

Virtual Environment Scenario
A typical virtual environment includes a domain manager, an AM remote agent computer, and various virtualization server types containing DSM agent and scalability virtual machines as shown in the following illustration:
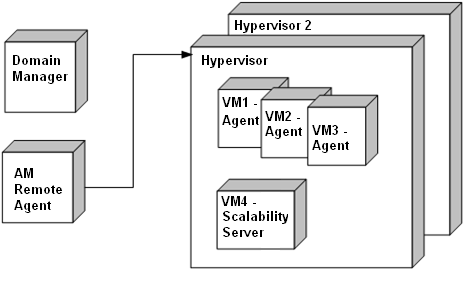
The DSM domain manager manages all computers, and the AM remote agent computer collects details about the VMs for both RVI and virtual WOL operations.
In this scenario, you can perform the virtual WOL using the following methods:
The job container is sent to the appropriate scalability server, which wakes up a VM using the WOL functionality of CAF API.
For more information, see Wake a Virtual Machine Using DSM Explorer.
You can configure the Wake-On-LAN option in the Setup OS Installation dialog during the activation of OS installation.
How CA ITCM Wakes a Virtual Machine
The method for waking a virtual machine differs from the method that is used to wake a physical computer. Each platform virtualization vendor provides their own SDK for WOL operations. As the AM remote agent already uses these SDKs to collect inventory, the agent can perform virtual WOLs using the new generic SendWOL method. CA ITCM uses the following process to wake virtual machines.
Note: The RVI agent cannot collect certain BIOS inventory attributes from Linux virtual machines that are running on Microsoft Hyper-V and XenServer servers, Virtual WOL is not supported on such Linux virtual machines.
Note: Typically, the string is a virtual GUID but it could be a system ID or serial number.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|