

This section contains the following topics:
Understanding Differences in Architectures
Configuring CA Technologies Adapters
Sending CA Audit Events to CA User Activity Reporting Module
Importing Data from a SEOSDATA Table
In planning how you to use CA Audit and CA User Activity Reporting Module together, you first should understand the differences in the architectures and the effects they have on your network structure.
CA User Activity Reporting Module uses an embedded event log store, and provides an Agent Explorer to configure and manage agents. New technology coupled with a common event grammar allows for faster event throughput to storage while supporting a higher number of event sources. The common event grammar allows CA User Activity Reporting Module to normalize events from many different event sources into a single database schema.
CA User Activity Reporting Module integrates at a certain level with CA Audit, but by design it is not completely interoperable. CA User Activity Reporting Module is a new and separate server infrastructure that can run in parallel with CA Audit, with the following event handling considerations:
|
CA User Activity Reporting Module does... |
CA User Activity Reporting Module does not... |
|---|---|
|
Receive event logs sent from CA Audit clients and iRecorders using configurable listeners. |
Directly access event logs stored in the CA Audit collector database. |
|
Provide a utility to import event log data stored in the CA Audit collector database (SEOSDATA table). |
|
|
Use agents to send event logs only to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server infrastructure. |
|
|
Permit CA User Activity Reporting Module agents and CA Audit clients with iRecorders to run on the same physical host. |
Allow CA User Activity Reporting Module agents and CA Audit clients with iRecorders on the same host to access the same log sources simultaneously. |
|
Use its built-in Agent Explorer to manage only CA User Activity Reporting Module agents. During side-by-side operation of the two systems, CA Audit uses its Policy Manager only to manage CA Audit clients |
|
|
|
Migrate CA Audit data held in table collectors, report templates or custom reports, alert policies, collection/filtering policies, or role-based access control policies |
The following illustration shows a simplified CA Audit implementation:
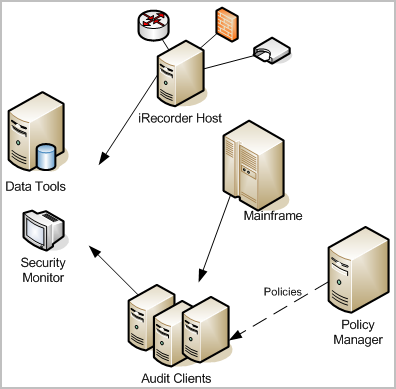
In some enterprise deployments of CA Audit, event data is stored by the collector service in a relational database running on the Data Tools server. A database administrator monitors and maintains this database, and works with a system administrator to ensure that the correct policies are in place to gather desired events, and to exclude events that are not needed.
Solid lines in this diagram show events flowing from CA Audit clients, recorder, and iRecorder hosts to the Data Tools server, or in some cases to an optional security monitor console. A dashed line represents the control flow between the Policy Manager server and the clients using policies.
The Data Tools server provides basic reporting and visualization utilities as well as event storage. Custom queries and reports are the norm in enterprise implementations, and require significant time to create and to maintain.
This network topology allows for collection of a variety of event types from different devices, applications, and databases. You have central storage of collected events that is usually part of, or managed by, the Data Tools server which also offers some reports.
However, you need additional capabilities to scale your solution to handle rapidly increasing event volumes. You need to generate reports that demonstrate compliance with a variety of federal and international regulations. And you need to be able to find those reports quickly and easily.
The following illustration shows a basic two-server CA User Activity Reporting Module implementation:
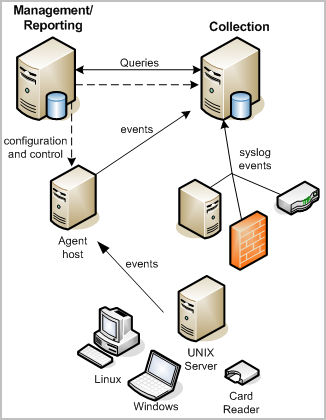
A CA User Activity Reporting Module system can have one or more servers, where the first installed server is the management server. There can be no more than one management server in a system, but you can have multiple systems. The management server maintains content and configuration for all CA User Activity Reporting Module servers and performs user authorization and authentication.
In a basic two-server implementation, the management server also performs the role of a reporting server. A reporting server receives refined events from one or more collection servers. The reporting server handles on demand queries and reports as well as scheduled alerts and reports. The collection server refines collected events.
Each CA User Activity Reporting Module server has its own internal event log store database. The event log store is a proprietary database that uses compression to enhance storage capacity, and to allow queries of active database files, files marked for archival, and defrosted files. No relational DBMS package is required for event storage.
The collection CA User Activity Reporting Module server can receive events directly using its default agent, or from an agent residing on the event source. Agents can also reside on a host that acts as a collector for other event sources in the network as for a VPN concentrator or router host.
Solid lines in this diagram represent event flows from event sources to agents to the collection server to the reporting role of the management/reporting server. The dashed lines show configuration and control traffic between the CA User Activity Reporting Module servers and from the management role of the management/reporting server to the agents. You can use any CA User Activity Reporting Module server in the network to control any agent in the network, so long as the CA User Activity Reporting Module servers were registered with the same application instance name in management server during installation.
Agents use connectors (not shown) to collect events. A single agent can manage several connectors to collect multiple, different types of events at the same time. This means that a single agent deployed on an individual event source can collect different types of information. The CA User Activity Reporting Module server also offers listeners that allow event collection from other CA Technologies applications using the existing iRecorder and SAPI recorders from your CA Audit network.
You can federate CA User Activity Reporting Module servers to scale your solution and to share reporting data between them without having that data transported out of bounds. This can give you a network-wide view of compliance while still following regulations about maintaining physical data locations.
Subscription updates to predefined queries and reports mean that you no longer have to maintain queries and reports manually. Supplied wizards allow you to create your own custom integrations for third-party devices and applications not yet supported.
The following diagram shows a typical CA Audit network with CA User Activity Reporting Module added to leverage its high volume event handling and compliance-based reporting capabilities:
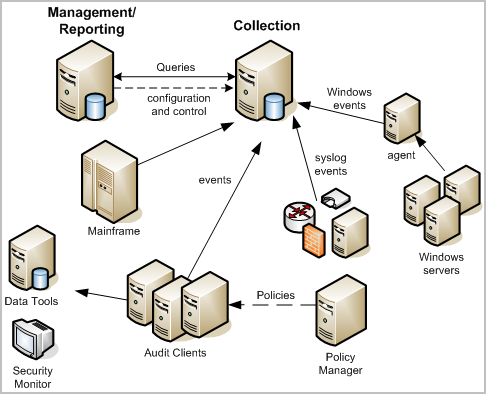
CA User Activity Reporting Module uses an integrated Agent Explorer, an embedded event log store, and single user interface to centralize and simplify log collection. CA User Activity Reporting Module agent technology coupled with the common event grammar allows for faster event throughput to storage while handling a higher number of event sources. A single agent can handle multiple connectors to event sources, simplifying agent management tasks, and taking advantage of predefined integrations for popular or common event log sources.
In this implementation, the CA User Activity Reporting Module collection server receives the syslog, iTechnology-based, and SAPI recorder events directly. The collection server receives events from Windows event sources through a separate Windows-based CA User Activity Reporting Module agent. You may have several agents deployed in your network, each of which can gather many different kinds of event data through its connectors. This can help to reduce event traffic to the SEOSDATA database and leverage the queries and reports available in CA User Activity Reporting Module. A simple policy rule change allows the CA Audit clients to send collected events to both the Data Tools server and the CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
In addition to higher throughput, CA User Activity Reporting Module offers out-of-the-box queries and reports that help you to demonstrate compliance with regard to multiple standards like PCI (DSS) and SOX. When you couple the predefined queries and reports with your existing CA Audit and CA SCC implementation, you can leverage your investments in your custom solutions while taking advantage of CA User Activity Reporting Module reports and higher throughput.
The CA Technologies Adapters are a group of listeners that receive events from legacy components such as CA Audit clients, iRecorders, and SAPI recorders as well as event sources that send events natively through iTechnology.
Set the CA Technologies adapter configuration options prior to changing the configurations of CA Audit policies or iRecorders. This ensures that the listener processes are operating before the events arrive. This prevents incorrectly mapped event data.
If you send events through an iRecorder to CA Audit, or if you use a CA Audit client with iRecorder, you will use the CA User Activity Reporting Module SAPI adapters to receive events. To send events to CA User Activity Reporting Module, you will modify an existing CA Audit policy for CA Access Control events. You can add either a Collector action or a Route action to an existing rule.
Refer to the SAPI source documentation for instructions on how to reconfigure to send events directly to CA User Activity Reporting Module.
If you plan to install a standalone iRecorder or you plan to use an existing iRecorder, you will configure the iTech Event Plugin to receive the events. For example, use this approach if you do not have CA Audit installed, but want to use a CA Technologies iRecorder to gather events from a supported event source. The process includes the following steps:
The SAPI services are generally used to receive events from existing CA Audit clients and integrated products. CA User Activity Reporting Module uses two instances of a SAPI listener service, one installed as the SAPI Collector, the other as the SAPI Router.
The SAPI modules use the iGateway daemon for command and control. The modules act as a SAPI router and a SAPI collector and uses either static ports or dynamic ports through the portmapper.
Use the SAPI collector when sending events from CA Audit clients so that you can use the built in fail-over support in the Audit Collector action.
Use the SAPI router when sending events from CA Audit clients using the Route action, or when sending events from SAPI recorders or integrations that support sending events directly to a CA Audit client. In this case you would configure the remote sender as if the CA User Activity Reporting Module server is the CA Audit client.
The SAPI listener opens its own port and listens passively for new events to be sent to it. Each instance of the SAPI module has its own configuration that specifies the following:
After receiving the event, the module submits it to the mapping library and then CA User Activity Reporting Module inserts it into the database.
Important: The data mapping library may contain one or more mapping files with the same name but different version numbers. The different files support varying release levels of the same event source, such as an operating system, a database, and so forth. It is critical that you select only one, version-relevant mapping file when you configure the SAPI collector or router.
If two files with the same name are present in the list of selected mapping files, the mapping engine uses only the first one in the list. If that is not the right file for the incoming event stream, the mapping engine cannot map the events correctly, This can, in turn, cause queries and reports to show information that doesn't include the mis-mapped events, or any events at all.
Use this procedure to configure the SAPI collector service.
You can modify CA Audit policies that use Collector actions to send events to a CA User Activity Reporting Module server in addition to, or in place of, sending events to the CA Audit collector database. Configure this service before you modify Audit policies to ensure that no events are lost.
To configure the SAPI collector service
The Log Collection subtab displays by default.
Use this procedure to configure a SAPI router service.
You can modify CA Audit policies which use Route actions to send events to a CA User Activity Reporting Module server in addition to, or in place of, routing events to other destinations. You can also redirect SAPI recorder events to go directly to the SAPI router listener by modifying their configuration files. Configure this service before you modify Audit policies or SAPI recorder configurations to ensure that no events are lost.
To configure the SAPI router service
The Log Collection subtab displays by default.
The iTechnology event plug-in receives events sent through the iGateway event handling mechanism. Configure the iTechnology event plug-in if any of the following are true for your environment:
After receiving an event, this service submits it to the mapping library after which CA User Activity Reporting Module inserts the mapped event into the event log store.
Use this procedure to configure the iTechnology event plug-in to receive from iRecorders and other iTechnology event sources.
Use the iTechnology plug-in when you configure a standalone iRecorder to send its events to a CA User Activity Reporting Module server. Configure this service before you configure or install an iRecorder to ensure that no events are lost.
Note: If you want to send events from an external client to the iTechnology Event Plug-in listener, you must send these events only to the secondary CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
To configure the iTechnology event plug-in
The Log Collection subtab displays by default.
The event plug-in service is preconfigured to include most of the major data mapping files.
You can integrate CA User Activity Reporting Module with your existing CA Audit implementation in the following ways:
CA User Activity Reporting Module receives events from iRecorders through the iTech Event Plugin Listener. You must configure the listener before you change the iRecorder's configuration. If you do not do this, you may lose event data. After you configure the Listener, use this procedure to configure the iRecorder to send events to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
iRecorders that are installed on the same computer as a CA Audit client send events to the client directly. For those machines, you should use the SAPI collector or router adapters.
Important! A standalone iRecorder can only send its events to a single destination. If you reconfigure an iRecorder using the procedure that follows, events are stored only in the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store. If you need to retain events in both the event log store, and the CA Audit Collector database, modify a rule action on an existing policy, or create a new policy for a CA Audit client.
To configure the iRecorder to send events to CA User Activity Reporting Module
<RouteEvent>true</RouteEvent>
This entry tells the iGateway to send its events, including all iRecorder events, to the host named in the RouteHost tag pair.
<RouteHost>CA_ELM_hostname</RouteHost>
This entry tells the iGateway to send its events to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server using its DNS name.
This action forces the iRecorder to use the new settings and starts the flow of events from the iRecorder to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
Use this procedure to enable a CA Audit client to send events to both CA User Activity Reporting Module and the CA Audit collector database. By adding a new target to the Route or Collector actions on an existing rule, you can send collected events to both systems. As an alternative, you can also modify specific policies or rules to send events only to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
CA User Activity Reporting Module collects events from CA Audit clients using the CA Audit SAPI Router and CA Audit SAPI Collector listeners. Collected events are stored in the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store only after you push the policy to the clients and it becomes active.
Important: You must configure the CA User Activity Reporting Module listeners to receive events before you modify and activate the policy. If you do not do this configuration first, you may have incorrectly mapped events if events arrive between the time that the policy becomes active and the listeners can correctly map the events.
To modify an existing policy rule's action to send events to CA User Activity Reporting Module
You can also use the Route action to create a rule to send events to a CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
For a CA User Activity Reporting Module implementations with two or more servers, you can enter a different CA User Activity Reporting Module host name or IP address in the Alternate Host Name field to take advantage of <Aus>'s automatic failover feature. If the first CA User Activity Reporting Module server is not available, CA Audit automatically sends events to the server named in the Alternate Host Name field.
Make any needed modifications to the rule and ensure that it compiles correctly before you activate it.
Use this procedure to enable an r8 SP2 CA Audit client to send events to both CA User Activity Reporting Module and the CA Audit collector database. By adding a new target to the Route or Collector actions on an existing rule, you can send collected events to both systems. As an alternative, you can also modify specific policies or rules to send events only to the CA User Activity Reporting Module server.
CA User Activity Reporting Module collects events from CA Audit clients using the CA Audit SAPI Router and CA Audit SAPI Collector listeners. Collected events are stored in the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store only after you push the policy to the clients and it becomes active.
Important: You must configure the CA User Activity Reporting Module listeners to receive events before you modify and activate the policy. If you do not do this configuration first, you may have incorrectly mapped events between the time that the policy becomes active and the listeners can correctly map the events.
To modify an existing r8 SP2 policy rule's action to send events to CA User Activity Reporting Module
The policy appears in the Details pane, displaying its rules.
The rule appears, with its actions displayed, in the Details pane.
The Edit Rule wizard appears.
After the policy is approved, the Policy Manager Distribution Server's settings determine when the new policy is distributed to the audit nodes. You can review the activation log to check on a policy's activation status.
If you have an existing CA Audit Data Tools server with a Collector database, you have a SEOSDATA table that contains event data. To run your CA Audit and CA User Activity Reporting Module systems side-by-side and view reports on data you have already collected, you may want to import data from your SEOSDATA table.
You can run the SEOSDATA import utility to perform an import of event data from your Collector database to a CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store. Typically, you import event data immediately after you deploy a CA User Activity Reporting Module server. If you are integrating the two systems, you may decide to perform the import of data more than once, depending on your use and network configuration.
Note: Importing data from the SEOSDATA table does not remove or modify any of the data stored there. The import procedure copies the data, parses it, and maps it into the CA User Activity Reporting Module event log store.
The import utility, LMSeosImport, uses a command line interface and supports both the Windows and Solaris operating systems. The utility performs the following actions:
The events are mapped to the common event grammar (CEG) that forms the basis for the event log store's database tables. You can then use the predefined queries and reports to gather information from your stored events.
Running the LMSeosImport utility against a live SEOSDATA table is not recommended, but at times may be unavoidable. If you must run the utility against a live database, the utility imports only a certain section of data. This happens because events that are added to the database after the LMSeosImport utility starts are not imported during that import session.
For example, if you do not specify the -minid and -maxid parameters in the command line, when the utility starts, it queries the database for the minimum and maximum existing entry IDs. The utility then bases its queries and import activities on those values. Events inserted into the database after the utility starts have entry IDs outside that range and so are not imported.
When an import session completes, the utility displays the last entry ID that it processed. You may need to run more than one import session to get all of your events, or you may choose to wait for a period of lower network and event activity to run the import utility. You can run additional import sessions, if needed, using the last session's ending entry ID as the new session's -minid value.
Use this process for importing data from a collector database (SEOSDATA table) to ensure the best results:
Note: The LMSeosImport utility requires the etsapi and etbase supporting libraries that are supplied with the CA Audit Client.
You may decide to run the preview import again to refine the command line options, if needed.
Before you can import data from your SEOSDATA table, you must copy the LMSeosImport utility from the CA User Activity Reporting Module Application installation DVD-ROM to your Solaris Data Tools server.
Note: The LMSeosImport utility requires the presence of the etsapi and etbase libraries. These files are part of the base Data Tools server installation. Before you try to use the LMSeosImport utility, ensure that the CA Audit install directory is included in your system PATH statement. The default directory is opt/CA/eTrustAudit/bin.
Before you run the utility, set the following environment variables with the env command:
To copy the utility
The utility is ready for use after you copy it to the designated directory and set the required environment variables. There is no separate installation to run.
Before you can import data from your SEOSDATA table, you must copy the LMSeosImport utility from the CA User Activity Reporting Module Application installation DVD-ROM to your Windows Data Tools server.
Note: The LMSeosImport utility requires the presence of the etsapi and etbase dynamic link libraries. These files are part of the base Data Tools server installation. Before you try to use the LMSeosImport utility, ensure that the directory, Program Files\CA\eTrust Audit\bin, is included in your system PATH statement.
To copy the utility
The utility is ready for use after you copy it to the designated directory. There is no separate installation to run.
The LMSeosImport utility offers a variety of command line arguments that let you control which events are migrated. Each event in the SEOSDATA table is a row, and has a unique entry ID to identify it. You can use the import utility to retrieve a report that lists several different kinds of useful information. The report lists the number of events in the SEOSDATA table (as a number of entry IDs), event counts by log type, and the date ranges of the events. The utility offers a retry option in case an error occurs during the import of an event.
You can also run a preview job to see what the import results would be with a specific command structure. Preview jobs do not actually import data. This allows you to refine your command line options prior to the actual migration.
You can run the migration utility more than once using different parameters to import different kinds of data. For example, you may choose to migrate your data in several, tailored sessions based on a range of entry IDs, the log type, or specific date ranges.
Note: The utility does not offer import tracking of prior sessions. It is possible to duplicate data in your CA User Activity Reporting Module database if you run the command with the same parameters more than once.
For the best results, break up your import by log type (using the -log option) or by entry ID (using the -minid and -maxid options) to improve import performance. Use the -retry option to help recover from any errors that may occur during event import. The utility uses a default -retry value of 300 seconds to maximize import success.
The LMSeosImport utility supports the following command line syntax and options:
LMSeosImport -dsn dsn_name -user user_name -password password -target target_name {-sid nnn -eid nnnn -stm yyyy-mm-dd -etm yyyy-mm-dd -log logname -transport (sapi|itech) -chunk nnnn -pretend -verbose -delay -report -retry}
Specifies the name of the host server where the SEOSDATA table resides. This parameter is required.
Specifies a valid user ID that has at least Read access to the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is required.
Specifies the password for the user account specified with the -user parameter. This parameter is required.
Specifies the hostname or IP address of the CA User Activity Reporting Module server to receive the migrated events from the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is required.
Indicates the starting ENTRYID used when selecting events from the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is optional.
Indicates the ending ENTRYID used when selecting events from the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is optional.
Indicates the starting time (in YYYY-MM-DD format) used when selecting events from the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is optional.
Indicates the ending time (in YYYY-MM-DD format) used when selecting events from the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is optional.
Specifies that the utility should select only event records with this specified logname. This parameter is optional. If the logname contains spaces, then it must be enclosed in double quotes.
Specifies the transport method that should be used between the import utility and CA User Activity Reporting Module. The default transport method is sapi.
Specifies the number of event records to select from the SEOSDATA table on each pass. The default value is 5000 events (rows). This parameter is optional.
Outputs the results of the event record selections to STDOUT, but does not actually import the data. This parameter is optional.
Specifies the port number to use if you set the transport option to SAPI and you configured the CA User Activity Reporting Module SAPI router to use a fixed port value (without using the portmapper).
Specifies that the utility sends detailed processing messages to STDOUT. This parameter is optional.
Specifies the number of seconds to pause between the processing of each event. This parameter is optional.
Displays a report of time range, ENTRYID range, and Log counts in the SEOSDATA table. This parameter is optional.
Specifies the total number of seconds during which retry attempts are made each time an error occurs during the import of an event. Processing continues when the send of that event is successful again. The utility automatically uses a default value of 300 seconds. You do not have to enter the parameter unless you want to specify a different value. Messages related to the retry status are sent to STDOUT.
You can use the following command line examples to create your own custom command when using the SEOSDATA import utility.
To run an import of records between ENTRYIDs 1000 and 4000
Enter the command line:
LMSeosImport -dsn eAudit_DSN -user sa -password sa -target 130.200.137.192 -minid 1000 -maxid 4000
To run an import of records for only NT-Application events
Enter the command line:
LMSeosImport -dsn eAudit_DSN -user sa -password sa -target 130.200.137.192 -log NT-Application
Running a SEOSDATA event report prior to the actual import of data provides you with needed information about the events in the table. The report shows the event time range, the event count per log type, and the entry ID range. You can use the values displayed in the report to refine your command line options for either a preview command or the actual import command.
To show a report of current SEOSDATA event information on Windows
LMSeosImport -dsn eAudit_DSN -user sa -password sa -target <Log_Manager_host_name> -report
The generated report display is similar to the following example:
SEOSProcessor::InitOdbc: successfully attached to source [eAudit_DSN] ---------- SEOSDATA Event Time Range ---------- Minimum TIME = 2007-08-27 Maximum TIME = 2007-10-06 ---------- Event Count Per Log ---------- com.ca.iTechnology.iSponsor : 3052 EiamSdk : 1013 NT-Application : 776 NT-System : 900 ---------- SEOSDATA EntryID Range ---------- Minimum ENTRYID : 1 Maximum ENTRYID : 5741 Report Completed.
You can run a test import with output to STDOUT to preview the import results without actually importing or migrating data. This is a good way to test the command line parameters you have entered for either a one-time migration or for a regularly scheduled import batch job.
To run a test import to preview import results
Solaris: /opt/CA/SharedComponents/iTechnology
Windows: \Program Files\CA\SharedComponents\iTechnology
For Solaris:
./LMSeosImport.sh -dsn eAudit_DSN -user sa -password sa -target <Log_Manager_host_name_or_IP> -minid 1000 -maxid 4000 -preview
For Windows:
LMSeosImport.exe -dsn eAudit_DSN -user sa -password sa -target <Log_Manager_host_name_or_IP> -minid 1000 -maxid 4000 -preview
You can use this procedure to import event data from a Collector database that resides on a Windows Data Tools server.
To import events from a SEOSDATA table on a Windows server
LMSeosImport.exe -dsn <dsnname> -user <UID> -password <password> -target <targethostname> <optional flags>
You can use this procedure to import event data from a Collector database that resides on a Solaris Data Tools server.
To import events from a SEOSDATA table on a Solaris server
./LMSeosImport -dsn <dsnname> -user <UID> -password <password> -target <targethostname> <optional flags>
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|