

CA ADS applications are developed and executed by using a variety of online tools. The following tools are used to develop the sample Department application.
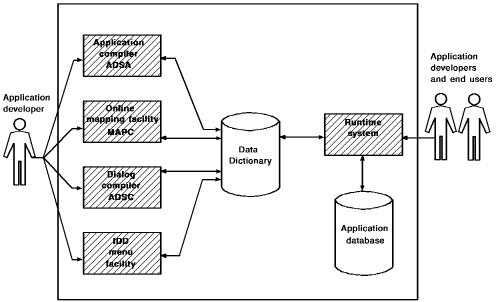
As an application developer, you can execute the application at any time in the development cycle by using the runtime system. Additionally, end users execute the application by using the runtime system.
Components defined by using ADSA, ADSC, MAPC, and the IDD menu facility are all stored in the data dictionary.
You can access any of the above development tools from CA IDMS/DC, the CA IDMS teleprocessing (TP) monitor, or DC/UCF, the teleprocessing monitor interface. Additionally, you can transfer directly among ADSA, ADSC, MAPC, and the IDD menu facility by using the transfer control facility (TCF).
Transfer Control Facility You can use TCF at any time during an application development session to suspend one development tool and transfer to another.
For example, while using ADSC to define a dialog, you might remember that the related map definition is still incomplete. You can suspend your ADSC session, transfer directly to MAPC to complete the map, and then transfer back to ADSC to resume your suspended dialog-definition session.
Task Codes
To invoke a development tool from CA IDMS/DC or DC/UCF (DC/UCF), or TCF, specify the task code associated with the tool. A task code is a unique invocation name defined for a development tool at system generation time. Sample task codes for CA ADS development tools are presented in the table below. The task codes shown allow you to operate under TCF and, therefore, switch from tool to tool.
Note: If you are not operating under TCF, you cannot switch to another tool without first returning to DC/UCF.
Task codes can vary from site to site.
|
Development tool |
Sample task code |
Site task code |
|---|---|---|
|
CA ADS application compiler (ADSA) |
ADSAT |
|
|
CA ADS dialog compiler (ADSC) |
ADSCT |
|
|
IDD menu facility |
IDDMT |
|
|
Online mapping (MAPC) |
MAPCT |
|
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|