Trigger Properties at the Domain Level
Configure SNMP Trigger Properties at the Domain Level
Activate Triggers for an Orchestrator
Configure Mail Trigger Properties at the Domain Level
Configure Catalyst Trigger Properties at the Domain Level
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|



