

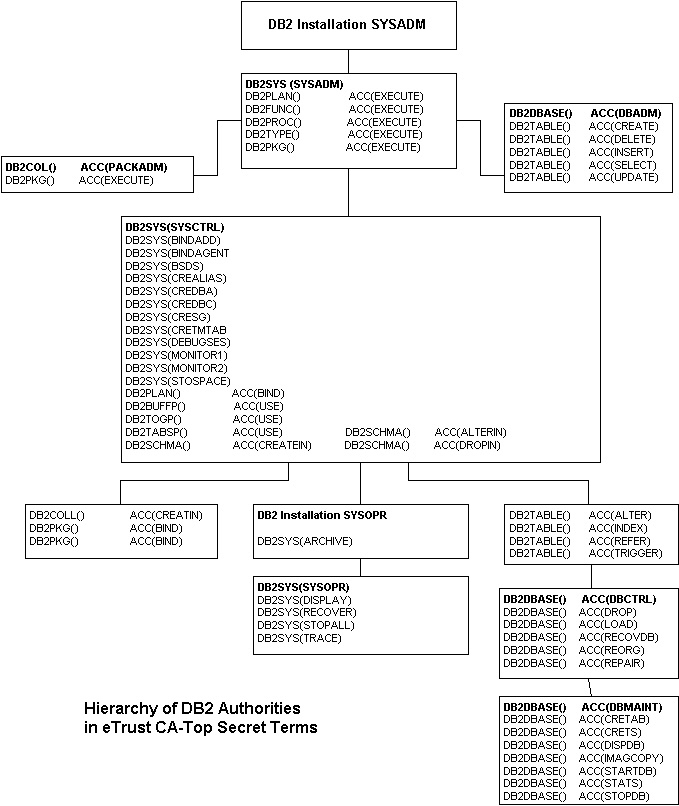
 Within native DB2, privileges are grouped into authorities, which are structured into a branched hierarchy of authorities. CA Top Secret Option for DB2 supports this concept of an authority hierarchy and illustrates this process in the following illustration.
Within native DB2, privileges are grouped into authorities, which are structured into a branched hierarchy of authorities. CA Top Secret Option for DB2 supports this concept of an authority hierarchy and illustrates this process in the following illustration.
The previous illustration shows the hierarchy of DB2 authorities with regard to CA Top Secret Option for DB2 terminology. DB2 authorities are highlighted with shadowed text. Each authority consists of both its own group of privileges (the non‑shadowed privileges in the same box as the DB2 authority) and all of the privileges in lower connected boxes.
Native DB2 privileges are defined as CA Top Secret Option for DB2 privileges or access levels for the DB2 resource classes. DB2 objects are defined as resource names in the resource class. Users are identified by an Accessor ID (ACID).
To give USER01 create table access to the DB2 database object PAYROLL, the native DB2 command would be:
GRANT CREATETAB ON DATABASE PAYROLL TO USER01
The CA Top Secret Option for DB2 command would be:
TSS PER(USER01) DB2DBASE(PAYROLL) ACC(CRETAB)
To give USER02 database control authority for the DB2 database object PAYROLL, the native DB2 command would be:
GRANT DBCTRL ON DATABASE PAYROLL TO USER02
The CA Top Secret Option for DB2 command would be:
TSS PER(USER02) DB2DBASE(PAYROLL) ACC(DBCTRL)
This single database control authority would then allow USER02 all of the access levels located in the “DB2DBASE() ACC(DBCTRL)” and the “DB2DBASE() ACC(DBMAINT)” boxes for the PAYROLL database.
“DB2 Installation SYSADM” and “DB2 Installation SYSOPR” are special authorities that are recognized by CA Top Secret Option for DB2, but are assigned by native DB2 during the installation of DB2. Because they are both extremely powerful authorities, you might want to create special ACIDs for them and limit their availability.
For more information about native DB2 authorities and privileges, see the “Native DB2 Security” chapter and the IBM DB2 Administration Guide.
This section provides detailed reference information for each of the DB2‑specific resources.
Also included are examples of the following command functions:
See the CA Top Secret for z/OS Command Functions Guide for details on administrative authorities and levels, access controls, and masking.
|
Copyright © 2011 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|