

Guidelines for performing interaction clustering:
The following steps are for performing interaction clustering:
This simply involves executing the cluster command while accessing the Entity Type Used By Elementary Process Matrix.
The following illustration shows the matrix before the clustering operation, with expected effects included.
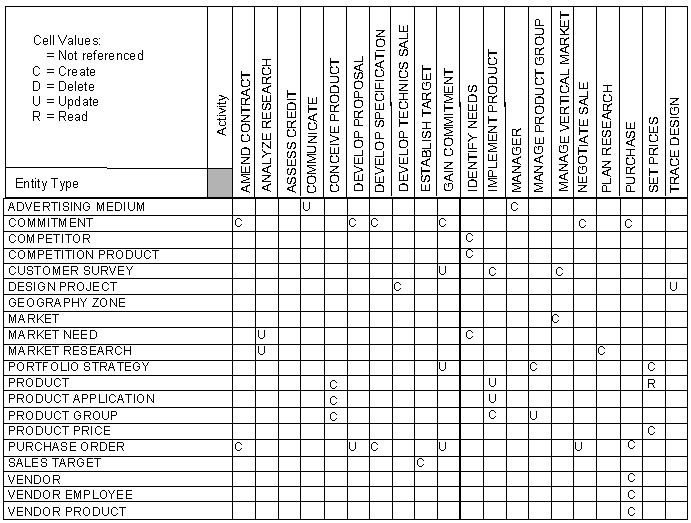
For clarity, only C and U expected effects are shown, but the matrices can contain R and D as well. You should complete any missing expected effects before clustering.
Following clustering, expect to see a matrix more like the one in the illustration which shows one specific R to illustrate an example issue.
Sometimes the clusters automatically calculated by CA Gen are not as tidy as those in the following illustration.
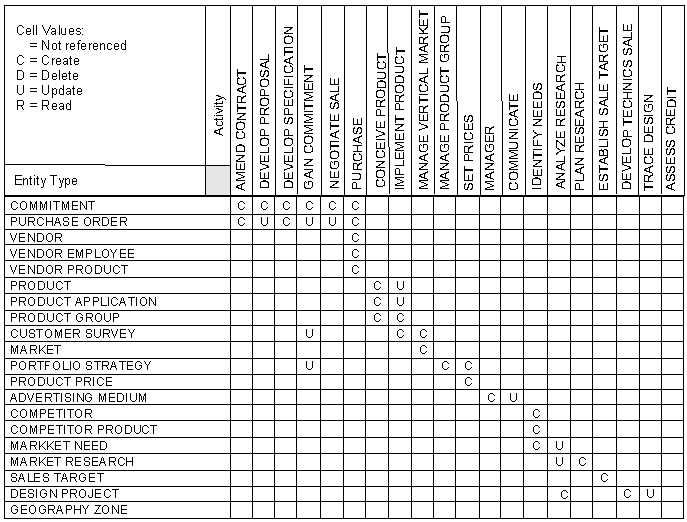
You may need to investigate the definitions of processes and expected effects where processes appear in unexpected clusters and to intervene to allocate dense or unclustered processes or entity types. If this is the case, use rhw Matrix Processor facilities to move rows and columns around until the appearance of the clusters is improved.
Finally, the results of clustering are used to identify business systems. Consider the following illustration.
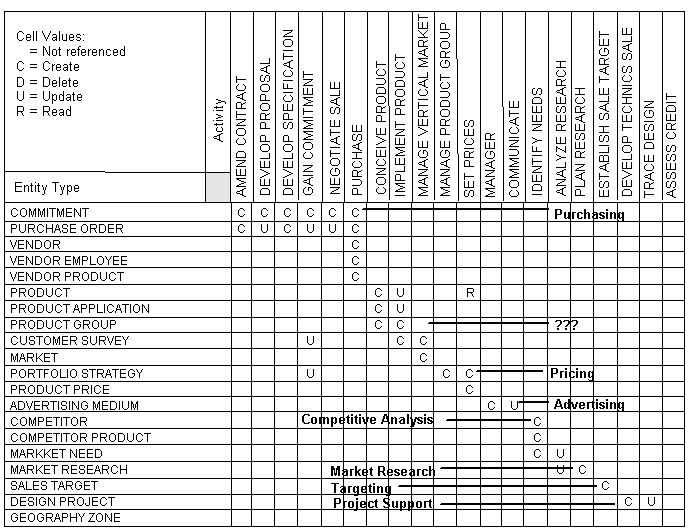
The results of interaction clustering in the illustration show that the analysis model includes eight design clusters:
At least four issues need to be resolved:
It would be technically simpler to implement the second design area cluster Product Development before the Pricing design area. However business priorities may require Pricing to be implemented first. If so, then an existing file of products will have to be accessed through bridging software until the second cluster is resolved and the fully defined product is implemented.
Before assuming that the cluster analysis is complete, consider comparing the results of this analysis with any existing Business Systems Architecture developed during Planning. Although the business systems just derived are much more detailed than those predicted during Planning, their shapes should be roughly the same. If not, reconcile the two views, either by revising the Business Systems Architecture or by changing the grouping of processes.
Since a business system is the basis for a development project, it must be sized appropriately for that project. Combine clusters to produce an appropriate development scope that:
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|