

The following diagram shows the tasks that are required to connect to the endpoint, and who does each task. It shows the process for connecting to Exchange 2010 without an agent on the endpoint.
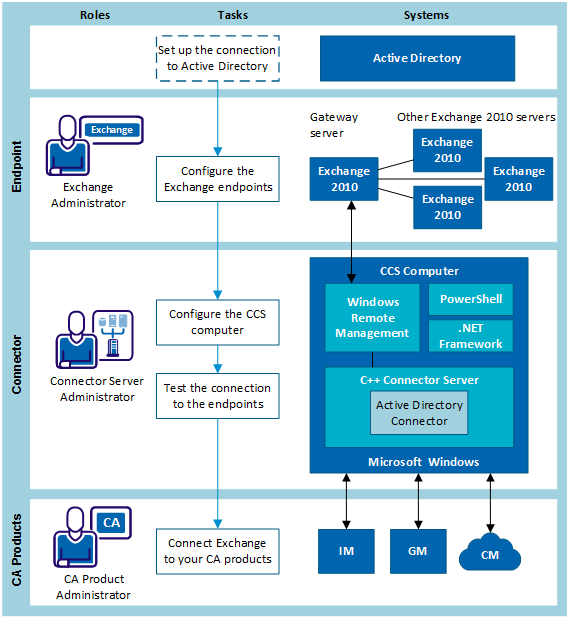
A gateway server is the Exchange server that the connector communicates with. The gateway server then passes any changes to other Exchange servers in the same domain.
In a mixed environment with Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010, the gateway server must be one of the Exchange 2010 servers.
We recommend that you choose a domain controller to be the gateway server. In Exchange 2007 and later, the Exchange server requires communication with Active Directory to perform actions on accounts. For this reason, timing issues may be encountered if accounts have not been fully replicated to the Domain Controller being queried by Exchange. If the timings are not right, the connector may attempt an operation on a new or modified AD account which Exchange does not yet recognize, thus returning an error.
For Exchange 2007 and 2010, this server must be running the Mailbox Server role.
If the gateway server is not also a domain controller, ensure that you choose an Exchange server that is in the same Active Directory replication site and configure the timeout settings if required.
If the gateway server is a mailbox server within a Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR) environment on Windows Server 2008, the server must have full access permissions to manage the cluster running the CCR (not applicable to Windows Server 2003). In CCR environments, install the Remote Agent on all Mailbox nodes.
Follow these steps:
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|