

In a proxy mode deployment, you use the federation system in the DMZ to forward requests to backend web servers that host federated applications. These backend systems sit behind a firewall and are not directly accessible.
Proxy mode offers the following advantages:
Note: You can protect the HTTP Headers against modification by an unauthorized user by setting an HTTP Header prefix. More information is available for protecting HTTP Headers in proxy mode.
In proxy mode, the federation system passes all requests to the backend network. Verify that all resources on a backend web server are protected by CA SiteMinder® or another access control product.
For example, a backend web server may host a federated application as well as unprotected resources behind the firewall. If the administrator exposes the federated application, the unprotected resources are also exposed because the federation system allows full access to the backend web server without checking for authorization. This assumes that the non-federated resources are URL-addressable.
The following figure shows a typical proxy mode deployment from the perspective of the relying party.
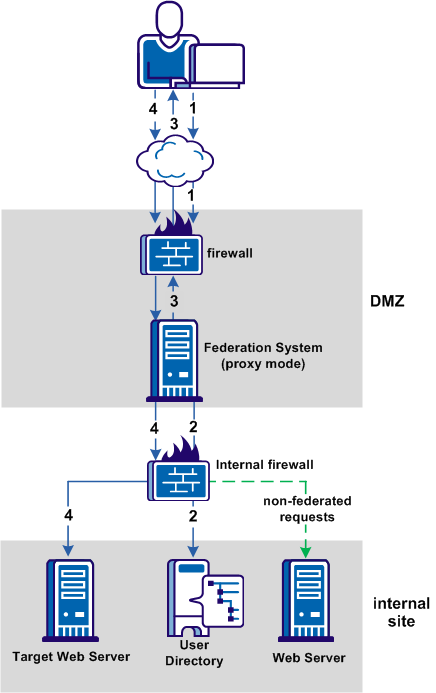
The previous figure shows the following communication flow at the relying party:
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|