

When you select Application Server from the EAR File Assemble Details panel, the following dialog appears:
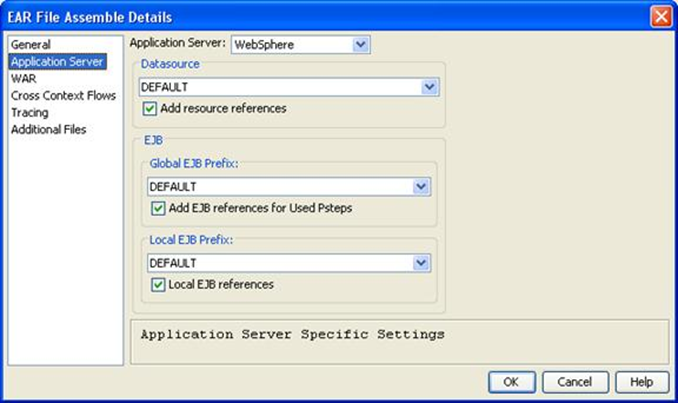
The fields in the Application Server dialog are as follows:
Specifies the application server that you are targeting. The options in the drop-down list are:
Specifies the JNDI name of the CA Gen database you want to find.
Allows a datasource to be entered.
Specifies a prefix name to be used when performing JNDI lookups for EJBs that are defined outside of this EAR file.
Allows a Global EJB Prefix to be entered.
Specifies a prefix name to be used when performing JNDI lookups for EJBs defined in the same EAR file and running in the same JVM.
Local EJB references
Defines all of the Server Beans that the client code can call and allow the actual location of the Server Beans to be obtained when the client module is installed. The client code can use Local References, Remote References, or direct JNDI lookup to find the Server Bean. Local References execute faster.
When Local EJB references is checked, the EJB references are local rather than remote. The local references must refer to Server Beans in the same EAR file as the referring client and the Beans must be installed on the same JVM as the client. The local and remote reference definitions are stored in the XML descriptors of the calling code.
Note: The JMS Configuration fields on this dialog, which are used for Cross-Context Flows, will be disabled when the Generic option is selected from the Application Server drop-down. JMS configuration is unique to each Application Server and Gen has only been certified with WebLogic and WebSphere. Therefore, the Assemble process only supports specifying JMS configuration information for these two Application Servers. This does not preclude the use of Cross-Context Flows when the Generic option is selected, but Application Server specific customizations will have to be made to the EAR file outside of the Assemble process, in addition to the usual JMS configuration steps that are required on the Application Server itself.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|