

The commands shown in the following table are available from the monitor interface. They allow you to view log data about serviced systems while you continue to monitor events in the event/message area.
The prompt used in the monitor interface is Command:, and it appears at the bottom of your screen as shown in the following figure.
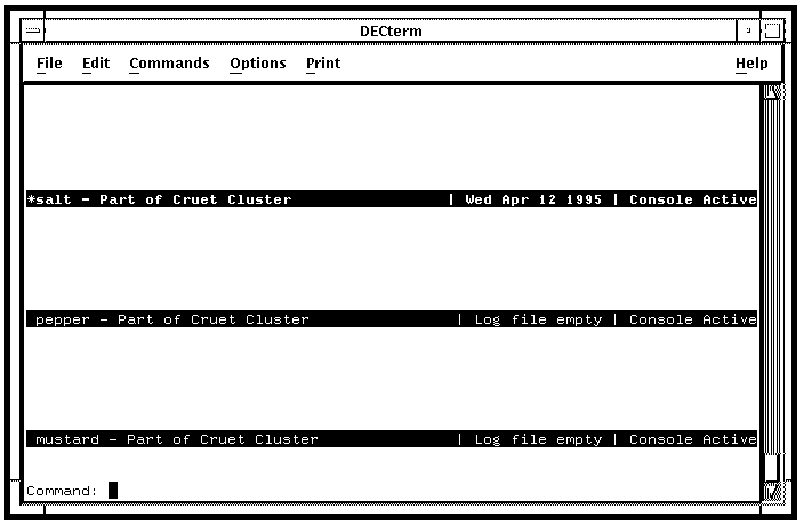
Note: If a command takes system-name as an optional argument, and you do not specify the name of a system when executing, the command performs the requested operation on the system with its banner line highlighted in bold reverse video and bearing an asterisk (*) to the left of its system name.
|
Command |
Arguments |
Description |
Example |
|---|---|---|---|
|
BOTTOM |
|
Moves you to the end of the log data for the currently displayed system. |
BOTTOM |
|
BREAK |
[system-name] |
Sends the halt sequence or a break signal. The behavior of the serviced system depends on its type. |
BREAK DANCE |
|
CONNECT |
[system-name] |
Connects your terminal to the system you specify and allows you to communicate with it as though you were on its local console. |
CONNECT SALT |
|
CYCLE |
Interval |
Switches you to one log window mode, and cycles the one log window displaying each of the systems being monitored in turn at intervals in seconds that you specify |
CYCLE 20 |
|
DIALOG |
dialog_filename [system-name, system-name…] |
Performs a predefined interaction with the specified system or systems according to the information you supply in the dialog file. This command has a further subset of commands. See the section, Performing a Dialog with a Serviced System, later in this chapter |
DIALOG SHUTDOWN.DAT SALT,PEPPER |
|
DOWN |
[lines] |
Displays the next screen of console log data. |
DOWN |
|
EXIT |
|
Exits the monitor interface, and returns you to the operating system command line. This command is synonymous with the quit command. |
EXIT |
|
FIND |
One of TIME, TEXT, EVENT, direction FORWARD or BACKWARD. See Finding Historical Console Log Data, later in this chapter. |
Finds and displays the portion of the log with the specified time, text or event, starting the search in the specified direction. The default direction is BACKWARD. |
FIND TIME +2 |
|
HALT |
[system-name] |
Sends the halt sequence or a break signal. The behavior of the serviced system depends on its type. |
HALT SALT |
|
HELP |
|
Displays the monitor interface help. |
HELP |
|
NEW |
|
Creates a new log window. You can use this command to view the log of multiple systems concurrently. The number of windows that can be depends on the number of rows on the display terminal. Once created, use the VIEW command to display the required system. |
NEW |
|
NEXT |
|
Changes the selected log window to the next log window when you are using multiple log windows |
NEXT |
|
ONE |
|
Changes from viewing multiple system's log data to a single systems log data. |
ONE |
|
OUTPUT |
“string” |
Outputs the specified quoted text string to the console of the currently highlighted system. No action results if you do not specify a string. |
OUTPUT “logout” |
|
PREVIOUS |
|
Changes the selected log window to the previous log window when you are using multiple log windows. |
PREVIOUS |
|
QUIT |
|
Exits the monitor interface, and returns you to the operating system command line. This command is synonymous with the EXIT command. |
QUIT |
|
REMOVE |
|
Removes the currently highlighted log window from the display. No action results from this command if only one log window is visible. |
REMOVE |
|
REVIEW |
[system-name] [pathname] |
Allows you to view previously archived log data for the named system. If the pathname is specified, the data will be found in that location. If not, it will be found in the default archive directory. This command does not extract the information. If you want to extract the information, use the EXTRACT command (see Chapter 6, “Using Console Manager From the Command Line Interface,” and Chapter 7, “Using Console Manager From the C3 Interface.” |
REVIEW SALT |
|
scriptname |
|
A pseudo-command used to invoke a file containing valid monitor interface commands. |
See Using Scripts, later in this chapter. |
|
SELECT |
[system-name] |
Place the cursor into the log window of the specified system. All subsequent commands are executed on that serviced system. This is the same as using the CONNECT command, except that all other log windows remain on the screen and are updated in real time. Escape sequences in the selected log window are not interpreted. |
SELECT SALT |
|
SET HALT_KEY |
key |
Allows you to change the Halt (Break) key. This is the keystroke that will indicate you wish to halt the system. |
SET HALT_KEY CTRL_P |
|
SET BREAK_KEY |
key |
Allows you to change the default Break key. |
SET BREAK_KEY CTRL_P |
|
SET ESCAPE_ KEY |
key |
Allows you to change the default Escape key from CTRL_G to the control character of your choice. |
Key |
|
SET EXIT_ KEY |
key |
Allows you to change the default Exit key from CTRL_E to the control character of your choice |
SET EXIT_KEY CTRL_A |
|
SET REFRESH_ |
Key |
Allows you to define the default Refresh key to repaint the screen after an interruption |
SET REFRESH_KEY CTRL_W |
|
SET TIMESTAMPS |
{ON | OFF} |
Allows you to specify whether or not timestamps associated with each line of console data are displayed at the left side of the log window. |
SET TIMESTAMPS ON |
|
SET WIDTH |
Width |
Sets the column width of the screen to the specified value. Valid values are 80 and 132. |
SET WIDTH 132 |
|
SHOW |
[{keys| systems}] |
Creates a special log window which displays either the current Halt, Escape, Exit and Refresh key definitions, or a list of the systems being monitored by this user session. |
SHOW KEYS |
|
TOP |
|
Moves you to the beginning of the log data for the currently displayed system. |
TOP |
|
TWO |
|
Allows you to view the log data for two of your serviced systems at the same time. |
TWO |
|
UNLOCK |
[system-name] |
Places the user currently connected into read only mode. |
UNLOCK SALT |
|
UP |
[lines] |
Displays the previous screen of console log data. |
UP |
|
VIEW |
[system-name] |
Places the latest console log data for the specified serviced system in the currently selected console log display area |
VIEW SALT |
|
Copyright © 2010 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|