

The Information Card Authentication Scheme (ICAS) feature lets you create multiple information card authentication schemes. Each one is configured as a custom authentication scheme.
Information cards are like the physical cards that we carry in our wallets. Each information card represents a set of identity information. For example, an information card that represents a driver's license can contain the following sensitive identity information: photo, birth date, first and last name, and license number. Information cards let users manage their identity information. Users can view their information cards and the associated identity information. They can choose from the available cards for a given information exchange. And they can authorize the release of the identity information that is associated with a selected card.
An Identity Selector is an application that exposes information cards.
An Identity Selector is an application that lets users manage their identity information and their online relationships with Relying Parties and Identity Providers. A Relying Party (RP) is the web site, application, or service that requires identity information to authenticate the user. The Identity Provider (IdP) is a third party that authenticates identity information and creates security tokens that the user can share with the Relying Party.
Identity Selectors allow users to access web-based resources without having to manage a multitude of user names and passwords. Likewise, businesses no longer have to maintain a database of user identity information that can be inaccurate and vulnerable to misuse. Eliminating the maintenance of users and databases reduces risk and liability while enhancing agility.
Identity Selectors also give the user control over the identity information is released to each Relying Party. And finally, Identity Selectors provide users with a consistent user interface and better user experience.
Windows CardSpace is the Microsoft implementation of an Identity Selector. CardSpace provides users with a consistent user interface for interacting with any Relying Party or Identity Provider. The Policy Server supports Windows CardSpace through a custom authentication scheme called Information Card Authentication Scheme (ICAS).
The Information Card Authentication Scheme (ICAS) available on the Policy Server supports Windows CardSpace. Each instance of ICAS is configured as a custom authentication scheme in the Administrative UI and implemented like any other custom authentication scheme.
Authenticating a user with ICAS involves these components and steps:
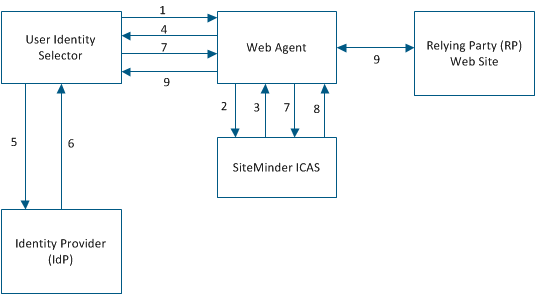
Note: The user can select a card that contains optional claims that are not required by the RP.
The following terms are useful for understanding ICAS:
An architecture that specifies how identity information is shared by users, Relying Parties, and Identity Providers.
The person whose identity information is being shared. Sometimes, the user is called the subject.
The Web site that requests and consumes identity information.
A third party that authenticates identity information and shares the information with Relying Parties by creating security tokens. Credit card companies, banks, government agencies, employers, and insurance companies are all examples of Identity Providers.
The technology that the Identity Providers use to create security tokens. A Security Token Service:
Note: SAML 1.0 and 1.1 specifications are supported.
A cryptographically signed and encrypted set of claims.
An assertion of truth. Each token contains one or more claims about the user's identity. Examples of claims are the first name, last name, email address, birth date, and so on. The user or a third-party Identity Provider can make claims.
A set of identity information. Information cards are comparable to the physical cards that we carry in our wallets. For example, an information card that corresponds to a driver's license can contain the following sensitive identity information: photo, birth date, first and last name, license number, state, height, and sex.
An information card that contains claims that the user asserts about himself, but a third party does not corroborate the claims. A personal card contains a Private Personal Identifier (PPID) that is generated when the card is created. Personal cards are appropriate for low-sensitivity identity information, such as an email address.
Note: Personal cards are also called self-issued cards.
An information card contains claims that the user asserts about himself and that are corroborated by a third party. A managed card contains a Private Personal Identifier (PPID) that is generated when the card is created and a pointer to the Identity Provider's STS. Managed cards are appropriate for sensitive identity information, such as a credit card number.
An application that lets users manage their relationships with Relying Parties and Identity Providers and control how their identity information is shared and used. An identity selector:
Microsoft's Identity Selector for the Windows operating system.
Support for Windows Cardspace, Microsoft's Identity Selector, implemented in SiteMinder as a custom authentication scheme.
Identifier generated by the Identity Selector when an information card is created.
Two files are required to configure each instance of ICAS: the fcc file and the properties file.
Specifies the authentication settings that you can customize for each instance of ICAS.
A sample fcc file that is shipped with the Web Agent kit.
Specifies how an instance of ICAS behaves.
A sample properties file
Note: When configuring an instance of ICAS in the Administrative UI, the administrator specifies the path to the properties file.
Before you can implement ICAS, the following conditions must be met:
Use one of the following web browsers:
The Web Server must be configured for SSL communication. This configuration protects the fcc file.
Note: For more information, see the Web Agent Configuration Guide.
The InfoCard.fcc file that is shipped with the Web Agent kit must be customized for each instance of ICAS.
Note: For more information, see the Web Agent Configuration Guide.
The Java Runtime Environment must be configured to decrypt security tokens that are encrypted with strong encryption algorithms.
Policy Server configuration includes the following tasks:
Configure the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) by installing the Java Cryptography Extension (JCE) Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction policy files. These files are needed to decrypt security tokens that are encrypted with strong encryption algorithms.
Important! Back up the default policy files that are shipped with the JRE before installing the new policy files.
Follow these steps:
security.provider.7=com.rsa.jsafe.provider.JsafeJCE
Configuring the Policy Server for ICAS includes the following steps:
Configure an ICAS Properties File
An ICAS properties file specifies how an instance of ICAS behaves. When configuring an instance of ICAS in the Administrative UI, the administrator specifies the path to the associated properties file. To configure a new properties file, open a sample properties file with a text editor and edit the contents. Always save and rename the new properties file.
Note: Multiple instances of ICAS can use the same properties file.
Example: A properties file named InfoCard.properties contains the following properties and sample values:
Specifies the location of the Information Card fcc file.
Example: fcc=https://web_server_home/siteminderagent/forms/InfoCard.fcc
Note: To activate the Identity Selector, specify "https".
Specifies the VPPID attribute value. The command UpdateUserStoreWithVPPID requires this attribute to update a user attribute.
Example: vppid_attribute=mail
Specifies the claim necessary to disambiguate the user.
Examples:
vppid_claim=http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/surname
vppid_claim=http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/givenname
vppid_claim=http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/emailaddress
Specifies the key in the certificate data store that is used to retrieve the SSL certificate of the Relying Party.
Example: alias=rpssl
If ICAS is configured in anonymous mode, this setting specifies the guest user login.
Example: guestuser=guest
Specifies the provider of the tokenPrim interface.
Example: tokenPrim=com.ca.sm.authscheme.infocard.higgins.TokenAdapter
Specifies the user attribute where the claims are stored when the command StoreClaimsToUserStore is executed.
Example: storeclaims_attribute=description
Defines a chain of commands to execute during user disambiguation.
Example: preprocessingchain=+vppidchain
Note: For more information, see Configure ICAS Command Chains.
Defines a chain of commands to execute during user authentication.
Example: postprocessingchain=+vppidchain;com.ca.sm.icas.command.StoreClaimsToContext
Note: For more information, see Configure ICAS Command Chains.
Defines a chain of commands to execute during error processing.
Note: For more information, see Configure ICAS Command Chains.
(Optional) Defines the location of the XML file that contains the White List that is specified by Federal Identity, Credentialing, and Access Management (ICAM).
Example: whiteListLocation=C:\\Program Files\\ca\\siteminder\\config\\WhiteList.xml
Note: For more information about ICAM White List, see Configure Support for the ICAM White List.
Configure ICAS Command Chains
Command chains are defined in the ICAS properties file. A chain is a set of commands that executes in an orderly manner.
The named chain commands include:
These named chains are present by default.
Consider the following information:
According to your requirements, configure the following class files:
Key Class Files to Configure ICAS
The following key class files are used to configure ICAS:
Stores extracted claims to the session store of Policy Server.
Executes a set of commands over a claim. For each claim name, which forms the last part of the namespace, ICAS looks for a chain that is defined as chainID.claimID in the properties file. If the chain definition is found, then ICAS executes it and passes the context with the specific claim.
Example: For executeClaimCommand1=com.ca.sm.icas.command.ExecuteClaimChain, define the email claim as follows:
Processes the DumpClaimsCommand if a token is found with an emailaddress claim.
Generates a hash of the VPPID claim attribute.
Sets the VPPID claim attribute value to anonymous. This class file is used for logging in with information cards that are not linked to any user accounts (anonymous access).
Sets the VPPID claim attribute value from the information card token to the context object.
Returns the value true, which stops the execution of the currently running chain.
Reads the claims from the information card token and store them to the application-specific context.
Stores the claims read from the information card token to a specified user attribute (in the ICAS properties file) in the user directory.
Escapes the script tags (<, >) in the claims using HTML entities. For example, <td> becomes <td;>
Escapes the characters in a claim value so that it can be passed to an SQL query.
Translates the exception string that is found within context. This translated string is stored back into the context.userText that is available in the FCC.
Translates the exception string that is found within the ICAS properties file. This translated string is stored back into the context.userText that is available in the FCC.
Stores the claims read from the information card token to a specified user attribute (available in the ICAS properties file) from the user directory.
Class Files to Check the Values of Claims
The following class files are used to check the values of claims:
Stores extracted claims to the session store of Policy Server.
Generates an exception when the claim is empty.
Generates an exception when the given claim has multiple values.
Generates an exception when the given claim is not empty.
Generates an exception when the given claim is not multivalued.
Generates an exception when the given claim is not null.
Generates an exception when the given claim is not single valued.
Generates an exception when the given claim is null.
Generates an exception when the given claim is single valued.
Class Files to Debug
The following class files are used for debugging purpose:
Displays the chain ID on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the VPPID claim details (name and value) on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the details of all the claims in the token on the console
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the details of the context object on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the details of the parameters that are specified in the ICAS properties file on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the details of the system environment on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays the stack trace of the executing thread on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Generates a new claim "_claims_" that has an HTML table representing the known claims. You can use this claim in an active response to create a cookie or header to show the retrieved claims to a user.
Generates an HTML table representing the parameters that are specified in the ICAS properties file. You can use this HTML table in an active response to create a cookie or a header to show the retrieved claims to a user.
Writes the claim details (name and value) in the chain context to the Policy Server trace logs.
Writes the details of all the claims in the token to the Policy Server trace log.
Logs the decrypted XML token to the Policy Server trace log.
Logs the encrypted token that is obtained from the IDP to the Policy Server trace logs.
Displays a START message on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Displays a STOP message on the console.
Note: To view the output, start the Policy Server in the console mode.
Generates an exception object that includes the claim value as a part of the message.
Store Claims for Later Use in Active Responses
You can store claims for later use in active responses. To store claims for later use, add the following property to the properties file:
Defines the chain of commands to execute during user authentication. This phase includes any claim transformation and storage commands.
Example: postprocessingchain=com.ca.sm.authscheme.infocard.command.StoreClaimsToContext
Configure the Certificate Data Store for ICAS
Consider the following information:
Follow these steps:
Note: For more information, see the Microsoft documentation. To import the SSL certificate from the pfx file, the Policy Server uses the password that you provide when exporting the SSL certificate to the pfx file.
Configure a User Directory for ICAS
Authentication of the user depends on finding a match between one of the claims that are presented to ICAS and a user attribute in the user database. During token disassembly, the specified claim value is used as a lookup value in the user directory. Therefore, configure the user directory so that the LDAP lookup string or SQL query scheme specifies the user attribute that corresponds to the specified claim.
The following examples show how to configure an LDAP lookup string and SQL query scheme for an email address.
LDAP User DN Lookup
(mail=
)
SQL Queries
SELECT EmailAddress, 'User' FROM SmUser WHERE EmailAddress = '%s' UNION SELECT Name, 'Group' FROM SmGroup WHERE Name = '%s'
SELECT EmailAddress FROM SmUser WHERE EmailAddress = '%s' AND Password = '%s'
Create an Instance of ICAS
You can create an instance of ICAS by specifying a custom authentication scheme in the Administrative UI.
Limit: Each policy store can support up to ten instances of ICAS.
Follow these steps:
The Scheme Setup group fields appear.
Note: ICAS does not support Password Policies.
smjavaapi
Note: The custom authentication scheme uses the Java Authentication API.
Leave these fields blank.
Note: The custom authentication scheme does not use the shared secret.
Type the following two parameters in the Parameter field and separate them by a space:
This is the fully qualified name of the class that implements the SmAuthScheme interface.
This is the location of the properties file.
com.ca.sm.icas.SmAuthInfoCard policy_server_home\config\icas\InfoCard.properties
The Create Authentication Scheme task is submitted for processing.
Configure an Active Response that Retrieves a Claim Value
To configure an active response that retrieves a claim value after authentication is complete, use the custom class com.ca.sm.icas.GetClaimValue
Note: Storing and retrieving claim values requires a session store. For more information about session stores, see the Policy Server Administration Guide.
Follow these steps:
Specifies the name of the claim.
Example: emailaddress
Specifies the name of the library.
Value: smjavaapi
Specifies the name of the function.
Value: JavaActiveExpression
Specifies the custom ICAS command and the location of the file, claims.xsd, that defines standard claim types according to the Information Card model.
Example: com.ca.sm.authscheme.infocard.GetClaimValue http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/ws/2005/05/identity/claims/emailaddress
The response that retrieves a claim value is created.
Configure Support for the ICAM White List
The ICAS implementation supports the Federal Identity, Credentialing, and Access Management Identity Metasystem Interoperability 1.0 Profile (ICAM IMI 1.0 Profile) specification, which is based on White List of issuers and LOA authorization.
Note: For more information about White List and LOA support, see ICAM IMI 1.0 Profile Release Candidate.
To enable White List processing, update the following parameters in the Infocard.properties file.
Defines the chain of commands to execute during user authentication.
Example: postprocessingchain=com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.whiteListChecker
Defines the location of the XML file that contains the White List that is specified by ICAM.
Example: whitelistlocation=C:\\Program Files\\ca\\siteminder\\config\\WhiteList.xml
The ICAS implementation supports the verification of three Level of Assurances (LOAs)
White List processing is mandatory to verify LOA1, LOA2, and LOA3. Append the following details to the postprocessingchain parameter to support LOA processing:
postprocessingchain=com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.whiteListChecker; com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.ErrorIfLOA1ClaimMissing
postprocessingchain=com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.whiteListChecker; com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.ErrorIfLOA2ClaimMissing
postprocessingchain=com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.whiteListChecker; com.ca.sm.icas.whiteListChecker.ErrorIfLOA3ClaimMissing
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|