

The following Policy Server components support multi-byte and ASCII characters in an internationalized environment:
Note: Password Services are limited to ASCII characters, but can support a multi-byte character URL as a redirection URL.
SiteMinder supports URLs that contain multi-byte characters (MBCS). MBCS URL support includes support for:
MBCS URL support lets:
Support for MBCS URLs in a SiteMinder environment requires that:
To enable support for MBCS URLs:
Web Browser Requirements for MBCS URLs
Web browsers must be able to send requests to Web servers that serve resources in UTF-8 format and whose domain names contain non-ASCII characters.
The Web browsers used to access the protected resources must be able to:
Web Server Requirements for MBCS URLs
A Web server can support MBCS URLs if it meets at least one of the following requirements:
or
Enable Multi-byte Character Support
MBCS support requires that you remove specific high‑bit ASCII character values from the Web Agent Configuration Object.
Note: Removing the high‑bit ASCII characters prevents the Web Agent from blocking the specific characters.
To enable MBCS support
The Modify Agent Configuration pane appears.
Agent configuration objects matching the search criteria appear.
Agent Configuration parameters are listed in the Parameters group box.
The Edit Parameter pane appears.
The edited values appear in the BadURLChars field.
The Web Agent Configuration Object is configured to support MBCS URLs.
Support for MBCS URLs lets SiteMinder protect resources that are accessed through URLs that contain non-ASCII characters.
When creating a realm and the associated rule or rules to protect the resource, you can enter a MBCS URL in the Resource field. Users can access the protected resource using a browser that supports IDNs and IRIs.
Note: More information on creating realms and rules exists in the Policy Server Configuration Guide.
You can configure the following authentication schemes with an IDN in the Server Name field and an IRI in the Target field:
Note: Netscape and Firefox do not accept redirections to URLs that contain an IDN. Entering an IDN for a forms-related authentication scheme results in a failure unless Punycode is used. More information about configuring authentication schemes exists in the Policy Server Configuration Guide.
You can configure SiteMinder data stores in SQL Server or Oracle databases. When configuring these data stores, be aware that the Policy Server only supports UTF-8 encoding and, as a result, you must use databases that support this encoding type.
Note: This section applies to configuring SiteMinder data stores in relational databases. More information on configuring these stores in LDAP servers exists in LDAP Directory Servers as a Policy Store or Key Store.
To create policy, keys, session, or key stores, configure a SiteMinder data store in the SQL Server database.
Note: By default, SQL Server supports UTF-8 character encoding.
To configure an international SiteMinder data store in Oracle
Note: For more information and instructions, see Oracle’s documentation.
To verify if an existing Oracle database supports UTF-8 character encoding, run the following query:
Select * from nls_database_parameters where parameter = ‘NLS_CHARACTERSET’
A Solaris/LINUX Red Hat Policy Server can log UTF-8 characters to an Oracle audit log database. To enable this configuration, you need to set the following environment variables:
For a simplified Chinese operating system
For a Japanese operating system
You set the LANG variable system-wide or just for the Policy server process.
Note: To avoid impacting any other applications, make sure that you set this variable for the Policy Server process only.
Database Driver Variable
You set this variable in the appropriate data source definition section of the system_odbc.ini file, installed in <policy_server_installation>/db.
Oracle Client Settings
Since the Policy Server uses the Oracle wire protocol driver, an Oracle client is not necessary. However, if you need an Oracle SQLPLUS client in your environment to read data from the audit log database, you may have to set one or both of the following environment variables to correctly display the multi-bytes characters:
For a simplified Chinese operating system
For a Japanese operating system
For the Oracle SQLPlus Client
Note: For more information, see the operating system and database client configuration manual.
Using the smsampleusers_sqlserver.sql file installed with the Policy Server, you can configure a user store in a SQL Server database. This file is installed in the siteminder_installation\db\SQL directory.
Note: User stores are not limited to UTF-8 format. You can create a user store in the local character set encoding.
Follow these steps:
Japanese example:
insert into SmUser ( UserID , Name, Password,
LastName, FirstName, ...)
values (12, N'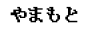 ',
',
'siteminder','guest','guest','guest@mycompany.com...)
Note: More information on importing the smsampleusers_sqlserver.sql file exists in Sample User Directories.
Example:
The following sample query scheme statements:
select Name, 'User' from SmUser where Name = '%s' Union select Name, 'Group' from SmGroup where Name = '%s'
should become:
select Name, 'User' from SmUser where Name = N'%s' Union select Name, 'Group' from SmGroup where Name = N'%s'
The user store configuration is complete and now supports multi-byte characters.
Using the smsampleusers_oracle.sql file installed with the Policy Server, you can configure a user store in an Oracle database. This file is installed in the <siteminder_installation>\db\SQL directory.
Note: User stores are not limited to UTF-8 format. You can create a user store in the local character set encoding.
To configure a Japanese user store in Oracle
Note: More information on importing the smssampleusers_oracle.sql file exists in Sample User Directories. Be aware that if you are inserting Japanese characters, import the file from a Japanese operating system.
The user store configuration is complete.
|
Copyright © 2012 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|