

The CA Process Automation interface provides an integrated development and administrative environment to view, manage, and run all objects in your automation systems. CA Process Automation is a web application that can be opened on any computer with access to the CA Process Automation Orchestrator.
Each major tab at the top of the page presents a unique section or functional area of the application. Common controls throughout the application make it easy to use. For example, you use the same basic steps to sort a list of entries and configure which columns appear.
|
Item: |
Description: |
|---|---|
|
|
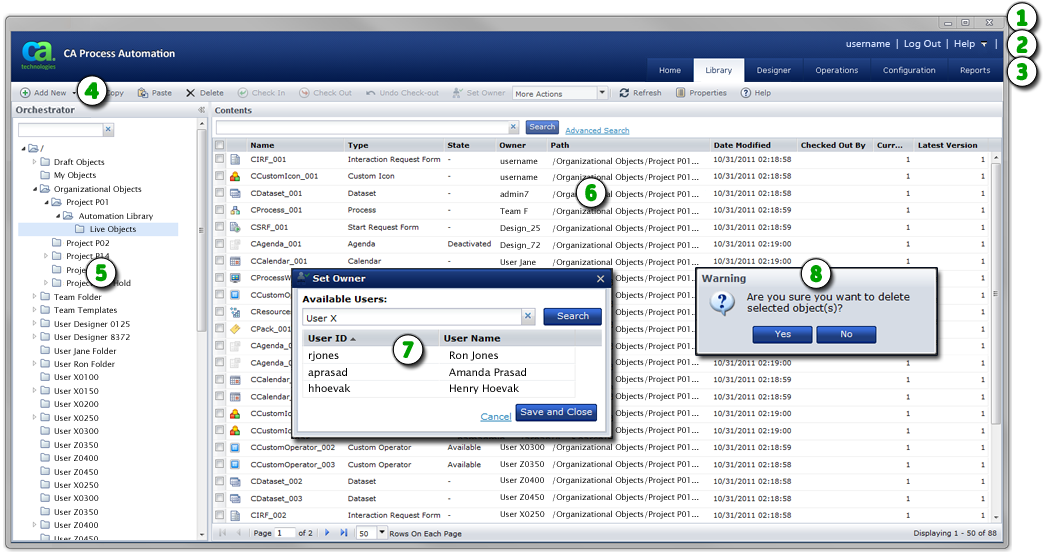
OS and Browser Controls: Although not part of CA Process Automation, your operating system provides controls for working with the current window for tasks such as Minimize, Maximize, Restore, and Close. Your browser also displays its own menus, toolbars, panes, and search areas. You can sometimes use browser features to supplement built-in CA Process Automation features such as refreshing a page or adjusting the view magnification (Zoom). |
|
|
Links: CA Process Automation provides common application links including User Settings, Help, and Log Out. Individual pages include appropriate links to related content. |
|
|
Main Application Tabs: Click a tab to focus on a specific CA Process Automation section. The Library tab is selected in the sample image, so the application displays folders and objects in the Library Browser. |
|
|
Toolbar: Many pages and dialogs display specific toolbars with appropriate tool buttons and icons. |
|
|
Panes: Panes divide a window or page. In this example, the Library Browser pane appears at left and features both a filter input field and an expandable folder hierarchy. The main page displays detailed information about the entry you select from a pane. |
|
|
Main Page: The main area of a page displays essential information about an item selected from a pane. CA Process Automation typically presents the data in a table, list, form, design canvas, or chart. As necessary, the main area is further divided into palettes, tabs, panes, or other visual controls. |
|
|
Dialog: When you click specific buttons, apply actions, or issue commands, the application often presents dialog boxes to collect additional input. |
|
|
Message: Predefined logic and events that you or the system initiate can result in the appearance of messages. Most of these alerts are informative and provide necessary feedback. However, some messages display critical warnings designed to protect your data. Error messages provide useful information that you can combine with log file data to troubleshoot issues. |
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|