

Each process or subprocess that you identify corresponds to a process object in the Library Browser. Process objects define a sequence of linked steps. A process operator represents each step. After you map a step-by-step process, identify the operators that perform each step. Sometimes a single operator can perform a given step. Other times, a step can require two or more separate operators.
Define steps in a process by placing icon-based operators that represent actions that CA Process Automation performs. Start operators begin processes. Stop operators end processes. Logical and control operators define starting and stopping points, branching, and iterations in a process. The design for a process reveals its structure and also maps, synchronizes, and defines both the sequence and dependencies between tasks.
Example: Operators in a Process
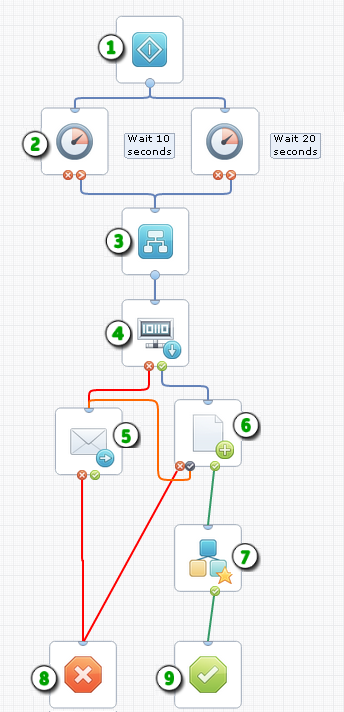
|
Item: |
Description: |
|---|---|
|
|
Start: The Start operator represents the single entry point where the process begins. Start operators can also indicate the first step in an independent branch. |
|
|
Delay: The Delay operator delays processing subsequent branches of a process until a specified interval of days, hours, minutes and seconds passes. |
|
|
Or Operator: Or and And operators control steps logically. The Or operator only completes (and lets processing continue) when one of the input operators completes. The And operator only completes (and lets processing continue) when all of the input operators complete. |
|
|
Get SNMP Variable: This operator returns the value of an SNMP variable. |
|
|
Send Email: Use this operator to notify other users by email. |
|
|
Write File: This operator writes a dataset variable to a file. The custom exit port |
|
|
Start Process: This operator starts another process. You can set an optional Loop property to run another process repeatedly. |
|
|
Stop Failure: The Stop Failure operator stops all branches in a process and sets the process to a Failed state. Use a Stop Failure operator for the abnormal outcome of a process or branch. |
|
|
Stop Success: The Stop Success operator stops all branches in a process and sets the process to a Completed state. Use a Stop Success operator for the normal outcome of a process or branch. |
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|