

The first task in specifying selection conditions for a READ (and a READ EACH) action is to add attribute conditions.
The following READ Action Statement shows the attribute condition format in a READ (and READ EACH) statement.
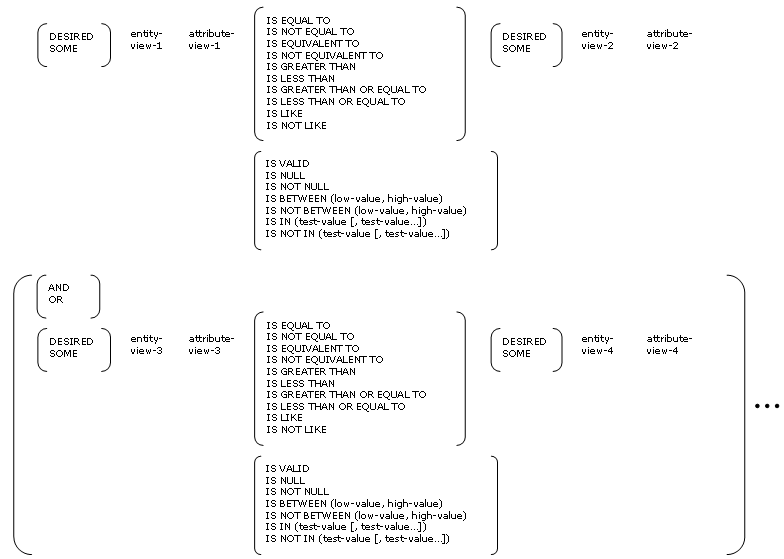
An attribute-view is an expression consisting of one or more of the following in valid combinations:
An attribute condition must include an attribute of an entity action view on at least one side of the comparison operator. Comparisons must involve combinations of operands of the same domain (character, number, date, or time).
Each reference to an attribute of an entity action view is preceded by a view qualifier (DESIRED, SOME, CURRENT, or THAT). DESIRED refers to one of the views being read. SOME refers to any other entity action view. THAT refers to a view previously referenced by SOME. CURRENT can refer to the current occurrence of any entity action view.
The following examples show the usage of attribute conditions for a READ statement in Action Diagrams. The first example discovers whether the business knows about the CUSTOMER who is attempting to place an ORDER (in the process Take Order):
READ customer WHERE DESIRED customer name IS EQUAL TO requesting customer name
The following example READs all customers whose name begins with Q:
READ customer WHERE SUBSTR(DESIRED customer name, 1,1) IS EQUAL TO "Q"
The last statement READs an explicitly indexed repeating group view and references a subscript for the group view which is incremented by one.
READ customer_order WHERE input customer order IS EQUAL TO SUBSCRIPT OF group_customer_order + 1
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|