

This section contains the following topics:
Perform Authorizations with an Attribute Authority
Flow Diagram for Authorizing a User with User Attributes
How to Configure an Attribute Authority and a SAML Requester
Set up the Attribute Authority
Set up a SAML Requestor to Generate Attribute Queries
The Policy Server authorizes a user with the following types of information:
The Policy Server also authorizes a user with user attributes that a SAML 2.0 Attribute Authority provides. When a user requests access to a protected resource, the Policy Server, as the authorizing entity, can request more user attributes. The Policy Server evaluates these attributes before granting access to the resource.
The SAML 2.0 Assertion Query/Request profile employs two entities:
The SAML Attribute Authority relies on an Attribute Service to process a query message and add attributes to an assertion. These assertions contain user attributes that a SAML Requester uses to authorize access to protected resources. The Attribute Service is part of the Federation Web Services application.
When an entity makes a request to an Attribute Authority, the message contains the user attributes that the requester wants to retrieve. The message also contains the Name ID and the Issuer of the request. The Attribute Service uses the NameID to disambiguate the user so it knows what values to return for the requested attributes. The Attribute Service returns a response message that includes an attribute assertion that is wrapped in a SOAP message. This response includes the user attributes.
Note: The user does not need to be authenticated at the Attribute Authority. Also, there is no need for a single sign-on relationship between the Authority and the Requester.
The SAML Requester is a SAML entity that uses the SAML 2.0 Assertion Query/Request profile to request attributes for a user. For SiteMinder, the SAML Requester is not a specific service, but a group of Policy Server features that can produce and process <AttributeQuery> messages. The Requester asks for the user attributes from the Attribute Authority because the protected target resource always resides at the SAML requester. The Requester resolves these attributes into variables that a policy expression uses.
Note: In a SiteMinder federated environment, the SAML Attribute Authority is the Identity Provider and the SAML Requester is the Service Provider. However, this condition does not have to be the case.
To evaluate an authorization request that is based on SAML 2.0 user attributes, add an attribute type named federation attribute variable to a policy expression. The policy protecting the target resource uses this variable. Based on the policy variable, the SAML Requester sends a query message to the Attribute Authority. This query message contains the Name ID for the SAML entity for which the attributes are being requested. The SAML Attribute Authority returns a response message containing assertions with the attribute statements.
A user must have a session at the SAML Requester; however, the user does not have to log in or authenticate at the Attribute Authority.
The following figure shows how an attribute query is processed.
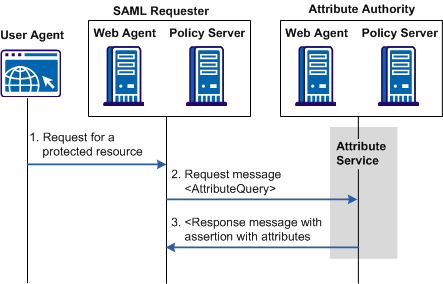
Note: The SPS federation gateway can replace the Web Agent and Web Agent Option Pack to provide the Federation Web Services application functions. For information about installing and configuring the SPS federation gateway, see the Secure Proxy Server Administration Guide.
The following flow diagram shows the authorization process with an Attribute Authority.
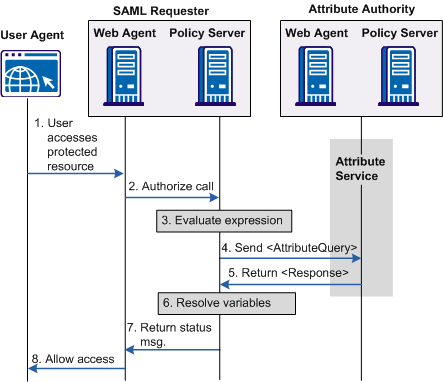
Note: The SPS federation gateway can replace the Web Agent and Web Agent Option Pack to provide the Federation Web Services application functions. For information about installing and configuring the SPS federation gateway, see the Secure Proxy Server Administration Guide.
The sequence of a user attribute request is as follows:
In a SiteMinder context, the Attribute Authority is the Identity Provider.
To configure SiteMinder to act as a SAML Attribute Authority
In a SiteMinder context, the SAML Requester is the Service Provider.
To configure SiteMinder as a SAML Requester
|
Copyright © 2012 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|