

Bind‑time security is used to prevent unauthorized remote regions from accessing your CICS region. A security check is performed when a request is made to establish a connection (bind) between two CICS regions. The bind process is accomplished in one of two ways:
In CICS, MRO bind‑time security checks to see if the local region ACID has permission to bind with the remote APPLID. To determine this, CICS obtains the NETNAME value for each remote CONNECTION as illustrated below.
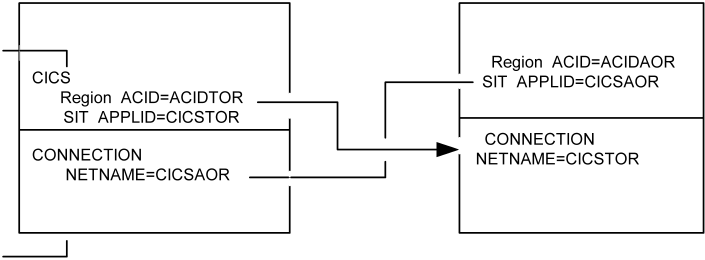
Before the bind, the local region ACID ACIDTOR is checked for the resource IBMFAC(DFHAPPL.cicsaor) and the remote region ACID is checked for IBMFAC(DFHAPPL.cicstor). In the TOR environment, this permission would be administered using the commands shown below.
TSS ADDTO(cicsdept) IBMFAC(DFHAPPL)
TSS PERMIT(acidtor) IBMFAC(DFHAPPL.cicsaor)
For the AOR, grant permission as shown below.
TSS PERMIT(acidaor) IBMFAC(DFHAPPL.cicstor)
External bind‑time security for ISC is established by specifying BINDSECURITY(YES) in the CICS definition for the link. Each pair of communicating systems must have the same bind password for the link between them to be successful.
A bind password consists of up to 16 hexadecimal digits (0 through F), and can be surrounded by quotes. If you specify less then 16 digits, the bind password is padded on the right with hexadecimal zeros.
The following figure shows how to define external bind‑time security for ISC connections.
RDO definition DEFINE CONNECTION(sysidnt) GROUP(groupname) ACCESSMETHOD(VTAM) NETNAME(name) PROTOCOL(APPC) SINGLESESS(N) SECURITYNAME(name) BINDSECURITY(YES)
For CICS, CA Top Secret lets you define:
TSS ADDTO(APPCLU) LINKID(netid.source‑applid.target‑applid)
SESSKEY(pass)
The VTAM ACTSTRxx NETID value
The local APPLID from the local region SIT
The remote APPLID from the remote region SIT
The 16‑digit hexadecimal password
An example of how external bind‑time security works for ISC connections is shown in the following figure:
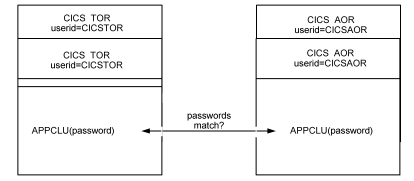
Specifying a bind password causes CA Top Secret to perform password checking each time a session is bound. If the two bind passwords do not match, the session is not bound, and the system reacts to a user request for a session with SYSIDERR (an IBM CICS error message).
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|