You have now defined the fields in which the Project entity will store data, and specified the class library fields from which those fields inherit. In this next step, you give the Project entity a user interface and functionality to interact with a database.
You again use inheritance to add this functionality. The inheritance triple gives your entity the objects necessary to display and process a user interface, and to read data from and write data to a database.
To add functionality to the Project entity:
![]()
Notice that there is no plus sign to the left of the Project entity. This tells you that there are no objects scoped to it.
You just created the triple Project is a OBASE/Grid Maintained Entity. This indicates that Project inherits the structure and functionality of the Grid Maintained Entity object in the OBASE class library.
For more information on defining entities, look in the online help index. For information on the Grid Maintained Entity object, select the pattern in the Object Browser and press Shift+F1.
![]()
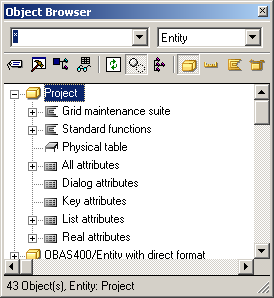
You can see that among the objects it inherited are several functions (with scoped panels) and views, and a physical table. These objects enable Project to display a user interface, and to store data to and retrieve data from a database.
Specifically:
You will learn more about panels in Modifying the User Interface, and functions and views in the chapter "Defining Owned By Relationships."
| Copyright © 2012 CA. All rights reserved. | Tell Technical Publications how we can improve this information |