

Policy Server Guides › Policy Server Configuration Guide › Authentication Schemes › How To Configure Kerberos Authentication
How To Configure Kerberos Authentication
Kerberos authentication supports various configuration scenarios, depending on the host environments of the client and server. Although each scenario is slightly different, implementing Kerberos authentication in a CA SiteMinder® environment requires a policy administrator to perform the tasks represented in the following diagram:
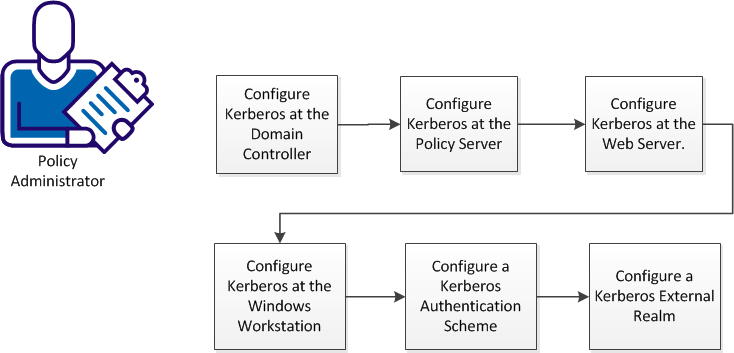
Complete these procedures to configure Kerberos authentication:
- Configure Kerberos at the Domain Controller.
- Configure Kerberos at the Policy Server.
- Configure Kerberos at the Web Server.
- Configure Kerberos at the Windows Workstation.
- Configure a Kerberos Authentication Scheme
- Configure a Kerberos External Realm.
Configure Kerberos at the Domain Controller
In a pure Windows environment, a Kerberos realm is equivalent to a Windows Domain. The domain controller host provides storage for the user, service accounts, credentials, the Kerberos ticketing services, and Windows Domain services.
A keytab file is required for Kerberos authentication, which lets users authenticate with the KDC without being prompted for a password. The keytab file is created with the ktpass utility. The ktpass command tool utility is a Windows support tool. The ktadd utility is the equivalent on UNIX.
KDC configuration for the Policy Server on the domain controller host (Windows or UNIX) follows this general sequence:
- Create a user account. This account is for logging in to the workstation.
- Create a service account for the web server for logging in to the web server host.
- Create a service account for the Policy Server for logging in to the Policy Server host.
- Associate the web server account with a web server principal name.
- Create a keytab file, which is transferred to the web server host.
- Associate the Policy Server account with a Policy Server principal name.
- Create another keytab file, which is transferred to the Policy Server host.
- Specify that the web server and Policy Server accounts are Trusted for Delegation.
Important! For any service to use Kerberos protocol, be sure to create the Service Principal Name (SPN) in a standard format, that is, service/fqdn_host@REALM_NAME.
More information:
KDC Configuration on Windows Example
KDC Configuration on UNIX Example
KDC Configuration on Windows Example
The following procedure shows how to configure a Windows domain controller/KDC to support Kerberos authentication. This example uses the following server and account names:
- Servers
Domain Controller: kdc.example.com
Policy Server: smps.example.com
Web Server: www.example.com
Active Directory Domain: EXAMPLE
Kerberos Realm: EXAMPLE.COM
- Accounts
User Account: testkrb
Web Agent Service Account: krbsvc-smwa
Policy Server Service Account: krbsvc-smps
Follow these steps:
- Add the Active Directory Domain Services role to your Windows server.
This action makes your Windows server a domain controller. A Windows domain controller operates as a Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC), implements the Kerberos V5 protocol, and performs Kerberos-related authentication functions.
- Run the Windows dcpromo utility from the command line, or click the link on Service Manager, which launches the dcpromo utiity.
- Verify the domain functional level:
- Open the Active Directory users and computers dialog from Administrative tools.
- Right-click the example.com drop-down on the left side of dialog.
- Click Raise domain functional level.
- Verify the domain functional level of Active Directory is at least Windows Server 2003. If not, raise the domain functional level.
Important! Raising the domain functional level is irreversible.
- Create a user account (for example, testkrb). Provide a password for this account. Clear the option, User must change password at next logon. The Windows workstation uses this account to log in to example.com.
- Create a service account for the web server (for example, krbsvc-smwa). Create a password for this account. Clear the option, User must change password at next logon.
- Create a service account for the Policy Server (krbsvc-smps). Provide a password for this account. Clear the option, User must change password at next logon.
- Associate the web server service account (krbsvc-smwa) with a Kerberos service principal name (HTTP/www.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM) and create a keytab file using the Ktpass utility. Always verify the version of support tools. The default encryption type is RC4-HMAC. The encryption type can be confirmed by running ktpass /? at the command prompt.
ktpass -out c:\krbsvc-smwa.keytab -princ HTTP/www.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM
dc.example.com -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -mapuser EXAMPLE\krbsvc-smwa -pass "*"
Targeting domain controller: dc.example.com
Using legacy password setting method
Successfully mapped HTTP/wwww.example.com to krbsvc-smwa..
Key created.
Output keytab to c:\krbsvc-smwa.keytab:
Keytab version: 0x502
keysize 82 dc.example.com ptype 1 (KRB5_NT_PRIN
CIPAL) vno 3 etype 0x17 (RC4-HMAC) keylength 16 (0xf3d3d2a17c7ea172ff22044806443
9a9)
The password is the same as the one used for creating the service account for the web server.
- Associate the Policy Server service account (krbsvc-smps) with a Kerberos service principal name (smps/smps.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM) and create another keytab file for the Policy Server host.
Ktpass -out c:\krbsvc-smps.keytab -princ smps/smps.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -mapuser EXAMPLE\krbsvc-smps -pass *
Targeting domain controller: dc.example.com.com
Using legacy password setting method
Successfully mapped smps/smps.example.com to krbsvc-smps.
Key created.
Output keytab to c:\krbsvc-smps.keytab:
Keytab version: 0x502
keysize 72 smps/smps.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM ptype 1 (KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL) vno 2 etype 0x17 (RC4-HMAC) keylength 16 (0xfd77a26f1f5d61d1fafd67a2d88784c7)
The password is same as the one used for creating the service account for Policy Server.
- Specify that the web server service account is Trusted for Delegation as follows:
- Right-click the service account (krbsvc-smwa) properties.
- Select the Delegation tab.
- Select the second option, Trust this user for delegation to any service (Kerberos only).
The domain controller is ready for Kerberos authentication.
KDC Configuration on UNIX Example
The following process shows how to configure a KDC Kerberos realm on a UNIX host to support Kerberos authentication. This example uses the following server and account names:
- Servers
Domain Controller: dc.example.com
Policy Server: smps.example.com
Web Server: www.example.com
Active Directory Domain: EXAMPLE
Kerberos Realm: EXAMPLE.COM
- Accounts
User Account: testkrb
Web Agent Service Account: krbsvc-smwa
Policy Server Service Account: krbsvc-smps
Follow these steps:
- Install MIT Kerberos, if necessary.
- Use the kdb5_util command to create the Kerberos database and an optional stash file. The stash file is used to authenticate the KDC to itself automatically before starting the kadmind and krb5kdc daemons as part of the host auto-boot sequence.
Both the stash file and the keytab file are potential point-of-entry for a break-in. If you install a stash file, it must be readable only by root, must not be backed up, and must exist only on the KDC local disk. If you do not want a stash file, run the kdb5_util without the -s option.
This example generates the following five database files in the directory specified in kdc.conf file:
- Two Kerberos database files: principal.db and principal.ok
- One Kerberos administrative database file: principal.kadm5
- One administrative database lock file: principal.kadm5.lock
- One stash file: .k5stash
[root@rhasmit init.d]# kdb5_util create -r EXAMPLE.COM -s
Initializing database '/var/kerberos/krb5kdc/principal' for realm 'EXAMPLE.COM',
master key name 'K/M@EXAMPLE.COM'
You will be prompted for the database Master Password.
It is important that you NOT FORGET this password.
Enter KDC database master key:
Re-enter KDC database master key to verify:
- Create a user principal (testkrb).
- Create a user principal (for example, testwakrb), a host principal (HTTP/www.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM), and a service principal (krbsvc-smwa) for the web server host. The password used for creating host account must be same as the password specified when using the ksetup utility on the web server host.
- Create a user principal (testpskrb), host principal (smps/smps.example.com) and service principal (krbsvc-smps) for the Policy Server host. The password used for creating host account must be same as the password specified when using the ksetup utility on the Policy Server host.
- Create a keytab file for the web server service principal as follows:
ktadd -k /tmp/krbsvc-smwa.keytab HTTP/www.example.com
- Create keytab for Policy Server service principal as follows:
ktadd -k /tmp/krbsvc-smps.keytab smps/smps.example.com
The Kerberos realm is configured on a UNIX host.
Configure Kerberos Authentication at the Policy Server
The Kerberos authentication scheme requires that you modify the Agent Configuration Object (ACO):
- Log in the Administrative UI.
- Click Infrastructure, Agent Configuration, Modify Agent Configuration.
- Click the edit button for the Agent Configuration object of your agent.
- Add these three parameters to the Agent Configuration Object:
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
|
KCCExt
|
.kcc
|
|
HttpServicePrincipal
|
Specifies the web server principal name.
Example: HTTP/www.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM
|
|
SmpsServicePrincipal
|
Specifies the Policy Server principal name.
Example: smps.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM
|
Complete these additional steps at the Policy Server:
- Deploy the keytab file on the KDC that contains the Policy Server principal credentials to a secure location on the Policy Server.
- Configure a Kerberos configuration file (krb5.ini) and place it in the system root path on Windows and in KRB5_CONFIG on UNIX.
Important! If the Policy Server is installed on Windows and the KDC is deployed on UNIX, perform the additional configuration on the Policy Server host using the Ksetup utility.
More information:
Kerberos Configuration at the Policy Server Example
Kerberos Configuration at the Policy Server Example
The following procedure shows an example of how to configure a Policy Server on Windows to support the Kerberos authentication scheme. The configuration on Windows and UNIX are similar except for the following differences:
- The Kerberos configuration file on Windows is C:\windows\krb5.ini. On UNIX, the file can reside anywhere as long as the KRB5_CONFIG environment variable is set to the fully qualified path.
- The location of the keytab is system dependent. For example, C:\windows\krbsvc-smps.keytab on Windows, or /opt/CA/siteminder/krbsvc-smps.keytab on UNIX. The Kerberos configuration file default_keytab_name configuration option specifies the fully qualified path to the file.
- The UNIX keytab merges the service account keytab and the host keytab into a single keytab file.
Note: If the Policy Server is installed on Windows and the KDC is deployed on UNIX, perform other required configuration on the Policy Server host using the Ksetup utility.
Follow these steps:
- Install and configure the Policy Server.
- Install and configure policy store directory services.
- Add a Host Configuration Object referencing the Policy Server.
- Create an Agent Configuration Object and add these three new parameters:
- KCCExt
-
Value: .kcc
- HttpServicePrincipal
-
Specifies the web server principal name.
Example: HTTP/www.example.com@EXAMPLE.COM
- SmpsServicePrincipal
-
Specifies the Policy Server principal name.
Example: smps@smps.example.com
- Create a user directory.
- Create a user, for example, testkrb, in the user directory.
- Configure a new authentication scheme using the Administrative UI. See Configure a Kerberos Authentication Scheme.
- Configure a policy domain.
- Add a realm to protect a resource using the authentication scheme.
- Add Rules and Policies to allow access for the user, testkrb.
- Configure a Kerberos configuration file (krb5.ini) and place krb5.ini in the Windows system root path. Configure krb5.ini to use the Windows 2008 KDC keytab file containing the Policy Server principal credentials. See the following sample krb5.ini:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = EXAMPLE.COM
default_keytab_name = C:\WINDOWS\krbsvc-smps.keytab
default_tkt_enctypes = rc4-hmac
default_tgs_enctypes = rc4-hmac
[realms]
EXAMPLE.COM = {
kdc = dc.example.com:88
default_domain = example.com
}
[domain_realm]
.example.com = EXAMPLE.COM
- Deploy the Windows KDC keytab file containing the Policy Server principal credentials to a secure location on the Policy Server.
The Policy Server on a Windows host is configured for Kerberos authentication.
Kerberos Authentication Configuration at the Web Server
Configuring a Windows or UNIX web server to support Kerberos authentication follows these general steps:
- Install a Web Agent with the Kerberos authentication scheme support.
- Register a trusted host with the Policy Server and configure the Web Agent.
- Deploy the keytab file (created on the KDC) containing the web server credentials to a secure location on the web server.
- Configure a Kerberos configuration file (krb5.ini):
- Configure the KDC for the Kerberos realm (domain).
- Configure krb5.ini to use the keytab file containing the credentials of the web server principal.
- Place krb5.ini in the system root path on Windows and in KRB5_CONFIG on UNIX.
Important! If the web server is installed on Windows and the KDC is deployed on UNIX, perform additional configuration on the web server using the Ksetup utility.
Configure Kerberos Authentication at the Windows Workstation
To support Kerberos authentication, several Internet Explorer settings are required, and the workstation host is added to the KDC domain.
Important! If the KDC is deployed on UNIX, perform the additional required configuration on the workstation using the Ksetup utility.
Follow these steps:
- Add the host for the Windows workstation to the KDC domain.
- Log in to the host using user account created on the KDC.
- Configure the browser to pass credentials automatically:
Configure a Kerberos Authentication Scheme
Kerberos provides a platform-independent architecture for authentication and single sign-on. Using this authentication scheme presupposes that you have a working Kerberos setup.
Note: The following procedure assumes that you are creating an object. You can also copy the properties of an existing object to create an object. For more information, see Duplicate Policy Server Objects.
Follow these steps:
- Click Infrastructure, Authentication.
- Click Authentication Schemes.
- Click Create Authentication Scheme.
Verify that the Create a new object of type Authentication Scheme is selected.
Click OK
- Enter a name.
- Enter a protection level. The default is 5.
- (Optional) Select Password Policies enabled for this authentication scheme.
- Select Kerberos Authentication Template from the Authentication Scheme Type list.
- Enter Server Name, Target, Principal Name, and User DN information. See the Help for descriptions of these fields.
- Specify the mappings between Kerberos realms and Windows domains. You can map one Kerberos realm to many Windows Domains.
Note: When you specify the DOMAIN variable in the User DN Lookup field, this mapping is required, even when the realm and domain names are the same.
- Click Submit.
The Kerberos authentication scheme is saved. Assign the scheme to a realm.
Configure Kerberos External Realm on Windows Host
For the Windows workstation to use a Kerberos KDC deployed on UNIX, you must configure both the Kerberos KDC server and the workstation.
In the Kerberos realm, create a host principal for the Windows host. Use the following command:
kadmin.local: addprinc host/machine-name.dns-domain_name.
For example, if the Windows workstation name is W2KW and the Kerberos realm name is EXAMPLE.COM, the principal name is host/w2kw.example.com.
Because a Kerberos realm is not a Windows domain, the KDC operating environment must be configured as a member of a workgroup, which happens automatically when you follow this process:
- Remove the host from the Windows domain.
- Add the test user, for example, testkrb, to the local user database.
- Add the Kerberos Realm:
ksetup /SetRealm EXAMPLE.COM
- Restart the host.
- Add the KDC :
ksetup /addkdc EXAMPLE.COM rhasmit
- Set a new password:
ksetup /setmachpassword password
Note: The password used here is same as the one used while creating the host principal account in the MIT KDC.
- Restart the host.
Note: Whenever changes are made to the external KDC and realm configuration, a restart is required.
- Set the Realm Flag
ksetup /SetRealmFlags EXAMPLE.COM delegate
- Run AddKpasswd:
ksetup /AddKpasswd EXAMPLE.COM rhasmit
- Use Ksetup to configure single sign on to local workstation accounts by defining the account mappings between the Windows host accounts to Kerberos principals. For example:
ksetup /mapuser testkrb@EXAMPLE.COM testkrb
ksetup /mapuser * *
The second command maps clients to local accounts of the same name. Use Ksetup with no arguments to see the current settings.
Troubleshooting SiteMinder Kerberos Authentication
Be aware of the following issues when working with Kerberos authentication:
- The Policy Server system clocks must be synchronized (within 2 minutes) to the KDC system clock. Otherwise, Kerberos authentication fails because of clock skew errors.
- All the hosts must have suitable entries for the IP Address, fully qualified domain name (FQDN) and hostname in the /etc/hosts file. The order of these entries also matters in some cases. Also, include at least single space between these entries:
IP Address FQDN hostname
- Use klist (UNIX KDC clients) to list tickets present in the credential cache. The flag –f provides information about tickets flags. These tickets are forwarded to complete the Kerberos authentication process.
For example, see sample klist output listed following.
bash-2.05$ klist
Ticket cache: /tmp/krb5cc_1002
Default principal: HTTP/sol8sunone.test.com@TEST.COM
Valid starting Expires Service principal
Wed Dec 26 15:00:03 2007 Wed Dec 26 21:40:03 2007 krbtgt/TEST.COM@TEST.COM
- Always use the kinit program for the user and service principal at the MIT KDC host and UNIX KDC client.
The kinit syntax for the user principal is:
kinit principalname
This command prompts for the password used while creating the user
principal.
The kinit syntax (it can vary from host to host) for service principal is:
kinit -k [-t keytab location containing service principal] principalname
The kinit command does not prompt for a password, because it uses a keytab file to authenticate the service principal.
- Install any network packet trace utility on the workstation to see the Kerberos tokens exchanged between the browser and web server. The token starting with TIR indicates NTLM tokens, and tokens starting with YII denote the Kerberos tokens.
- Log off the workstation host after any change in encryption type at the KDC. Also, restart the Policy Server and web server services after any changes are made to the Kerberos configuration or the keytab files.
- The KDC does not support post-dated tickets.
- Only DES-CBC-MD5 and DES-CBC-CRC encryption types are available for MIT interoperability.
- Always enable the Policy Server and the Web Agent logs to record the authentication error messages.
- Verify that the name and location of keytab file for any host matches the ones in the krb5.conf file.
- The SPN is always case-sensitive. The krb5.keytab files for the Policy Server and the web server hosts must contain the host and service principals.
- Verify the version of ktpass utility. The ktpass command tool utility is included in the Windows support tools and can be installed from MSDN download.
- Always confirm the encryption type used while creating the keytab file. Windows by default supports RC4-HMAC encryption.
- Confirm the Kerberos version number (kvno). The kvno of the service principal must match the kvno of its keytab file. The kvno number of any keytab is displayed when it is created.
To determine the kvno of a service account for Windows Active Directory, use the ADSI Edit as follows:
- Run adsiedit.msc from command prompt.
- Go to service account, under CN=Users, DC=domain, DC=com under drop-down Domain (fqdn_ADhost) at the left.
- Right-click the service account and click properties.
- Verify the value of the msDs-KeyVersionNumber attribute, which matches the one shown while creating the keytab file for the service account.
The kvno for any user account changes every time its password is changed. If the version numbers do not match, create an account and keytab, or change the password to match the kvno to the kvno of the keytab.
To determine the kvno of a service account for a UNIX MIT KDC, use the kvno utility. The syntax of this command is:
Kvno principalname
- Verify the keytab file validity
Windows: Verify whether the keytab file is valid by installing Windows support tools on the Policy Server and Web Agent. Run the following command:
Kinit -k -t <keytab file location> <respective spn>
For example:
kinit -k -t C:\Windows\webserver.keytab HTTP/websvriis6.test.com@KRISH.COM
This command returns no error when the keytab file is valid.
Solaris: Verify both keytab files validity by running the following commands:
Kinit -k -t <keytab file> <SPN>
For example:
kinit -k -t host.keytab host/<fqdn>@DOMAIN.COM
kinit -k -t smps.keytab smps/<fqdn>@DOMAIN.COM
- If you get no errors, keytab files are fine, and the krb.conf file has valid values.
- If you get an error, check whether the SPN is valid in KDC using the following command:
Kinit host/<fqdn>@DOMAIN.COM
This command usually asks for password. If you provide a valid password, you do not get an error message. If this command does not ask for password, the SPN was not identified. Check the property of that object. The SPN entry is on the Account tab, for example, host/fqdn. Make sure no other object has the same entry set as SPN.
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


