

CA Process Automation can read values that a shell process generates into dataset variables. Before a UNIX Script or Windows Script operator runs its associated script, it creates a folder to accept values that the script generates. The C2OSVD environment variable specifies the full path to the folder (for example, C:\TMP\_VS_559) that is created for the script operator. A script can then copy data to text files in the folder to pass the data back to CA Process Automation. Data that is passed back to CA Process Automation using the C2OSVD directory populates variables in the script operator dataset.
A script must save data to text files in the C2OSVD directory. After a script operator completes its script (but before it performs the post-execution actions), it determines whether the location to which C2OSVD points contains files. CA Process Automation then creates operator dataset variables according to the following rules:
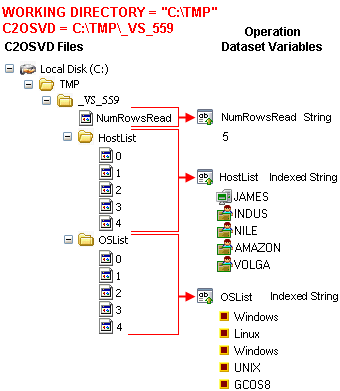
The following illustration shows the file-to-variable conversion when the working directory is set to C:\TMP. The operator appends \_VS_599 to the working directory path to create the C2OSVD value C:\TMP\_VS_599. The folder name (in this case _VS_599) is unique for every instance of any operator.
The illustration also shows two folders %C2OSVD%/HostList and %C2OSVD%\OSList that contain five files named 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4. The script writes a computer name to each numbered file in the HostList folder. The script writes an operating system name to each numbered file in the OSList folder. CA Process Automation creates two zero-based indexed variables after running the script, HostList and OSList. The application assigns the contents of the numbered files in the HostList and OSList folders to the corresponding elements of the indexed variables.
In the example, the Windows script uses the C2OSVD variable to create the file %C2OSVD%\NumRowsRead. CA Process Automation creates a corresponding variable (NumFilesRead) in the script operator dataset after it runs the script. The product then assigns the contents of the NumFilesRead file to the variable.
When a script operator finishes, it deletes the C2OSVD folder and its contents. The script operator post-execution code can access the operator dataset variables. The code typically copies the operator dataset variable values to local variables in the process dataset or to operator dataset variables in subsequent process operators. The three example scripts in this chapter show how the example illustrated in this section is implemented using UNIX script, VBScript, or PerlScript.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|