

The Logic Server uses the USM schema and the Persistence Service interface to enact operations that create a unified, Persistent Store of USM data from the domain manager data retrieved by connectors. The following illustration shows the flow of data from connectors through the Logic Server:
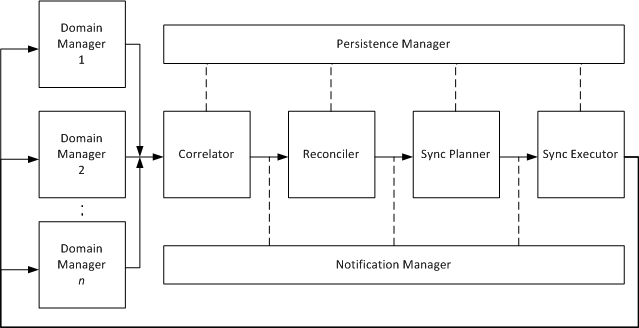
Matches USM entities coming from multiple domain managers that represent the same managed object (for example, a database server managed by CA NSM, CA Spectrum, and CA eHealth). This SA Manager component evaluates data against common properties named correlation keys. Each CI enters the SA Manager as a projection sheet. If correlation keys match, the Correlator creates a notebook with all projection sheets that the Correlator determined refers to the same CI. Correlation occurs in the SA Manager and notebooks are transmitted to the Reconciler in the Logic Server.
Creates a reconciled sheet of common properties for correlated projection sheets, so that objects managed by multiple domains appear as one reconciled CI in CA SOI that uses the unified set of properties in the reconciled sheet.
Note: For more information about how reconciliation works and how to customize reconciliation policies and formulas, see How Reconciliation Works.
Transmits data to and from the Persistence Service for creating, updating, and deleting CI sheets and notebooks and running named queries on objects.
Manages the subscription and buffering of events from the Persistence Service. This component notifies the Logic Server modules when USM data requires modification.
Determines when to synchronize data from the Persistent Store with source domain managers based on synchronization plans.
Performs the synchronization operations indicated by the Sync Planner. The Executor pushes synchronization changes to the connector framework, after which the connector carries out the necessary inbound operations on its domain manager to change the domain manager data so that it matches the records in the Persistent Store.
Note: For more information about how synchronization works, see Synchronization.
Important! The functionality enabled by the Sync Planner and Sync Executor components is only supported for specific synchronization use cases.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|