

To delete a record occurrence from the database, perform the following steps:
Areas should be readied whether they are affected explicitly or implicitly (for example, as owner of a set whose members are being erased).
What ERASE Does
The ERASE statement performs the following functions:
ERASE is a two-step procedure that first cancels the existing membership of the named record in specific set occurrences and then releases for reuse the space occupied by the named record and its db-key. Erased records are unavailable for further processing by any DML statement.
Currencies after an ERASE
Following successful execution of an ERASE statement:
The preserved currencies enable you to retrieve the next or prior records within the area or the next, prior, or owner records within a set in which the erased record participated.
ERASE Statement with No Options
To issue the ERASE statement with no options:
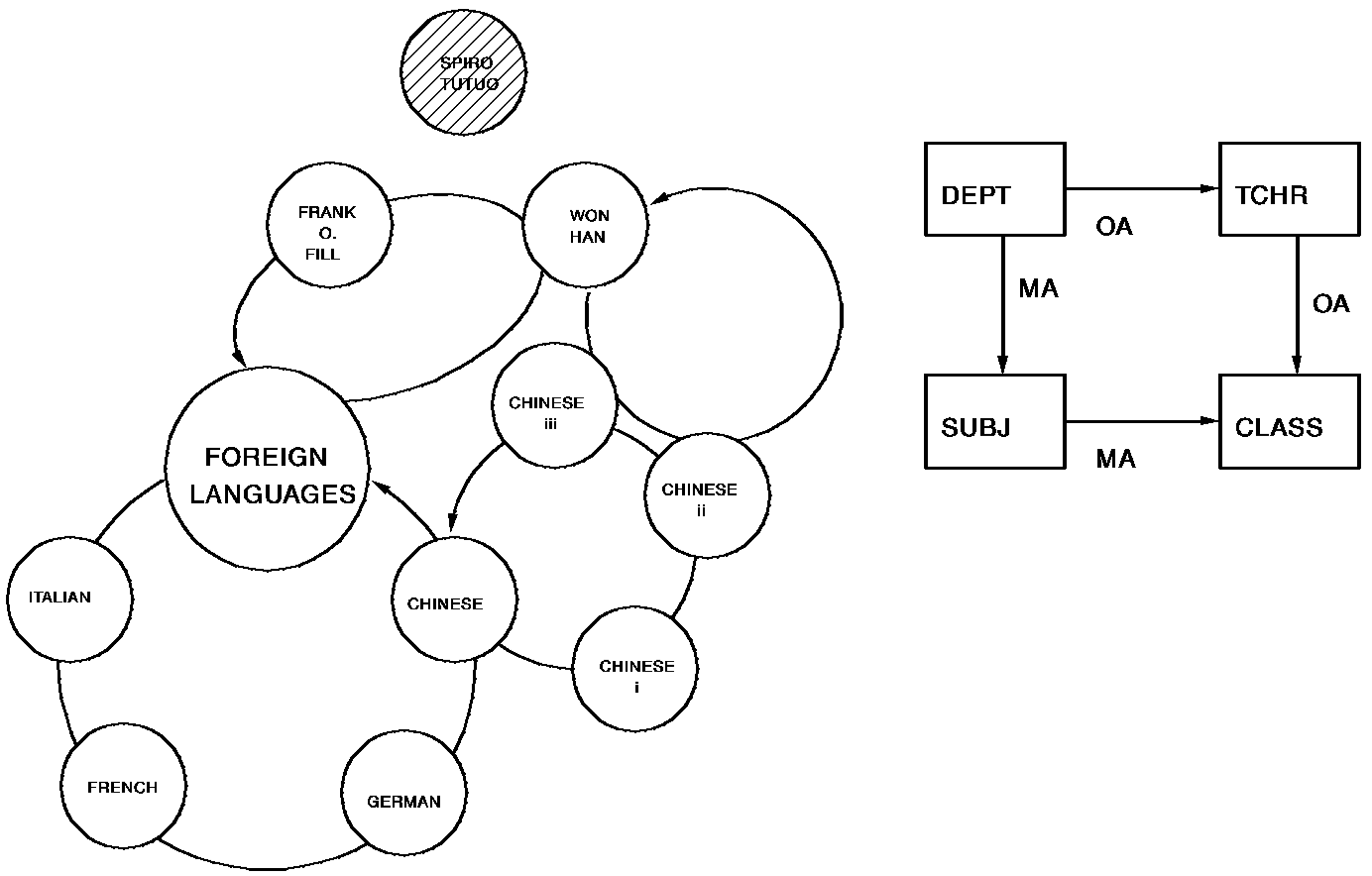
In the illustration below, an ERASE TCHR statement with no options disconnects the shaded occurrence (SPIRO TUTUO) from membership in the DEPT-TCHR set and then erases the record occurrences. This statement executes without error because the TCHR-CLASS set owned by record occurrence SPIRO TUTUO is an empty set (he doesn't have any classes).
ERASE Options
You can qualify the ERASE statement with these options to specify how the ERASE statement affects member occurrences:
ERASE PERMANENT
ERASE PERMANENT erases the specified record and all mandatory member record occurrences owned by the specified record. Optional member records are disconnected. If any of the erased mandatory members are themselves the owners of any set occurrences, they are erased as if they were directly the object record of an ERASE PERMANENT statement (that is, all mandatory members of such sets are also erased). This process continues until all direct and indirect members have been processed.
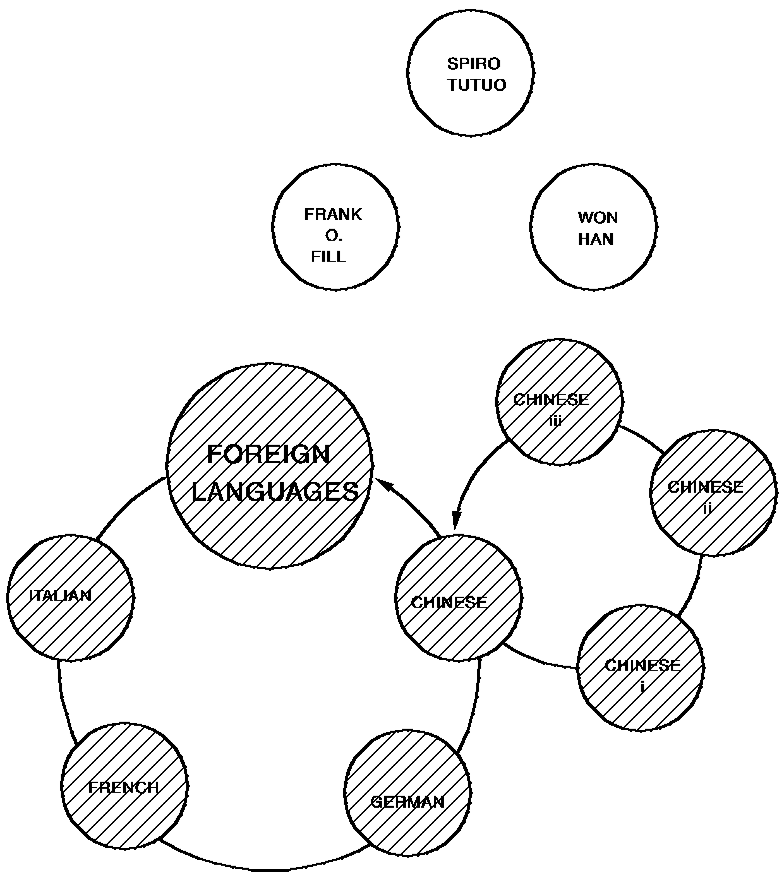
In the illustration below, currency has been set on the FOREIGN LANGUAGES occurrence of the DEPT record, and an ERASE DEPT PERMANENT statement has been issued. All subjects are erased because they are mandatory members of the DEPT-SUBJ set. All classes are also erased because they are mandatory members of the SUBJ-CLASS set. However, since membership in DEPT-TCHR is optional, members of the set owned by FOREIGN LANGUAGES are disconnected, not erased.
ERASE SELECTIVE
ERASE SELECTIVE erases the specified record and all mandatory member record occurrences owned by the specified record. Optional member records are erased if they do not currently participate as members in other set occurrences. All erased member records that are themselves the owners of any set occurrences are treated as if they were the object of an ERASE SELECTIVE statement.
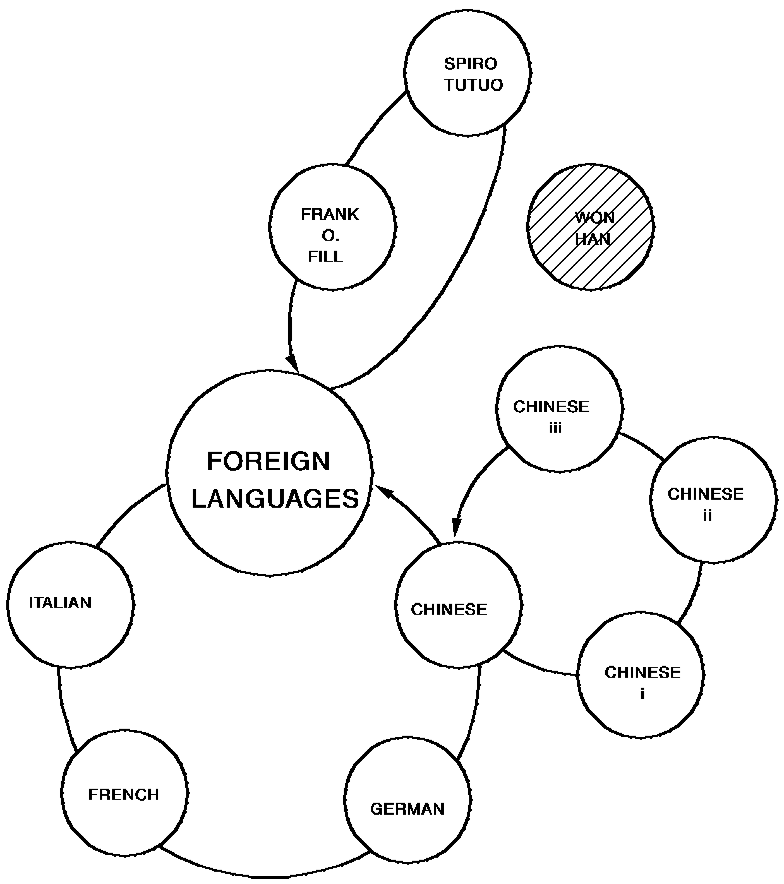
In the illustration below, currency has been set on the WON HAN occurrence of the TCHR record, and an ERASE TCHR SELECTIVE statement has been issued. Since WON HAN was the owner of two occurrences of the TCHR-CLASS set, an ERASE statement without an option would fail. The SELECTIVE option prevents these occurrences from being erased because they currently participate in another set (SUBJ-CLASS). This means, in effect, that the department still offers the classes even though the teacher is gone.
ERASE ALL
ERASE ALL erases the specified record and all mandatory and optional member record occurrences owned by the specified record. All erased member records that are themselves the owners of any set occurrences are treated as if they were the object record of an ERASE ALL statement.
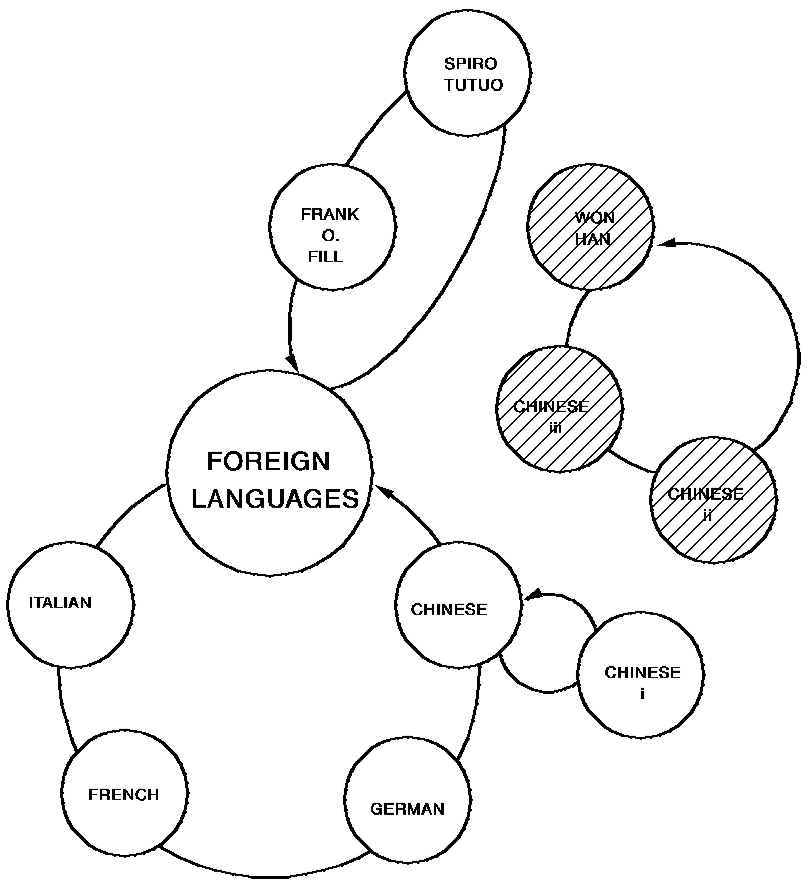
In the illustration below, currency has been set on the WON HAN occurrence of the TCHR record, and an ERASE TCHR ALL statement has been issued. Since WON HAN was the owner of two occurrences of the TCHR-CLASS set, the ERASE ALL statement erases these member occurrences. This means, in effect, that when the teacher leaves the department, his classes are dropped.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|