

You can open the EDL editor from service definition dialogs or from the class definition dialog. The following shows you an example of the EDL Editor dialog:
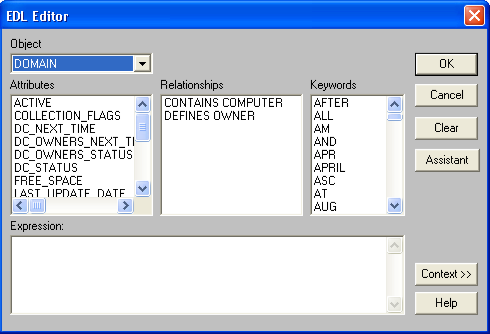
The EDL editor opens with slight variations, depending on the dialog from which you call it. The EDL editor provides access to the following functions:
|
Function |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OK |
Exits the editor and inserts the EDL expression into the service definition dialog from which the editor was called. |
|
Cancel |
Exits the editor without saving anything. |
|
Save* |
Saves the class definition. |
|
Clear |
Deletes the entire statement. |
|
Syntax* |
Checks the validity of the EDL statement and issues a message indicating whether the syntax is correct. |
|
Assistant |
Provides help with the formulation of EDL conditional statements in class definitions, filter definitions, and in supplying sources to services in EDL format. |
|
Context |
Provides context-sensitive help (brief description with example) for the selected item in a secondary dialog. |
* Only in the Class definition dialog.
The EDL editor dialog offers several building blocks to help you write EDL statements. Double-click any building block to transfer the element to the Expression text box at the bottom of the dialog.
The following EDL building blocks appear in the editor:
CA SRM associates each attribute with a data type. When used in comparisons, the expressions on the right must match the attribute type.
If you select the object COMPUTER from the Object list and double-click the attribute FREE_SPACE, the string COMPUTER_FREE_SPACE is transferred to the Expression text box.
Attributes can assume values of different types, as shown in the following examples:
FILE_SIZE = 2 MB (size), USER_NAME = "JDOE" (string)
FILE_HAS_VALID_OWNER = TRUE (Boolean)
VOLUME_TYPE = "FAT" (Enum string)
The attribute can assume any value from a finite list of values. For more information, see the online help.
Some network objects are related to each other. Because computers can be part of domains, the relationships between these objects is expressed as follows:
FILE WHERE USER_NAME = "JSMITH"
to replace the more explicit statement:
FILE WHERE FILE IS_OWNED_BY USER "JSMITH"
Similarly, using the implied relationship of IS_REGISTERED_ON between TSM nodes and TSM servers, you can write a statement such as:
TSM_NODE WHERE TSM_SERVER_NAME = "ATLANTA"
to replace the more explicit statement:
TSM_NODE WHERE TSM_NODE IS_REGISTERED_ON TSM_SERVER “ATLANTA"
EDL statements appear in the Expression text box at the bottom of the window. You can enter the statements directly or use the objects listed in the typing aid.
|
Copyright © 2016 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|