

This section contains the following topics:
How the CA SiteMinder® SPS Interacts with SiteMinder
CA SiteMinder® SPS and SharePoint Resources
CA SiteMinder® SPS and ERP Resources
Configuring Managed Self Registration for the SPS
Keep Alive and Connection Pooling
HTTP Header Configuration for Sun Java Web Servers
HTTP Header for SiteMinder Processing with SPS
SiteMinder is a solution for securely managing e-business. SiteMinder consists of a Policy Server that allows you to specify policies for your enterprise, and Web Agents that are installed on web servers. The Web Agents communicate with the Policy Server to provide authentication, authorization, and other functions.
The CA SiteMinder® SPS contains a Web Agent that is compatible with the SiteMinder Web Agent and Policy Server technology. As all SiteMinder Web Agents, the CA SiteMinder® SPS must be configured as an object in SiteMinder. Policies must be created that determine authentication and authorization requirements for accessing destination servers.
SiteMinder objects are configured using SiteMinder <adminui>. You can configure the following objects:
Configure an agent object with settings for the Web Agent included in the SPS. Specify this Web Agent when creating realms.
Configure connections to any user directories that authenticate and authorize users.
Configure policy domains that contain realms, rules, and policies.
Configure realms that contain resources you want to protect with SiteMinder.
Configure rules that identify specific resources and actions that you want to protect with SiteMinder.
Configure any responses that can return information to applications, or to the SPS. Information returned to the CA SiteMinder® SPS can determine how to route user requests.
Configure policies that bind users and groups to rules and responses.
Note: For complete information about how to configure SiteMinder objects, see the CA SiteMinder Configuration Guide.
SiteMinder enforces authentication schemes to protect resources. When users attempt to access protected resources through a SiteMinder Web Agent or the SPS, SiteMinder asks for credentials based on the authentication scheme protecting the resource.
SiteMinder also provides protection levels to each authentication scheme. The protection levels are enforced during single sign-on when the user tries to access resources protected by different authentication schemes. In such scenarios, the users can access resources protected by different authentication schemes without reauthentication if the protection levels for each of the authentication schemes are equal or lower. When moving from a lower protection level to a higher protection level, the user is challenged for authentication. When moving from a higher protection level to a lower protection level, the user is not challenged for reauthentication.
When the CA SiteMinder® SPS is integrated with SiteMinder, the CA SiteMinder® SPS behaves similar to a SiteMinder Web Agent. However, CA SiteMinder® SPS using basics authentication behaves similar to a Web Agent only if the CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured to use default SessionCookieScheme scheme to track user sessions. If the CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured to use any of the other advanced or cookieless session schemes, the user has to reauthenticate. Single sign-on does not work.
For example, a basic authentication scheme with a protection level of 5 protects two resources, resource1 and resource2. The CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured to use a mini-cookie session scheme (or any other cookieless session scheme) to track user sessions. When a user tries to access resource1, the CA SiteMinder® SPS forwards the request to SiteMinder. SiteMinder verifies the authentication scheme for resource1 and challenges the user for credentials.
The CA SiteMinder® SPS collects the credentials from the user and after successful authentication by SiteMinder, allows the user to access resource1. If the user then tries to access resource2, the CA SiteMinder® SPS forwards the request to SiteMinder. SiteMinder verifies the authentication scheme for resource2 and challenges the user for credentials. Because the CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured to use mini-cookie session scheme, the CA SiteMinder® SPS requests the user to reauthenticate. If the CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured to use the default SiteMinder cookie session scheme, then the user need not reauthenticate to access resource2.
Note: For more information about authentication schemes and their protection levels, see the CA SiteMinder Policy Configuration Guide.
A number of settings in the WebAgent.conf configuration files for Web Agents installed behind the DMZ in an enterprise have specific implications for the SPS.
The settings that must be modified in the destination server WebAgent.conf files include:
As an optimization, the proxytrust directive can be set on the destination server Web Agent sitting behind the SPS. Enter one of the following settings:
The destination server web agent automatically trusts the authorizations made by the SPS.
The destination server web agent requests authentication every time. (Default)
Instructs the Web Agent on the destination server to time out the single sign-on token used in requests made by the SPS. Enter a value in seconds.
Default: 120 seconds.
In some deployments, when the CA SiteMinder® SPS is running in proxy trust mode, the CA SiteMinder® SPS can protect resources from one set of users, while a Web Agent on a destination server protects the same resources from another set of users.
In the following illustration, Destination Server 2 has its own Web Agent. Extranet users are authenticated and authorized at the SPS, while Intranet users are authenticated and authorized through the Web Agent on the destination server. In such situations policies must exist in SiteMinder policy store for the embedded CA SiteMinder® SPS Web Agent and the Web Agent on the destination server.
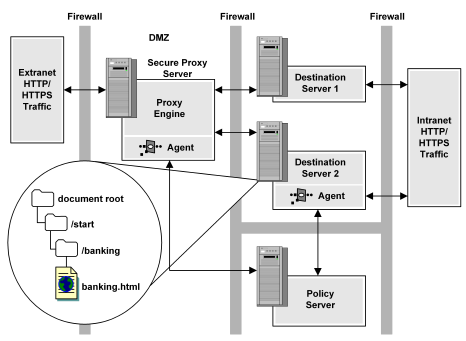
Note: When creating policies, administrators must be sure that the policies do not conflict with each other. If policies contradict one another, it is possible that SiteMinder may allow unwanted or unexpected behavior.
To correctly create policies and other required SiteMinder objects for the resources contained on Destination Server 2, the following objects could be created in SiteMinder:
The following illustration shows how two policies must be created to protect a single resource when Compatibility Mode is used in environments that include both the CA SiteMinder® SPS and Web Agents.
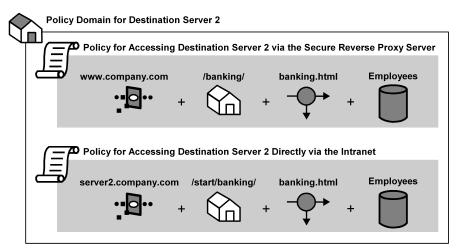
In the preceding illustration, the rules and realms for the same resources may have different paths based on the location of the resources on the destination server and the proxy rules used to forward requests.
For example, using the sample configuration in the preceding illustration, a resource called banking.html may be located on Destination Server 2 in the server2.company.com/start/banking/ directory, but the CA SiteMinder® SPS may have proxy rules that forward all requests for www.company.com/banking/banking.html to the same destination on Server 2. Therefore, the same resource can have two different SiteMinder rules that represent the same resource. One rule authorizes access to the resource directly for employees on the intranet, and the other authorizes employees on the road who want to access the same resource from the extranet.
SiteMinder provides the ability to create response objects that redirect a request under certain conditions. For example, you can create a response that redirects a request to a custom error page after a failed authentication (OnRejectRedirect). By default for cookieless session schemes that rewrite a requested URL (Simple URL Rewriting), the CA SiteMinder® SPS recognizes a user session information after a redirection.
To terminate a user session after a redirection, create a response attribute in SiteMinder for the relevant policy that modifies the value of the SiteMinder SM_REWRITE_URL header. This HTTP header must be set to NO to force a new session after a redirection.
For example, if you have a resource in realmA that is protected by an authentication scheme with a protection level of 5, and a second resource in realmB protected by authentication scheme with a protection level of 10, a user who successfully authenticates in realmA will be challenged for credentials when moving to realmB (due to the higher protection level).
If an OnRejectRedirect response is associated with realmB and the user fails to authenticate when challenged for credentials in realmB, the default behavior of the CA SiteMinder® SPS maintains the user’s original session information even after the user is redirected to a custom error page.
To terminate the user’s session after the redirect and force an entirely fresh session on the next login attempt, you must create a response attribute that sets the SM_REWRITE_URL=NO, and associate the response with the appropriate policy.
If you want to use the CA SiteMinder® SPS to secure resources managed by Microsoft SharePoint, make the configuration changes listed following.
The server name must match the value set for the ServerName field in the httpd.conf file. Most often, the ServerName is a fully qualified host name, but the value can be an IP address.
Note: These parameters can also be added to the CA SiteMinder® SPS LocalConfig.conf file.
<VirtualHost name="VHName"> hostnames="host_name, host_name" enableredirectwrite="yes" redirectwritablehostnames="server1.company.com, domain1.com" </VirtualHost>
Note: For more information, see the CA SiteMinder Agent for SharePoint Guide.
You can use the CA SiteMinder® SPS to secure resources managed by an ERP system. The CA SiteMinder® SPS can function as a proxy in front of ERP agents protecting the following ERP systems:
While the ERP agent must be installed on the ERP server, the CA SiteMinder® SPS secures the ERP resources at the Policy Server.
Note: For information about the Policy Server settings required to support the ERP server, see the appropriate CA ERP agent guide.
To configure the CA SiteMinder® SPS as a reverse proxy for an ERP agent
<VirtualHost name="sales">
hostnames="sales, sales.company.com" enableredirectrewrite="yes" redirectrewritablehostnames="server1.company.com,domain1.com"
</VirtualHost>
addquotestocookie="no"
Note: For information about any required settings on the ERP Server side, refer to the documentation for your ERP server.
The CA SiteMinder® SPS is configured as a proxy for the ERP agent.
Password services are a SiteMinder feature that provides an additional layer of security to protected resources by allowing a SiteMinder administrator to manage user passwords. Password services allow an administrator to create password policies that define rules and restrictions governing password expiration, composition, and usage.
When configuring password services in SiteMinder, a password policy is associated with a directory. All users contained in the directory, or some part of the directory identified by an LDAP search expression, must adhere to the password policy. Password services are processed from inside the Apache Web server rather than from a back-end Web server hosting an agent.
Note: For more information about password services, see the Policy Design Guide.
For SiteMinder to implement Password Services in a CA SiteMinder® SPS deployment, the redirection URL specified in the Policy Server User Interface must refer to the CA SiteMinder® SPS server, with the addition of a specific virtual directory path.
To configure a password policy for SPS
The User Directory Properties dialog appears.
Note: For more information on the User Directory Properties dialog, see the Policy Server User Interface help.
The Password Policy Properties dialog appears.
/siteminderagent/pw/smpwservicescgi.exe
The configuration is complete.
After you have configured Password Services for the SPS, you can perform a simple test to see whether Password Services are in effect.
To verify whether Password Services is working
The User Management dialog appears.
When you next request a protected page in CA SiteMinder® SPS and are challenged, enter the credentials for the specified user. The Password Change screen appears, indicating the Password Services is working.
Managed Self-Registration (MSR) is a SiteMinder feature that allows users to login to a web site and establish a new user account. New users can access the web site, provide personal information, and receive an account on the site. In addition, users can also define a hint that may be used to retrieve a forgotten password.
When configuring MSR in SiteMinder, a registration scheme must be configured. This registration scheme can be specified in the realm that contains the registration URL. The registration realm requires an HTML forms-based authentication scheme that points to an appropriate template for MSR services.
The following illustration shows the user of MSR with SPS.
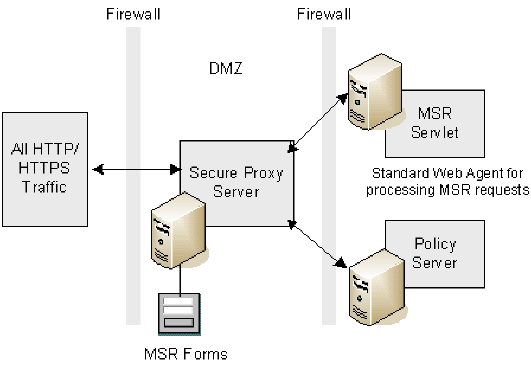
The additional web server, which should reside outside of the DMZ , must contain a SiteMinder Web Agent installation. This web agent installation provides the processing required by MSR, and ensures that the processing of sensitive data occurs behind the DMZ.
To use MSR with the SPS, you must install a SiteMinder Web Agent on a Web server behind the DMZ. For information about installing a Web Agent, see the CA SiteMinder Web Agent Installation Guide.
After the Web Agent is installed, note the following:
The CA SiteMinder® SPS uses the MSR servlet configured for the web agent. The web agent is not used for authentication or authorization.
For SiteMinder to properly implement MSR in a CA SiteMinder® SPS deployment, the template path specified in the Registration Properties dialog must be defined as follows.
To configure the policy server user interface for MSR
The Registration Properties dialog opens.
/siteminderagent/selfreg
The CA SiteMinder® SPS supports the Managed Self Registration services through proxyrules.xml for forwarding the request to the Web Agent (6.x) hosting MSR Servlet. The forwarding is based upon the URI of the incoming request. For example, if the URI begins with /siteminderagent/selfreg, the request is forwarded to the Web Agent hosting MSR Servlet; otherwise, the request is forwarded to the backend server.
An example of a proxy rule for forwarding the password services request is following.
<nete:cond type="uri" criteria="beginswith"> <nete:case value="/siteminderagent/selfreg"> <nete:forward>http://MSR_server.company.com$0</nete:forward> </nete:case> <nete:default> <nete:forward>http://default_backendserver.company.com$0</nete:forward> </nete:default> </nete:cond>
MSR_server.company.com stands for the server behind the DMZ on which the Web Agent hosting MSR Servlet is installed, and default_backendserver.company.com stands for destination server.
When configuring firewalls for the DMZ that will contain the SPS, the CA SiteMinder® SPS uses ports 8007 and 8009 for internal communication. These ports should be protected from access by entities outside of the DMZ.
Note: You can change the ports used by the CA SiteMinder® SPS by altering the appropriate directives in the server.conf file.
The CA SiteMinder® SPS is designed to use a connection pool to provide better performance by spreading out the workload generated from initiating server connections. It is recommended for performance reasons that KEEP ALIVE settings should be turned on for destination servers.
All destination server products have individual methods and attributes for managing keep alive settings. These settings should be reviewed and understood when configuring SPS.
By default, some web servers, such as Sun Java Web servers limit the number of header variables that can accompany a request. You might have to increase this upper limit to accommodate transactions that contain many custom headers.
The server typically returns 413 Request Entity Too Large error is # of headers is greater than allowable maximum. For more information refer to your destination server's administration guide.
To change the maximum number of headers
MaxRqHeaders 50
Be sure to set the maximum value at a level above the number of headers created by your CA SiteMinder® SPS transactions.
The CA SiteMinder® SPS introduces an additional layer in the traditional SiteMinder architecture. This layer forwards or redirects all requests to destination servers in the enterprise. When the CA SiteMinder® SPS processes a request, the URL requested by the user is preserved in an HTTP header variable called SM_PROXYREQUEST. This header may be used by other applications that require the original URL requested by a user before the CA SiteMinder® SPS proxied the request.
The value of the ProxyAgent parameter in the Agent Configuration object must be set to YES to enable sending the SM_PROXYREQUEST HTTP header to the backend.
Note: This header is only added when a request is made for a protected resource.
Web servers can process both encoded and decoded normalized or unescaped URLs. How a Web server handles encoded URLs differs based on the type of server. For security reasons, and to provide consistent behavior, the CA SiteMinder® SPS always decodes or normalizes a URI before processing. This provides a universal representation for a single URL, and protects against attempts to exploit the CA SiteMinder® SPS using encoded strings.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|