

This section contains the following topics:
About ODBC/JDBC Access in CA User Activity Reporting Module
Creating ODBC and JDBC Queries for Use with CA User Activity Reporting Module
Example: Use an Access Filter to Limit ODBC Results
Example: Preparing to Use ODBC and JDBC Clients with Crystal Reports
Use Crystal Reports to Access the Event Log Store with ODBC
Accessing Events from Crystal Reports with JDBC
Remove the ODBC Client on Windows Systems
CA User Activity Reporting Module provides read-only ODBC and JDBC access to the event log store to allow you to do the following things:
These features allow you to create and format your own custom reports using log information already retrieved by CA User Activity Reporting Module. In addition, you can retrieve data for use with your existing correlation engines, malware detection packages, and other functions.
After installing the CA Technologies-supplied client on the system you plan to use to access the event log store, configure a connection to the data source and then begin retrieving data. The subscription service installs the server-side components.
Support for ODBC and JDBC in CA User Activity Reporting Module is limited to read-only queries using SELECT statements on the following tables:
Build your SELECT statements using ANSI SQL format and rules. The server-side components contain a SQL parsing engine. The parser implements a large portion of the entry level SQL as defined in the X3.135-1992, "Database Language SQL" specification. The parser also supports SQL features from ANSI SQL99 and commercial databases like Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle. The parser is also compliant with the ODBC minimal grammar specification.
The common event grammar serves as the schema for this table. See the CEG Reference Guide for details on the schema.
CA User Activity Reporting Module does not support stored procedure calls, data control language (DCL) commands, or data definition language (DDL) commands.
CA User Activity Reporting Module does not support the following data manipulation language (DML) operations and keywords:
The following are the supported SQL functions for use in building SELECT statements:
CA User Activity Reporting Module processes an ODBC or JDBC client-initiated query in the following way:
Any errors encountered are returned directly to the client driver.
Any errors encountered are returned to the client driver.
As part of its query state management, CA User Activity Reporting Module provides support for aliased result column names. Therefore you can display common event grammar fields in your custom reports using your own labels and headings.
The alias names are persisted and used for proper data mapping when the CA User Activity Reporting Module server transfers a result set back to the client driver.
To manage disk space, CA User Activity Reporting Module limits the number of result rows. CA User Activity Reporting Module uses a subset of the Transact-SQL TOP keyword with only a fixed value. The percentage variant of the keyword is not supported.
The default TOP value used in CA User Activity Reporting Module is 5000 rows, with a maximum value of 50,000 rows.
The following are the ODBC and JDBC error codes that can occur while accessing the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store. Each error message provides specific error details.
The accompanying error message provides details about the unsupported functionality.
The accompanying error message provides details.
The following errors are SQL statement execution errors:
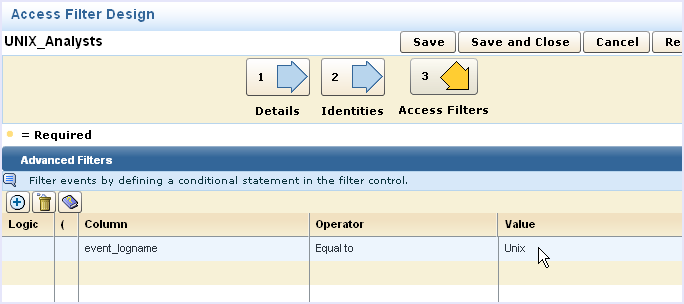
You can create an access filter to limit the data returned to an ODBC access request. When members the named application group accesses CA User Activity Reporting Module event data using the ODBC client, they see only the information allowed by the filter.
This example assumes that you have an application group named UNIX_Analysts and that you want to restrict all members of that group to see only UNIX events from the event log store. The filter created in this example limits event data views from within the CA User Activity Reporting Module user interface and external requests through ODBC.
More information about access filters is available in the online help.
To create an access filter
A list of identities matching your search criteria appear in a shuttle control so that you can select the desired identities.
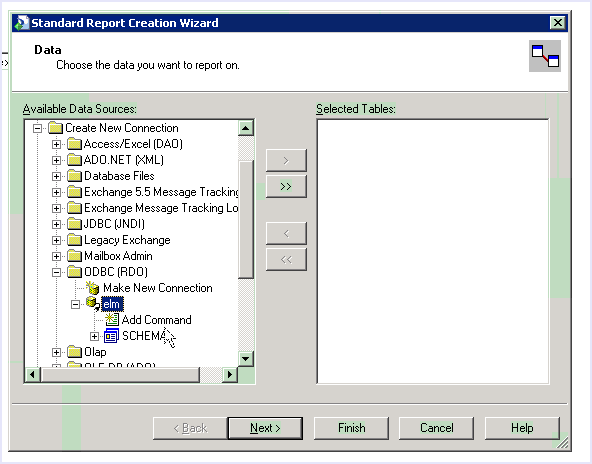
Preparing for ODBC or JDBC client access to CA User Activity Reporting Module events using BusinessObjects Crystal Reports involves the following steps:
If you are sure that the event log store already contains events of the type queried, you can omit this step.
Note: This process and the related example assume that you are familiar with creating basic SQL statements and using Crystal Reports. More information about using Crystal Reports is available in the BusinessObjects online help.
Use this procedure to create a user account named ELM_Access for use with your JDBC and ODBC clients.
CA User Activity Reporting Module users with the dataaccess permission can use ODBC or JDBC to access event data. Each of the default user roles provided with CA User Activity Reporting Module has this permission. For this example, you could create a user with any of the default CA User Activity Reporting Module roles - Administrator, Analyst, or Auditor.
To create the new user
Note: In a production environment, you would assign the least permission needed for a user to access the data. You can limit access in many ways including user roles, access policies, and access filters.
Use this procedure to configure the CA User Activity Reporting Module ODBC and JDBC service settings.
Note: Changes made to this area cause a restart of the server-side processes that enable ODBC and JDBC communications.
To configure the ODBC Service
Use this procedure to create a data source named "CA-ELM."
Note: Install the ODBC client before you can configure the data source.
To create a data source
The DataDirect OpenAccess SDK ODBC Driver Setup utility displays a configuration screen.
querytimeout=600 (seconds);queryfederated=true;queryfetchrows=1000;offsetmins=0;suppressNoncriticalErrors=false
If your connection parameters are correct, a successful connection message appears.
The following are the descriptions of the ODBC data source fields as they relate to CA User Activity Reporting Module:
Create a name for this data source. Client applications that want to use this data use this name to connect to the data source.
Specifies the name of the CA User Activity Reporting Module server which the client connects. You can use either a hostname or an IPv4 address.
Specifies the TCP service port on which the CA User Activity Reporting Module server listens for ODBC client connections. The default value is 17002. The value you set here must match the setting for the ODBC Server service or the connection fails.
Leave this field blank, otherwise the connection attempt fails.
Specifies whether to use encryption on the communications between the client and the CA User Activity Reporting Module server. The default value is to have SSL enabled. The value you set here must match the setting for the ODBC Server service or the connection fails.
Specifies the connection properties for use with the event log store. The delimiter between the properties is a semi-colon with no space. The recommended default values include the following:
Specifies the timeout value in seconds with no data returned after which the query is closed. The following is the syntax for this property:
querytimeout=300
Specifies whether to perform a federated query. Setting this value to false performs a query only on the CA User Activity Reporting Module server to which the database connection is made. The following is the syntax for this property:
queryfederated=true
Specifies how many rows to retrieve in a single fetch operation, if the query is successful. The minimum value is 1, and the maximum value is 5000. The default value is 1000. The following is the syntax for this property:
queryfetchrows=1000
Specifies the offset for the timezone for this ODBC client. A value of 0 uses GMT. You can use this field to set your own timezone offset from GMT. The following is the syntax for this property:
offsetmins=0
Indicates the Interface Provider’s behavior in case of noncritical errors such as a database not responding or a host not responding.
The following is the syntax for this property:
suppressNoncriticalErrors=false
Before you can use Crystal Reports with the CA User Activity Reporting Module JDBC client, you must first provide some configuration settings. After you configure the Crystal Reports XML configuration file, you are ready to prepare and send ANSI SQL standard queries to the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store.
To configure Crystal Reports settings for JDBC
jdbc:ca-elm://127.0.0.1:17002;encrypted=1;ServerDataSource=Default;CustomProperties=(querytimeout=600;queryfederated=true;queryfetchrows=1000;offsetmins=0;suppressNoncriticalErrors=false)
See the section on JDBC URL considerations for more explanation of these parameters.
Refer to the documentation supplied with Crystal Reports for additional information on setting connection parameters in that product.
com.ca.jdbc.openaccess.OpenAccessDriver
When using the JDBC client to access event data stored in CA User Activity Reporting Module, you need both the JDBC Classpath and a JDBC URL. The JDBC Classpath names the driver JAR file locations. The JDBC URL defines the parameters the classes in the JARs use when they load.
The following is a complete, sample JDBC URL:
jdbc:ca-elm://127.0.0.1:17002;encrypted=1;ServerDataSource=Default;CustomProperties=(querytimeout=600;queryfederated=true;queryfetchrows=1000;offsetmins=0;suppressNoncriticalErrors=false)
The following descriptions explain the URL components:
Defines the protocol:subprotocol string that designates the JDBC driver provided with CA User Activity Reporting Module.
Names the IP address that represents the CA User Activity Reporting Module server whose data you want to access. The port number is the port to use for the communications, and must match the setting in the CA User Activity Reporting Module ODBC Service configuration panel. If the ports do not match, the connection attempt fails.
Determines whether SSL encryption is used for the communications between the JDBC client and the CA User Activity Reporting Module server. The default value is 0, not encrypted, and does not require specification in the URL. Setting encrypted=1 turns encryption on. Set the connection to encryption explicitly. In addition, this setting must match what you configure in the CA User Activity Reporting Module ODBC Service dialog or the connection attempt fails.
Specifies the name of the data source. Set this value to Default for access to the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store.
These properties are the same as the ODBC custom properties. If you do not specify them explicitly, the default values shown in the example URL apply.
For the example query to display, create some relevant events by causing failed activities like the following:
You can use the ODBC access feature to query CA User Activity Reporting Module event data from a third party reporting tool like BusinessObjects Crystal Reports. After you complete the required installation and configurations, you are ready to prepare and send ANSI SQL standard queries to the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store.
The database schema for the event log store is the common event grammar (CEG). The CA User Activity Reporting Module online help contains a CEG reference component to help you create queries. You can also review the underlying SQL statements for the out-of-the-box queries, but use ANSI SQL to access the database from outside CA User Activity Reporting Module.
To access event data from Crystal Reports
For example, you could create the following query:
SELECT source_username as source_username , SUM(event_count) AS FUNC_SUM_event_count FROM view_event WHERE event_result = 'F' GROUP BY source_username ORDER BY FUNC_SUM_event_count DESC;
A report template appears in which to place the data columns returned by the query.
Running the query displays the values associated with the fields. You can use Crystal Reports to create any visualization or customization you need.
The following tasks enable you to use JDBC to access the event log store:
Note: This process and the related example assume that you are familiar with creating basic SQL statements and about how to use Crystal Reports. More information about using Crystal Reports is available in the BusinessObjects online help.
Before you can use the JDBC driver to access events from a CA User Activity Reporting Module server, copy the related JAR files to the server you want to use for access.
To copy the files
The report package you are using requires a specific location for these files. Consult the documentation supplied with your application.
You can use the JDBC access feature to query CA User Activity Reporting Module event data from a third party reporting tool like BusinessObjects Crystal Reports.
The database schema for the event log store is the common event grammar (CEG). The CA User Activity Reporting Module online help contains a CEG reference component to help you create queries. You can also review the underlying SQL statements for the out-of-the-box queries, but use ANSI SQL to access the database from outside CA User Activity Reporting Module.
To access event data from Crystal Reports
Note: Use the value, Default, for the Database name in the Connection Information dialog when it appears.
SELECT source_username as source_username , SUM(event_count) AS FUNC_SUM_event_count FROM view_event WHERE event_result = 'F' GROUP BY source_username ORDER BY FUNC_SUM_event_count DESC;
Running the query displays the values associated with the fields. You can use the Crystal Reports tools to create any visualization or customization you need.
On all Windows platforms, the Remove option of the client installation package deletes product files and entries in the system information.
Important! If you created any IP source files under the Local ODBC Client installation directory, back the files up to a different location before removing the ODBC client on a Windows system.
If you have the Local ODBC Client installed and want to install it in a different location, use the Remove option. Remove the installed the Local ODBC Client, then re-install it in the new location.
To remove the ODBC client
To uninstall the JDBC client, remove the installation directory.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|