

This section contains the following topics:
Configure the CA SiteMinder® SPS to Support the SessionLinker
The SessionLinker synchronizes the CA SiteMinder® session with the third-party application session for better security. By default, CA SiteMinder® SPS installs SessionLinker in a disabled mode.
The following diagram describes how the SPS administrator and policy administrator can configure CA SiteMinder® SPS to support the SessionLinker:
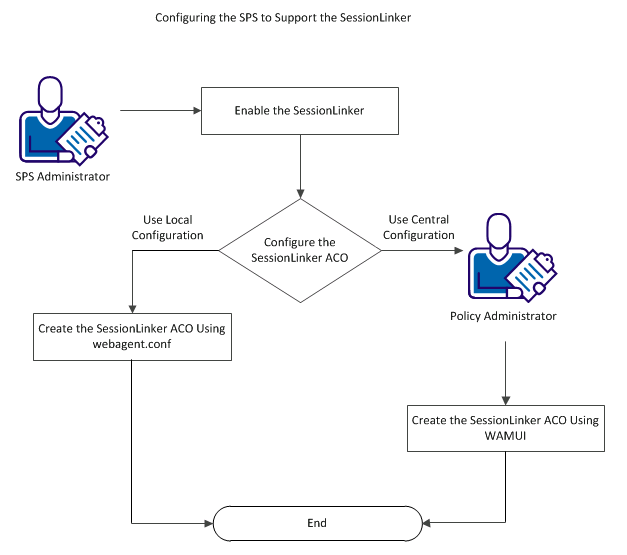
The SessionLinker synchronizes a SiteMinder session with a third-party application session for better security. If a user logs out of SiteMinder, the SessionLinker invalidates the related session of the third-party application.
When a user authenticates, SiteMinder assigns a unique session identifier to that user session. The session identifier, called the SiteMinder Session ID, remains constant for that user for the life of the user session. If the user logs out of SiteMinder through the Logout URL, SiteMinder deletes the SMSESSION cookie that SiteMinder uses to track the SiteMinder Session ID.
The SessionLinker module takes application session cookies and associates them, one by one, with a SiteMinder session. Once associated, the application cookie (referred to here as the foreign cookie) can only be used in conjunction with that particular SiteMinder session. The SessionLinker prevents attempts by other SiteMinder sessions to use the same foreign session.
To understand the SessionLinker operation, associate the SiteMinder session and corresponding foreign cookies that SiteMinder tracks together in a table, as shown in the following example:
|
SiteMinder Session ID |
Foreign Cookie |
|---|---|
|
ONE |
ABCD |
|
TWO |
LMNO |
|
THREE |
PQRST |
|
FOUR |
VWXY |
The SessionLinker uses the following process:
The entire process is repeated for each Foreign Cookie. The resulting table may appear as follows:
|
SiteMinder Session ID |
Foreign Cookie |
|---|---|
|
***Orphaned*** |
ABCD |
|
ONE |
HIJK |
|
TWO |
LMNO |
|
THREE |
PQRST |
|
FOUR |
VWXY |
|
FIVE |
RSTU |
The SessionLinker does not do any of the following tasks:
SessionLinker accomplishes the linking by preventing the user from presenting an invalid Foreign Session cookie.
Enable the SessionLinker to synchronize the CA SiteMinder® session with the third-party application session. You can configure the SessionLinker ACO after you enable the feature.
Follow these steps:
CA SiteMinder® SPS manages the SessionLinker configuration through an ACO. The SessionLinker ACO has the following syntax:
SessionLinker=Cookie=cookie_value;BLOT|NOBLOT;Orphantimeout=timeout_value;
Where
Specifies the name of the cookie holding the foreign session. If cookie names may change, use an asterisk as a wildcard character.
(Optional) Specifies how the SessionLinker responds to invalid sessions. If you set the value of this parameter to BLOT, the user is granted access but the foreign session cookie is not passed through the web server to the target page. If you set the value of this parameter to NOBLOT, the foreign cookie is deleted from the request and the user is then redirected to the URL specified in the URL parameter. If you do not specify the URL in the URL parameter, the internal server error is displayed.
Default: BLOT
Specifies the number of seconds that the SessionLinker maintains orphaned sessions.
Default: 86400 (24 hours)
Limits: Cannot be less than the maximum number of seconds that cookies from the third party (foreign) application are accepted.
To configure CA SiteMinder® SPS to support SessionLinker, create the ACO named SessionLinker in one of the following ways:
If you want to use the local configuration to create the SessionLinker ACO, create the ACO using the webagent.conf file.
Follow these steps:
SessionLinker= Cookie=cookie_value;BLOT|NOBLOT;Orphantimeout=timeout_value;
The SessionLinker ACO is created. The SPS is configured to support the SessionLinker.
If you want to configure SessionLinker to work with cookies, see Working with Cookies. If you want to troubleshoot any errors that are caused by the SessionLinker, see Troubleshooting.
If you want to use the central configuration to create the SessionLinker ACO, the policy administrator must create the ACO through the WAMUI.
Follow these steps:
Name: SessionLinker
Value: Cookie=cookie_name;BLOT|NOBLOT;Orphantimeout=timeout_value;
The SessionLinker ACO is created. The SPS is configured to support the SessionLinker.
If you want to configure SessionLinker to work with cookies, see Working with Cookies. If you want to troubleshoot any errors that are caused by the SessionLinker, see Troubleshooting.
In most cases, an application has a specific name that is always used for an associated session cookie. In other cases, the name of the cookie begins with a known string, such as ASPSESSIONID or MYAPPSESSION, and ends with a random or unpredictable suffix. In such cases, the SessionLinker prevents users from presenting more than one of these cookies and enforces the expected session linking.
If the SessionLinker detects multiple potential session cookies, it performs the following steps:
You can add the following parameters of the ACO configured on the Policy Server to the configuration settings already selected:
Specifies that a cookies beginning with the specified name must be considered as a potential foreign session cookie. The cookie value may end in an asterisk (*). If you specify a cookie value other than a wildcard syntax, you must specify COOKIEPATH and COOKIEDOMAIN values that determine how to destroy the incoming cookies.
Specifies the cookie path. If you specified a wildcard syntax for the COOKIE parameter, do not specify this parameter. The COOKIEPATH value depends on the session cookie, and has the following format:
COOKIEPATH=<Path for outbound cookies or cookies>
Default Value: /
Example: COOKIEPATH=/
Specifies the cookie domain. If you specified a wildcard syntax for the COOKIE parameter, you can specify this value in the following format:
COOKIEDOMAIN=<domain name for outbound cookie or cookies>
Default Value: Blank
Example: COOKIEDOMAIN=.ca.com
To determine the cookie name settings, perform the following steps:
If the name of a session cookie for an application starts with the same text string but ends differently, specify a cookie name in the following format:
COOKIE=cookiename*
The domain name of a cookie consists of any of the following items:
The fully qualified computer name or a blank name are equivalent.
Note: Internet Explorer deletes the leading period before displaying a domain. So, we recommend that you test various configurations in a staging environment to determine the correct settings.
The path associated with a cookie is typically a directory, but could be a file or another string. Examine the path shown in the cookie warning dialog of your web browser. If the path shown is not a forward slash (/), enter the correct value for the COOKIEPATH setting.
Some web applications use more than one cookie simultaneously within the same area of the site. You can configure the SessionLinker to maintain links from a single CA SiteMinder® session to a number of cookies. A maximum of ten foreign session cookies can be linked to a single CA SiteMinder® session.
Follow these steps:
Note: Each configuration string requires at least a COOKIE directive, but any of the directives can be combined.
Note: You can use any number for each set of directives but the settings for a single cookie require the same number.
If an error occurs, consider the following possibilities to troubleshoot the error:
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|