

This section contains the following topics:
Selecting Parameters and Limiting Migration
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator Parameter Statements
Notation Conventions and Syntax Rules
This chapter is a guide to understanding and using CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator parameters. It begins with a summary of all parameters, notation conventions, and syntax rules. The chapter then describes each parameter, shows its appropriate syntax, explains its rules for use, and describes its default. The parameters are presented in the order in which they are shown in the parameter summary. If a parameter option can be used in more than one statement, the option is presented and described in each statement.
If you need to move your dictionary entities from one dictionary to another, you should consider the following parameters and their explanation of how they relate to migration.
|
Item |
Parameters |
|---|---|
|
Parameters that describe environment. (Required) |
IDSOURCE and IDOBJECT DICTIONARY and OBJDICTIONARY NODE and OBJNODE SYSIDMS and SYSCTL files are also needed to completely define the environment. |
|
Parameters that describe the migration starting point and path. (Required) |
EXTRACT entity name LEVEL |
|
Parameters that describe output requested. (Optional) |
RUN (required), NOPRINT, NOXREF, clistname, clistversion |
|
Parameters that limit migration. (Optional) |
EXLOAD EXSOURCE DISCONNECT ADDONLY CHANGEONLY DOMAIN DATE SQLONLY |
When certain conditions that pertain to migration are known, you can specify additional CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator parameters that will allow for even quicker and easier migrations.
In most cases, limiting what is migrated can help you in two ways:
The following is a table defining conditions and actions.
|
Condition: If you know... |
Action: then use these parameters: |
|---|---|
|
The schema definition has not changed. |
EXSOURCE=DATABASE EXLOADS=SUBSCHEMA |
|
Any of: 1. The message area is not used to store dialog messages. 2. The message area is shared between the source and target dictionary. 3. Variable names are used in the Display Message Code statement. 4. Display Message Code is not used in process code. |
EXSOURCE=MESSAGE |
|
All dialogs that need to be migrated are named in an extract statement. |
EXSOURCE=SUBPROG |
|
Migration method: 1. Move source and regenerate. 2. Move source and load modules (no regeneration). 3. Move load modules only. |
EXLOADS=(SUBS, MAP, TABLE) Do not execute upload steps that use files TABLLOD, RHDCLOD, or SUBSLOD. EXSOURCE=(ALL) |
|
User registration is not used, or different users are registered in the target dictionary. |
DISCONNECT=USER |
|
Attributes in the source dictionary are not relevant to the target dictionary. |
DISCONNECT=ATTRIBUTE |
|
(virtually always) |
DISCONNECT=SYNONYM |
|
If the source and target dictionaries are in different Central Versions that are not accessible to each other through node communication. |
RUN=EXPORT For accessing the target dictionary. |
|
If you want to migrate the named entity with all of its related entities: |
LEVEL=DIALOG or PROGRAM |
|
If you want to limit the migration to the named entity and its subcomponents: |
LEVEL=ENTITY |
|
If you want to limit the migration to the named entity without any other entities: |
LEVEL=ONLY |
|
If you want to review the list of extracted entities and reports prior to creation of the syntax for the target dictionary population execute with: Assuming these meet with your satisfaction then execute with: |
RUN=VERIFY RUN=CREATESYNTAX |
Use these parameters to limit which entity occurrences are migrated:
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator has three parameter statements:
There are many optional parameters available for each statement. The next three graphics display the requirements and options for the three statements.
To initiate processing, you must enter one PROCESS statement for each execution of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator. You must specify which type of migration run you want to use, and additional global limitations.
The EXTRACT statement identifies a source dictionary entity as the starting point of the migration. In a single run of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator you can enter as many EXTRACT statements as you need, but each statement can identify only one entity type and name, or mask.
The CHANGE statement is an optional statement which allows you to alter the contents of the upload syntax files.
Be sure to review the following table for CA notation conventions and the next table for parameter syntax rules.
|
Example |
Rule |
|---|---|
|
PROCESS |
Keywords appear in UPPERCASE. The required portion of each keyword is underlined. You can omit the portion of a keyword that is not underlined without altering the meaning of the statement. |
|
DIALOG=dialog-name |
Variables appear in lowercase. You must substitute an appropriate value for each variable. |
|
/ / APPLICATION \ \ │ │ DIALOG │ │ │ │ │ │ (< < MAP > > ...) │ │ │ │ │ │ SUBSCHEMA │ │ \ \ TABLE / / |
An ellipsis (...) indicates that one or more options that are separated by commas can be selected and entered. |
|
< version > |
Braces enclose two or more options. You must select only one of the options. |
|
[,DATE=start-date] |
Square brackets indicate optional clauses. |
|
Item |
Rule |
|---|---|
|
Order of Parameter Statements |
Enter the PROCESS statement first. You can enter the other parameter statements in any order. |
|
Required Parameter Statements |
You must enter all parameters included in this chapter, except the Environment parameter. |
|
Continuing a Parameter Statement |
To continue a parameter statement onto the next record, key in a trailing comma. Do not split a keyword between two records. |
|
Entering Blanks in Parameter Statements |
You can enter blanks (character spaces) to separate keywords and improve readability in a parameter statement without affecting processing. When you include blanks in a value field, you must enclose the entire field in single quotes. |
|
Entering Quotes in Value Fields |
You may need to enter quotes within a value field that is delimited by quotes. To do this, enter two single quotes wherever a quote is needed within the value field. |
|
Entering Parameter Statements |
On an 80-character input record, enter all parameter syntax between columns 1 and 72 (inclusive). |
|
Comments |
Enter an asterisk (*) in column 1 to indicate a comment. |
|
Synonyms |
The PROGRAM and DIALOG options can be interchanged in parameter statements. Use the option to which you are most accustomed. |
|
Series of Variables |
When entering values for a series of variables, separate the values with commas and enclose the entire series with parentheses. |
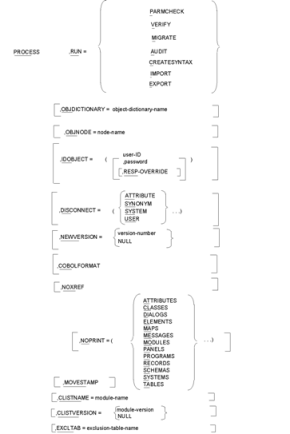
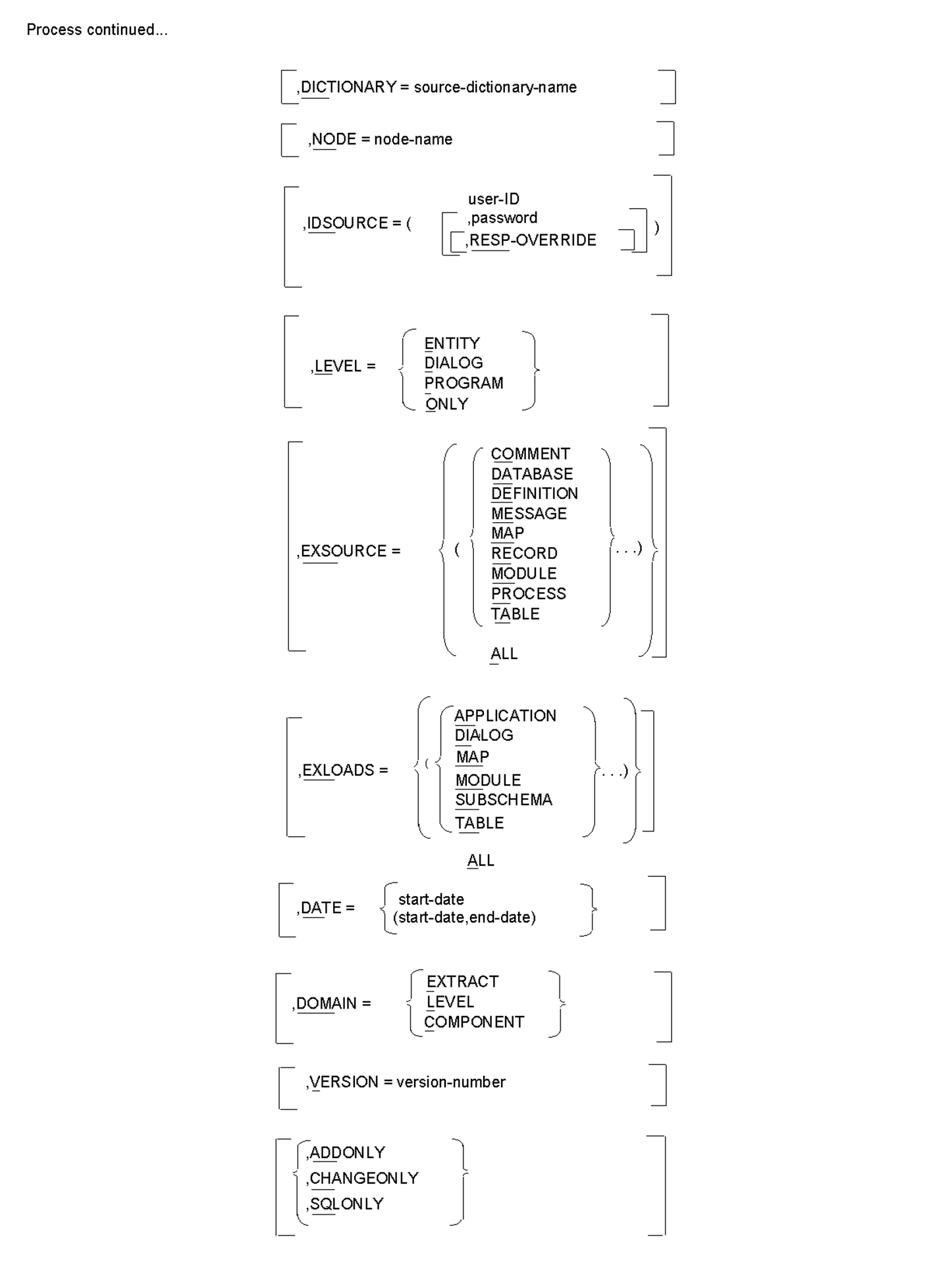
A single PROCESS statement is required for each run of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator. The PROCESS statement must be the first statement entered. It must also specify the type of run to be performed as well as identify the CA IDMS environments of the source and object dictionaries.
The two required parameters of the PROCESS statement are:
In addition to PROCESS statement requirements, you can also include parameter options that globally control processing. The first of the previous four parameter summaries displays parameter requirements and options for the PROCESS statement.
The PROCESS parameter initiates execution of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator and indicates that processing requirements and options follow.
/ PARMCHECK \ │ VERIFY │ ,RUN < MIGRATE > │ AUDIT │ │ EXPORT │ \ IMPRT /
The RUN parameter is a required parameter that controls CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator processing and separates its activities. Each run type directs CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to perform specific activities, stop processing, and produce reports with the results of each activity. The selection of run types allows you to control processing for both single job and two-job executions.
You can specify run types to perform these activities:
The following report shows the output from each run type. The functions and activities of each run type are also presented on the following pages.
Run = Report Parmcheck Verify Migrate Audit Export Import Create Syntax Parameter X X X X X X X Verification Source Dictionary X X X X Verification Extract X X X X Summary Extract X X X X Detail Entity X X X X Discrepancy Entity Cross X X X X Reference Syntax Production X X X X Report Syntax Files X X Display Syntax X X X X Files Catalog Navigation X Report
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator provides five run types to be used when you are performing a migration that transfers entities from one dictionary to another within the same Central Version (CV). These run types are also used when you are performing a migration between two CVs that share node communication. Node communication is discussed in the CA IDMS System Operations Guide. The first two run types, PARMCHECK and VERIFY, ensure that the migration is performed correctly. The actual upload to the object dictionary is performed after either a MIGRATE or an AUDIT run, or a CREATESYNTAX run providing a verify run that has been executed previously. The Operations Section contains additional details, a system flow, and a description of migration in a single job execution of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator.
,RUN=
Indicates that a run type follows.
PARMCHECK
Indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to check parameter statements for errors and produce a report of the results.
VERIFY
Indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to check parameter statements for errors, check the source dictionary for requested entities, check extract and sort entities, compare them to the object dictionary, and produce reports of the results.
MIGRATE
Indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to perform parameter checking, verification activities, and produce reports of the results. MIGRATE also directs CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to generate syntax for CA IDMS utilities. The syntax is not displayed on reports produced from this run type.
AUDIT
Indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to perform parameter checking and verification activities as well as produce detailed reports of the results. AUDIT also directs CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to generate syntax for CA IDMS utilities that populate the object dictionary. The syntax is displayed on the Syntax Files Display Report.
CREATE SYNTAX
Indicates that the extract file created in a verify run is used to generate syntax for the CA IDMS utilities that populate the object dictionary. Create syntax is used after running the verify run and not finding any errors that require correction.
Rule: An EXTRACT statement is not allowed when RUN=CREATESYNTAX.
Two options of the RUN parameter--EXPORT and IMPORT--allow you to perform a migration between dictionaries that exist on different Central Versions (CVs) without sharing node communication. This type of migration requires at least two runs of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator. The chapter "Operations" illustrates the system flow for the two-job execution and contains additional details and model JCL to perform EXPORT/IMPORT runs.
The previous report lists output from the EXPORT/IMPORT run types.
,RUN=
Indicates that a run type follows.
EXPORT
Indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to perform only the activities that access the source dictionary.
EXPORT directs CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to create an extract file from the source dictionary and to generate syntax files for CA IDMS utilities. The extract file is used for entity comparison in the IMPORT run. The syntax files are used by the CA IDMS utilities to populate the object dictionary.
IMPORT
indicates that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to perform only the activities that compare the extracted entities to the object dictionary and produce reports with the results.
Note: No comparison activities are carried out for extracted SQL entities from the source catalog.
Rule: An EXTRACT statement is not allowed when RUN=IMPORT.
Extraction of SQL entity definitions can be performed as a stand-alone run by specifying the SQLONLY parameter on the PROCESS statement. You can also perform SQL entity extraction in conjunction with regular network extractions.
A separate file, ddname=BCFUPD, containing SQL CREATE syntax will be created. The primary use of this enhancement is for transferring SQL definitions from a source catalog to a target catalog where these definitions do not already exist.
The SQL syntax file (BCFUPD) is used by the IDMSBCF facility to populate a target catalog.
The parameter options available in the PROCESS statement provide two functions:
The graphic PROCESS Statement Parameter Summary shows the parameter options and requirements available in the PROCESS statement.
By including options that tailor both the output to the object dictionary and reports, you can direct CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to:
The options used for tailoring the selection of information from the source dictionary direct CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to:
When the parameter options are specified in the PROCESS statement they will provide global control. If component types are excluded in the PROCESS statement, you cannot include them in the EXTRACT statement. If you have individual parameter requirements, you should indicate them in the EXTRACT statement. Some parameters can be specified in both the PROCESS and EXTRACT statements.
For example, if you specify :
EXSOURCE = MESSAGE
on the PROCESS statement and:
EXSOURCE = RECORD
on the EXTRACT statement, both MESSAGES and RECORDS would be excluded.
If the same parameters are used in both the EXTRACT and PROCESS statements, the values are combined for EXSOURCE, EXLOAD, and DOMAIN. For options with a single value the EXTRACT statement value, if any, will override the PROCESS statement.
,OBJDICTIONARY=dictionary-name
is an optional parameter that identifies the object dictionary that will be populated with the extracted entities. This parameter is useful when a central version or local mode can access more than one dictionary and you do not want the default dictionary to be populated.
Default: The default is the default dictionary of the central version or the dictionary specified in the JCL.
,OBJNODE=node-name
Is an optional parameter that identifies a node as the communication link between central versions and CPUs. By identifying the node you can populate an object dictionary that exists in a CV other than the one in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing. You must specify a node name when running a single job where the object dictionary is in a CV other than the one pointed to by the SYSCTL file.
,IDOBJECT=(user-id,[password,[RESP-OVERRIDE]])
Is an optional parameter that provides standard sign-on security to control access to the object dictionary. ID object must be specified if the dictionary signon security is on.
user-id
Indicates the standard identification of the user.
password
Indicates a valid password that identifies the user of the object dictionary.
Default: There is no default value. If the dictionary sign-on security is required, you must enter a valid-ID and password.
RESP-OVERRIDE
Releases dictionary security by generating a REGISTRATION OVERRIDE in the IDD SET OPTIONS statement. This option requires a user-ID that has full authorization.
/ ATTRIBUTE \ ,DISCONNECT = ( < SYNONYM > ...) │ SYSTEM │ \ USER /
DISCONNECT is an optional parameter that prevents the transfer of attributes, systems, and users connected to entities in the source dictionary and prevents syntax from being formulated with synonym specification. The source dictionary retains the original attribute and system connections. You can use any of the options of this parameter in the same run of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator.
ATTRIBUTE
Indicates that attributes connected to entities are not moved when the entities are transferred to the object dictionary. If ATTRIBUTE is selected, class associations connected to entities also are not moved when the entities are transferred to the object dictionary.
SYNONYM
Indicates that all syntax is formulated without synonym specification. If the root-element name cannot be located, an extended extraction search is attempted against the ELEMENT SYNONYM structure. If SYNONYM is not selected, this feature is disabled.
SYSTEM
Indicates that systems connected to entities are not moved when the entities are transferred to the object dictionary.
USER
Indicates that user security structures are not moved when the entities are transferred to the object dictionary.
Default: All system, attribute, synonym, and user associations in the source dictionary will be transferred to the object dictionary.
/ version-number \
,NEWVERSION = < NULL >
NEWVERSION is an optional parameter that allows you to assign a different version number to entities as they are transferred from the source dictionary to the object dictionary. The version numbers of records, subschemas, and maps embedded in load modules are also changed.
version-number
The new version number keeps the entities distinct from the production environment. For example, you can transfer entities from production environment dictionaries to a test dictionary, assign a new version number to the entities, and use them for testing. The version numbers of the entities as they exist in the production environment will not be changed.
Rule: The version number must be an integer from 0 through 9999. If a NULL is used, the dictionary must have a default of an absolute number instead of a relative value.
NULL
Indicates that all version qualifications are removed from the derived syntax in order to facilitate dictionary-level default version specification.
Default: The default value is the version number of each entity in the source dictionary.
,COBOLFORMAT
Is an optional parameter that directs CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to generate COBOL-like syntax, instead of DDDL syntax, to transfer records with elements.
NOXREF is an optional parameter that allows you to prevent the creation of the Entity Cross Reference Report.
Default: The Entity Cross Reference Report is produced.
,NOPRINT=(entity-type ...)
NOPRINT is an optional parameter that allows you to prevent specific entities from appearing on the Extract Detail Report and the Entity Cross-Reference Report.
,NOPRINT=
indicates that one or more entity types follow.
entity-type
Indicates that extracted entities of the specified type are not to appear on the reports. You can enter one or more of these entity types for the NOPRINT parameter:
Default: Every extracted entity appears on the Extract Detail Report and the Entity Cross-Reference Report.
,DICTIONARY=dictionary-name or source-catalog-name
Is an optional parameter that allows you to access an alternate source dictionary instead of the default dictionary as specified in the central version. Identifying an alternate source dictionary in the PROCESS statement is useful when more than one dictionary is accessible through the central version in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing. For SQL entities, this parameter allows you to access a catalog other than the default system catalog.
Default: The default dictionary as specified in the central version. For SQL entities, the default is the system catalog.
,NODE=node-name
Is an optional parameter that identifies a node as the communication link between central versions and CPUs. By identifying the node you can access a central version that exists in a CPU or region other than the one in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing.
Default: You access the dictionaries that exist in the central version in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing (as defined by the sysctl file).
,IDSOURCE=(user-id ,[password[,RESP-OVERRIDE]])
Is an optional parameter that provides standard sign-on security to control access to the source dictionary.
,IDSOURCE=
Indicates that valid user identification follows.
user-id
Indicates the standard identification of the user in the source dictionary.
password
Indicates a valid password that identifies the user of the source dictionary.
Default: There is no default value. If the dictionary sign-on security is required, you must enter a valid-ID and password.
RESP-OVERRIDE
Allows access to entity occurrences that are registered to a user other than the one named on IDSOURCE
Default: This option requires a user-ID that has full authorization, there is no default value.
LEVEL is an optional parameter that allows you to specify the path that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator follows to extract an entity from the source dictionary.
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can extract an entity by using one of three methods. First, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can locate the programs or dialogs that use the entity specified in the EXTRACT statement and extract all existing relationships. Second, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can bypass program or dialog relationships for a specific entity so that only the entity specified in the EXTRACT statement and its lower-level entities will be extracted. Finally, only the entity in the EXTRACT statement will be extracted.
You can direct CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to bypass program or dialog relationships in EXTRACT statements that specify these entity types:
For example, if you specify a record in an EXTRACT statement and include LEVEL=ENTITY, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator extracts only the specified record and the elements connected to the record.
/ DIALOG \ ,LEVEL = < PROGRAM > │ ENTITY │ \ ONLY / ,LEVEL=
Indicates that a starting point option follows. The DIALOG and PROGRAM options indicate the same level.
DIALOG
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator traces an entity specified in the EXTRACT statement to its dialog level. All the dialogs, programs, and the components of the dialogs and programs where the entity participates are extracted.
PROGRAM
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator traces an entity specified in the EXTRACT statement to its program level. All the programs and the components of the programs in which the entity participates are then extracted.
ENTITY
Indicates that an entity is to be extracted with its lower-level relationships only. This option applies to schemas, subschemas, records, elements, modules, maps, panels, tables, classes, and attributes.
ONLY
Indicates that the entity is to be extracted by itself.
Default: All entities except messages are extracted with their dialog or program relationships. Messages are extracted with any lower-level relationships.
/ / COMMENT \ \ │ │ DATABASE │ │ │ │ DEFINITION │ │ │ │ MESSAGE │ │ │ │ MAP │ │ ,EXSOURCE = < (< RECORD >...)> │ │ MODULE │ │ │ │ PROCESS │ │ │ │ TABLE │ │ │ \ SUBPROGRAM / │ \ ALL /
The EXSOURCE parameter (exclude source) is an optional parameter that prevents CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator from extracting specific source components. You can specify as many as nine component types to be bypassed in a single execution.
,EXSOURCE=
indicates source component types follow.
COMMENT
Indicates that all comments associated with entities are not to be extracted.
DATABASE
Indicates that all schema-related entities that exist in the source dictionary are not to be extracted. These include all schemas, schema records and elements, subschemas, and subschema records and elements.
DEFINITION
Indicates that definitions associated with entities are not to be extracted.
MESSAGE
Indicates messages are referenced by maps and dialog module source are not to be extracted.
MAP
Indicates that all map-related entities are not to be extracted. These include maps and panels, tables and messages used by the map, and records and elements owned by the map.
RECORD
Indicates that all records and elements are not to be extracted.
PROCESS
Indicates that a process code is not to be extracted.
MODULE
Indicates that the modules (other than process code) are not to be extracted.
TABLE
Indicates that table source code is not to be extracted from the source dictionary.
SUBPROGRAM
Indicates that programs or dialogs referenced by dialogs found from the EXTRACT statement will not be extracted.
ALL
Indicates that all EXSOURCE options are not to be extracted from the source dictionary.
Default: All source component types are extracted.
EXLOADS (exclude loads) is an optional parameter that limits the load modules that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator extracts from the DDLDCLOD (load) area of the source dictionary. You can enter up to four load module types in the same run.
/ / APPLICATION \ \ │ │ DIALOG │ │ │ │ MAP │ │ ,EXLOADS = < (< MODULE >...)> │ │ SUBSCHEMA │ │ │ \ TABLE / │ \ ALL / ,EXLOADS=
Indicates that a load module type follows.
APPLICATION
Indicates that load application modules are not extracted from source dictionary. The ADSA application cannot be updated unless the load module is migrated.
DIALOG
Indicates that dialog load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Consequently, you cannot regenerate the dialog if it does not already exist in the object dictionary.
MAP
Indicates that map load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Map load modules should not be extracted if map source is being extracted and the map will be regenerated.
MODULE
Indicates that map help load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Map help load modules should not be extracted if map source is being extracted and the map will be generated.
SUBSCHEMA
Indicates that subschema load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Subschema load modules should not be extracted if subschema source is being extracted and the subschema will be regenerated or if no database components are to be migrated.
TABLE
Indicates that table load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Table load modules should not be extracted if table source is being extracted and the table will be regenerated.
ALL
Indicates that no load module types are to be extracted.
Default: All load modules are extracted.
,DATE=start-date
,DATE = < start-date >
\ (start-date,end-date) /
Is an optional parameter that allows you to specify a time period in which an entity was updated. The DOMAIN parameter determines which entity occurrences will be tested.
,DATE=
Indicates that a date or date range follows.
start-date
Indicates the date, specified as mmddyy, which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to search for in the dictionary. Once the entity with the indicated date or a more recent date is located, the entities which will be extracted are determined by the domain parameter.
start-date,end-date
Indicates a date range with a starting date and ending date, specified as (mmddyy,mmddyy), which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to search for in the source dictionary.
Default: All entities are extracted without regard to date updated.
/ EXTRACT \
DOMAIN = < LEVEL >
\ COMPONENT /
DOMAIN specifies where the date selection criteria will be applied.
EXTRACT
Indicates that the date range in the date parameter is tested on each entity named in an Extract Statement. If a test fails, the entity is not used as the starting point for extraction.
LEVEL
Indicates that the date range in the date parameter is tested on each entity serving as the top level of an extract path. This is dependent on the Level parameter. If the test fails neither the entity nor any of its components will be migrated.
COMPONENT
Indicates that the data range in the date parameter is tested on each entity occurrence found in the extract path. If the test fails the entity is not extracted.
Default: Date range is tested on each entity named in an EXTRACT statement.
,VERSION=version-number
Is an optional parameter that allows you to locate an entity occurrence based on a specific version number. This parameter is used when an entity has multiple versions in the source dictionary. Entities often have more than one version when they are being used for application development.
The specified version number applies only to the entry point. You can specify values 0-9999.
Default: The default version number is 1.
CHANGEONLY
CHANGEONLY is an optional parameter that allows you to limit migration to changed entities.
ADDONLY
Is an optional parameter which allows you to limit migration to entities that are new to the target dictionary.
SQLONLY
Is an optional parameter which you use to limit the migration to SQL entities only. Only Parameter Verification and Catalog Navigation reports are produced for SQLONLY runs.
CLISTNAME=module-name
The CLISTNAME parameter is an optional parameter which allows you to assign a 32-character module name for the module used to contain the CLIST for new-copying, migration-related load modules.
module-name
Indicates the module name.
Default: If CLISTNAME is not specified, a module name based on the date and time will be specified. The default module name will be DBMSYYDDDHHMMSSTT. YYDDD indicates the current Julian date. HHMMSSTT indicates the current time to thousandths of a second
/ module-version \
CLISTVERSION = < NULL >
The CLISTVERSION parameter is an optional parameter used in conjunction with the CLISTNAME parameter to specify a version number for the module specified in the CLISTNAME parameter.
module-version
Indicates the module version number.
NULL
Indicates that the dictionary-level default version will be used.
Default: If no CLIST version is specified, the default version is 1.
MOVESTAMP
MOVESTAMP is an optional parameter which indicates that the map is to be decompiled with the DATETIME=YES parameter specified. Specifying MOVESTAMP ensures that the generation of the map in the object dictionary will leave the date/time stamp from the source dictionary unchanged.
,EXCLTAB = exclusion-table-name
EXCLTAB is an optional parameter which allows you to reference an entity exclusion table other than the default.
exclusion-table-name
Is a user defined list of entity occurrences which will always be excluded from migration to avoid needless migration or complications arising from changing particular entities. When you specify alternate tables, you can alter the exclusion list as needed for special migrations.
Default: The exclusion table USMEXCLT will be used.
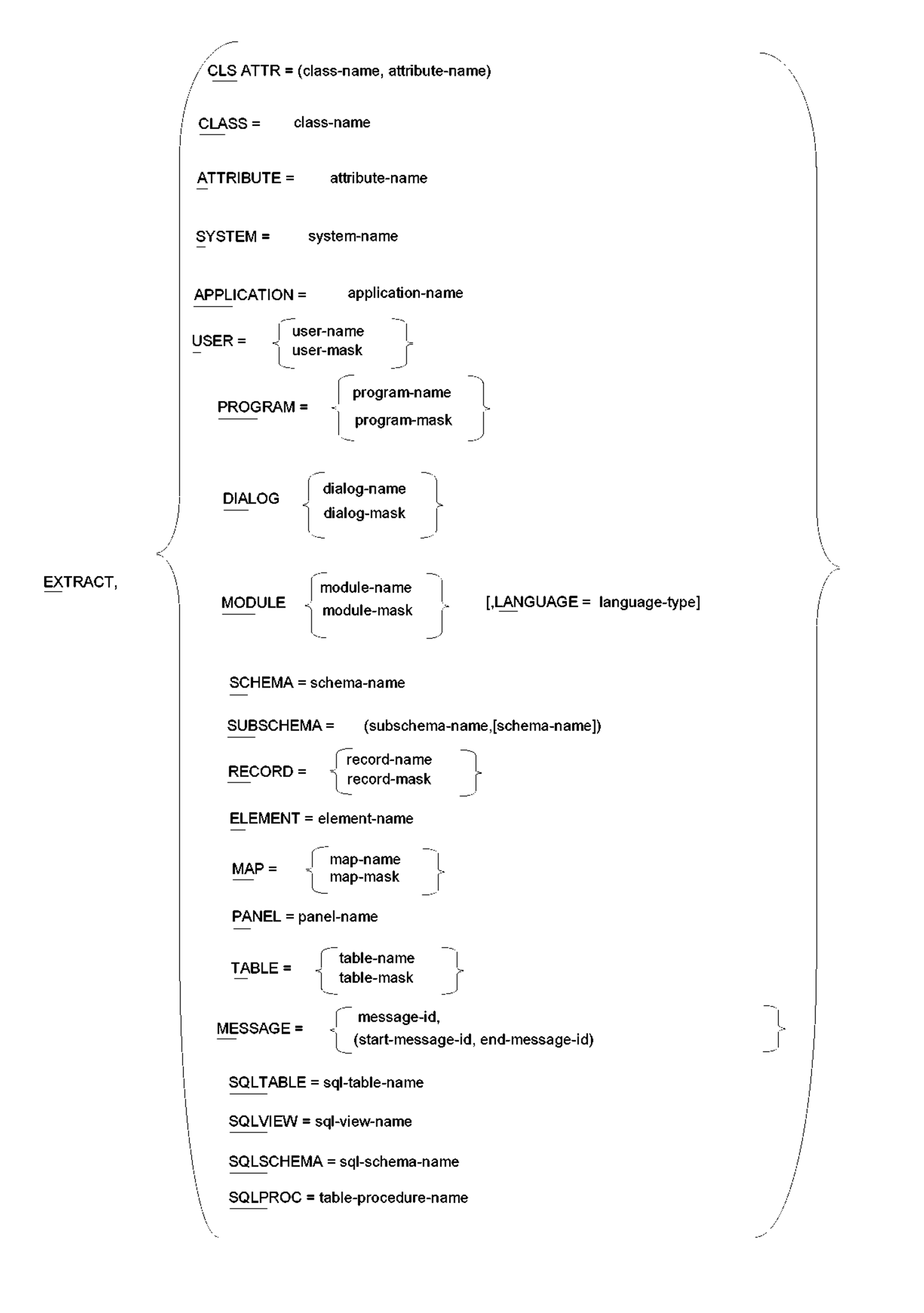
The EXTRACT statement identifies a source dictionary entity type and name as the starting point of the migration. This statement is required to access the source dictionary every time CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is run except RUN = IMPORT, or RUN = CREATESYNTAX in a two-job execution.
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator normally locates a dialog or program and extracts all of its components and their relationships. By including the LEVEL=ENTITY parameter you can bypass program and dialog relationships and extract specific entity types with their lower-level components only. See the LEVEL Parameter section in this chapter for details. By including LEVEL=ONLY parameter you can by pass all relationship and extract specific entities by themselves.
Each EXTRACT statement must specify one, and only one, entity type and name. You can enter as many EXTRACT statements as you need in the same run of CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator. More than one EXTRACT statement is required to access entities that exist in different version numbers, in alternate dictionaries, or on another machine. Even though a single entity may appear in multiple relationships, it will be extracted only once.
The following two graphics display the requirements and options of the EXTRACT statement.
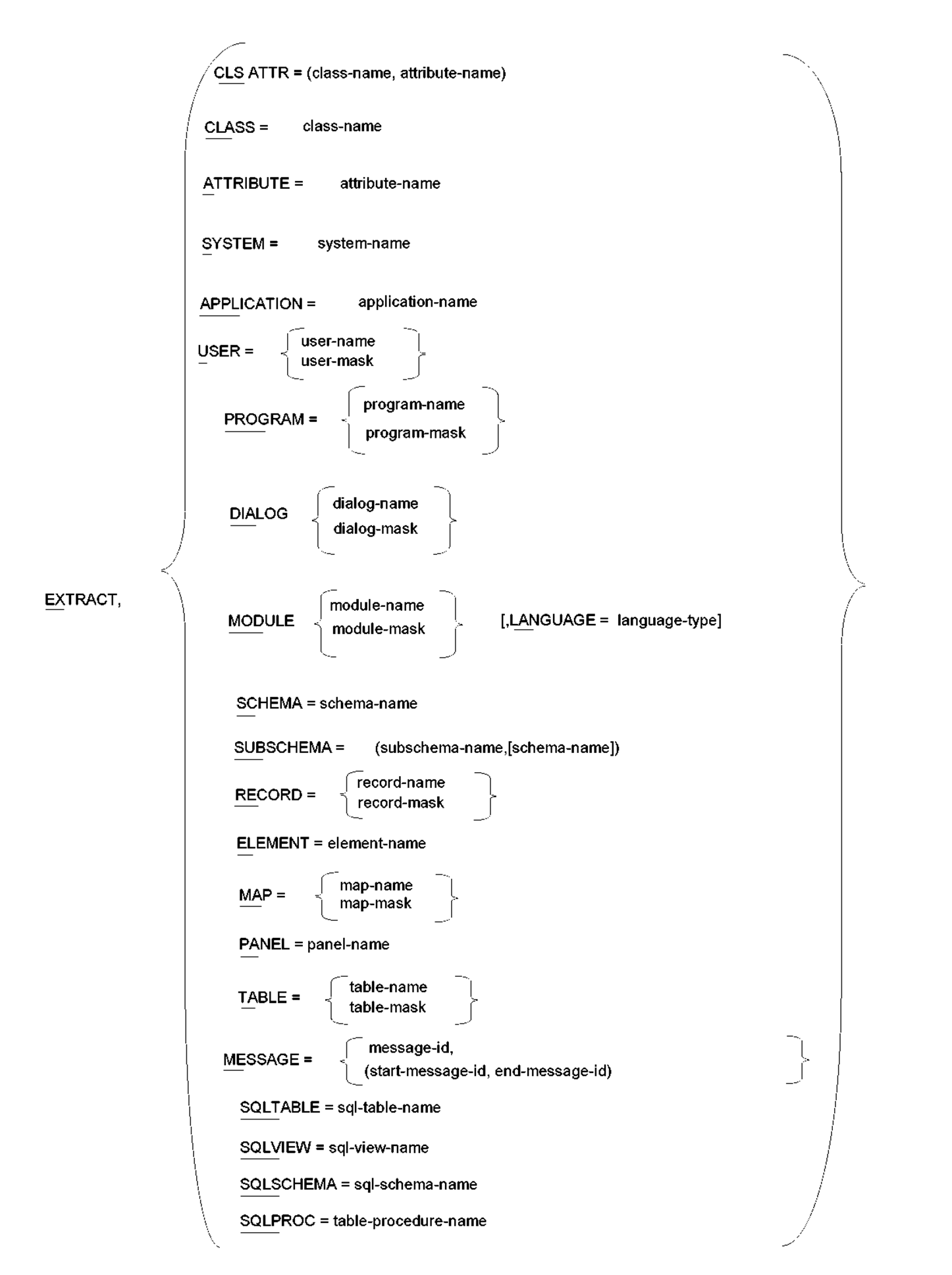
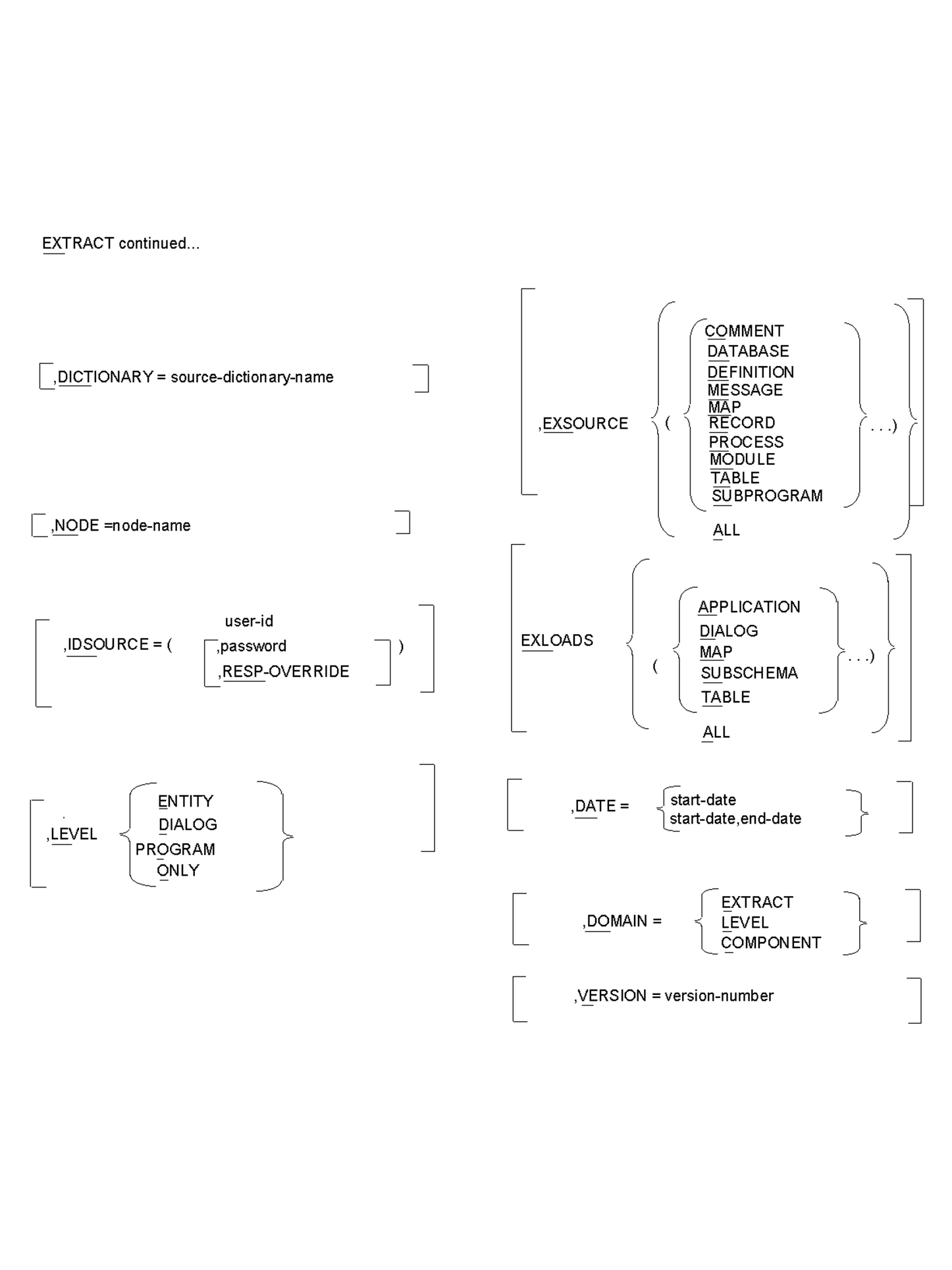
EXTRACT,
Indicates that an entity type to be extracted from the source dictionary follows. The EXTRACT statement must contain an entity-type and a name.
Note: Selection of entities related to the starting point named in the EXTRACT statement is controlled by the LEVEL parameter.
One and only one of the following entity types must be selected.
CLSATTR=(class-name),(attribute-name)
Indicates that the specified attribute of the specified class is the starting point.
CLASS=class-name
Indicates that the specified class is the starting point.
ATTRIBUTE=attribute-name
Indicates that the specified attribute is the starting point. If more than one attribute with the same name exists, all attributes will be used as starting points.
SYSTEM=system-name
Indicates that the specified system is the starting point and that dialogs or programs associated with it are to be extracted.
APPLICATION=application-name
Indicates that the specified ADSA application is the starting point and that the application and dialogs or programs associated with the application are to be extracted.
USER=user-name
Indicates that the specified user is the starting point.
user-mask
Indicates that every user with a user name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the user's thirty-two position name. For example, HLP**032 specifies that every user that includes HLP and 032 in the name in the indicated positions will be extracted. If blanks occur at the end of the user-mask, then blanks must occur at the end of the user-name.
/ program-name \
PROGRAM = < program-mask >
program-name
Indicates that the specified program is to be extracted with its related entities.
program-mask
Indicates that every program with a program name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the program's eight-position name. For example, HLP**010 specifies that every program that includes HLP and 010 in its name in the indicated positions is to be extracted.
/ dialog-name \
DIALOG = < dialog-mask >
dialog-name
Indicates that the specified dialog is to be extracted with its related entities.
dialog-mask
Indicates that every dialog with a dialog name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the dialog's eight-position name. For example, HLP**010 specifies that every dialog that includes HLP and 010 in its name in the indicated positions is to be extracted.
/ module-name \
MODULE = < module-mask >
module-name
Indicates that the specified module is to be extracted with its related entities.
module-mask
Indicates that every module with a module name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the module's thirty-two position name. For example:
HLP**************************010
Indicates that every module that includes HLP and 010 in its name in the indicated positions is to be extracted. If blanks occur at the end of the module-mask, then blanks must occur at the end of the module-name.
LANGUAGE=language-type
A language type may be specified to select modules of a particular language or to differentiate between like named modules. Language can only be specified with entity type of module.
SCHEMA=schema-name
Indicates that every dialog owning a subschema in the specified schema is to be extracted with its related entities.
SUBSCHEMA=(subschema-name ,[schema-name])
Indicates that every dialog owning the specified subschema is to be extracted with its related entities. You must also specify the schema name if the subschema is defined in more than one schema. This uniquely identifies the subschema used as an entry point.
RECORD=record-name
Indicates that every dialog owning the specified record is to be extracted with the dialog's related entities.
record-mask
Indicates that all dialogs owning every record with a record name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the record's thirty-two position name. For example, HLP**32 specifies that every record that includes HLP and 032 in the record in the indicated positions is extracted. If blanks occur at the end of the record-mask, then the blanks must occur at the end of the record-name.
ELEMENT=element-name
Indicates that every dialog owning records that use the specified element is to be extracted with its related entities.
MAP=map-name
Indicates that every dialog owning the specified map is to be extracted with its related entities.
map-mask
Indicates that all dialogs owning every map with a map name that matches a position-dependent identifier is extracted with its related entities.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the map's eight position name. For example, HLP**008 specifies that every map that includes HLP and 008 in the map in the indicated positions is extracted.
PANEL=panel-name
Indicates that every dialog owning a map that uses the specified panel is to be extracted with its related entities.
/ table-name \
TABLE = < table-mask >
table-name
Indicates that the table with the specified name is to be extracted with its related load modules.
table-mask
Indicates that every table with a table name that matches a position-dependent identifier are extracted with their related load modules.
Asterisks are used to replace characters in the table's eight-character name. For example, XXX***** indicates that every table whose name includes XXX in positions 1, 2 and 3 is to be extracted together with its related load modules.
MESSAGE=message-id
/ message-id \
MESSAGE = < (start-message-id,end-message-id) >
message-id
Indicates that a message with the specified ID is to be extracted from the source dictionary.
start-message-id,end-message-id
Indicates messages with ids that fall in the specified range are to be extracted from the source dictionary.
Table Procedure Name
specified as 'schema-name'.'proc-name' where both 'schema-name' and 'proc-name' are 1-18 character SQL identifiers.
Indicates that the table procedure, along with all of its associated keys, is to be extracted from the source catalog specified.
SQL-table-name
specified as 'schema-name'.'table-name' where both 'schema-name' and 'table-name' are 1-18 character SQL identifiers.
Indicates that the SQL table, along with all of its related SQL tables and entities, is to be extracted from the source catalog specified.
SQL-view-name
specified as 'schema-name'.'view-name' where both 'schema-name' and 'view-name' are 1-18 character SQL identifiers.
indicates that the SQL view, along with all of its related SQL tables and entities, is to be extracted from the source catalog specified.
SQL-schema-name
specified as 'schema-name' where 'schema-name' is a 1-18 character SQL identifier.
Indicates that the SQL schema is to be extracted from the source catalog specified.
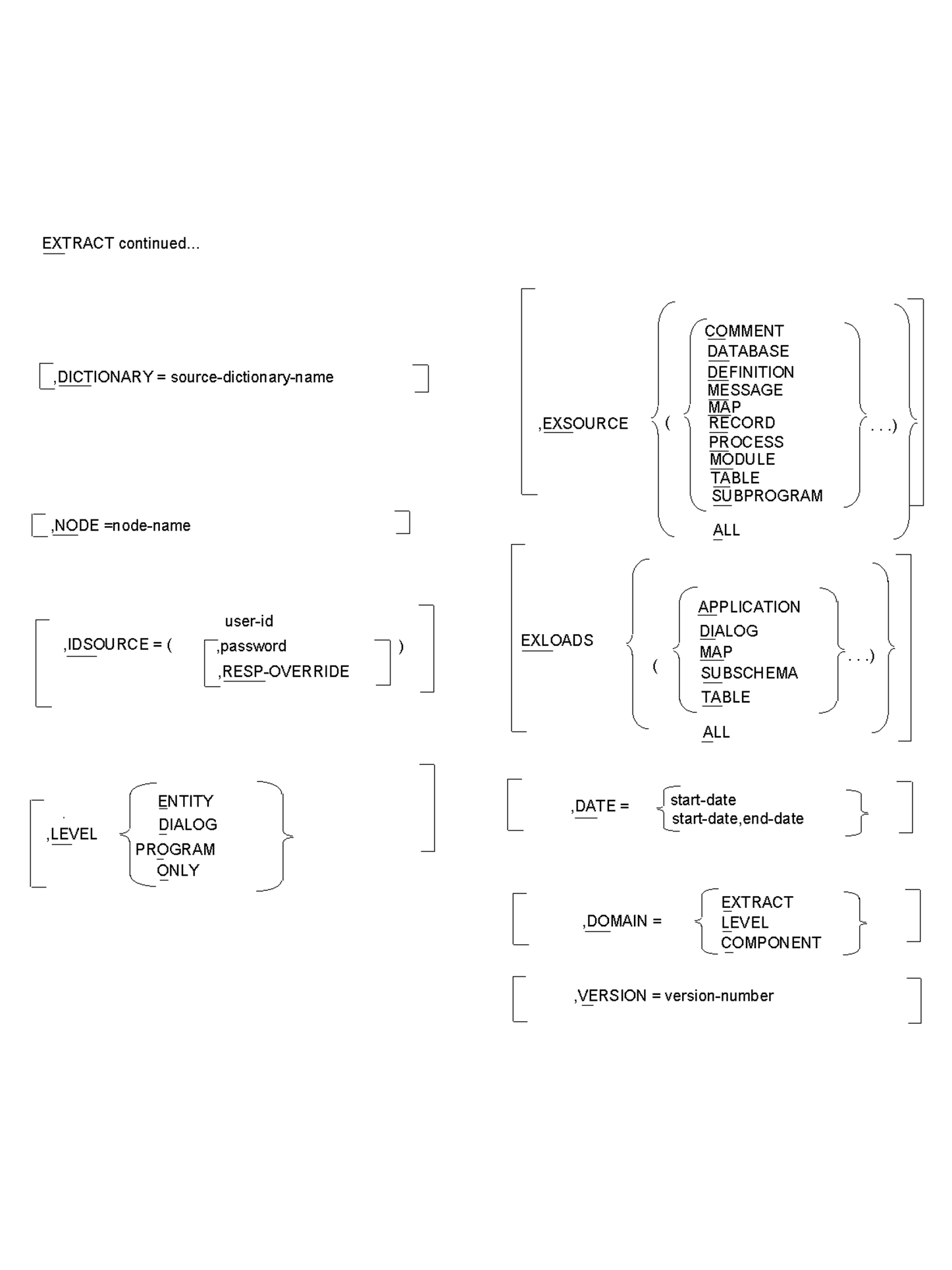
The parameter options available in the EXTRACT statement allow you to tailor the selection of each entity from the source dictionary.
When the parameter options are specified in the PROCESS statement, they will provide global control. If component types are excluded in the PROCESS statement, you cannot include them in the EXTRACT statement. If you have individual parameter requirements, you should indicate them in the EXTRACT statement. Some parameters may be specified in both the PROCESS and EXTRACT statements.
For example, if you specify:
EXSOURCE = MESSAGE
on the PROCESS statement and:
EXSOURCE = RECORD
on the EXTRACT statement, both MESSAGES and RECORDS would be excluded.
If the same parameters are used in both the EXTRACT and PROCESS statements, the values are combined for EXSOURCE, EXLOAD, and DOMAIN. For options with a single value, the EXTRACT statement value, if any, will override the PROCESS statement.
,DICTIONARY=source-dictionary-name or Source-catalog-name
Is an optional parameter that allows you to access a dictionary other than the dictionary specified in the PROCESS statement or the central version's default dictionary.
For SQL entities, this parameter allows you to access a catalog other than the default system catalog.
Identifying an alternate source dictionary in the EXTRACT statement is useful when more than one dictionary resides in the central version in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing.
Default: The dictionary as specified in the PROCESS statement. If no source dictionary is specified in the PROCESS statement, the default is the central version's default dictionary. For SQL entities, the default is the system catalog.
,NODE=node-name
Is an optional parameter that identifies a node as the communication link between central versions and CPUs. By identifying the node you can access a central version that exists in a CPU or region other than the one in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing.
Default: You access the dictionaries that exist in the central version in which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is processing.
,IDSOURCE=(user-ID[[,password ,[RESP-OVERRIDE]])]
Is an optional parameter that provides standard sign-on security to control access to the source dictionary.
,IDSOURCE=
indicates that valid user identification follows.
user-id
Indicates the standard identification of the user.
password
Indicates a valid password that identifies the user of the source dictionary.
Default: There is no default value. If the dictionary sign-on is required, you must enter a valid ID and authorized password with this parameter.
RESP-OVERRIDE
Releases dictionary security by generating a REGISTRATION OVERRIDE in the IDD SET OPTIONS statement. This option requires a user-ID that has full authorization.
LEVEL is an optional parameter that allows you to specify the path that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator follows to extract an entity from the source dictionary.
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can extract an entity by using one of three methods. First, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can locate the programs or dialogs that use the entity specified in the EXTRACT statement and extract all existing relationships. Second, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator can bypass program or dialog relationships for a specific entity so that only the entity specified in the EXTRACT statement and its lower-level entities will be extracted. Finally, only the entity in the Extract statement will be extracted.
You can direct CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator to bypass program or dialog relationships in EXTRACT statements that specify these entity types:
For example, if you specify a record in an EXTRACT statement and include LEVEL=ENTITY, CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator extracts only the specified record and the elements connected to the record.
/ DIALOG \ ,LEVEL = < PROGRAM > │ ENTITY │ \ ONLY / ,LEVEL=
indicates that a starting point option follows. The DIALOG and PROGRAM options indicate the same level.
DIALOG
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator traces an entity specified in the EXTRACT statement to its dialog level. All the dialogs, programs, and the components of the dialogs and programs in which the entity participates are then extracted.
PROGRAM
CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator traces an entity specified in the EXTRACT statement to its program level. All the programs and the components of the programs in which the entity participates are then extracted.
ENTITY
Indicates that an entity is to be extracted with its lower-level relationships only. This option applies to schemas, subschemas, records, elements, modules, maps, panels, tables, classes, and attributes.
ONLY
Indicates that the entity is to be extracted by itself.
Default: All entities except messages and tables are extracted with their dialog or program relationships. Messages and tables are extracted with any lower-level relationships.
/ / COMMENT \ \ │ │ DATABASE │ │ │ │ DEFINITION │ │ │ │ MESSAGE │ │ │ │ MAP │ │ ,EXSOURCE = < (< RECORD >...)> │ │ MODULE │ │ │ │ PROCESS │ │ │ │ TABLE │ │ │ \ SUBPROGRAM / │ \ ALL /
EXSOURCE (exclude source) is an optional parameter that prevents CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator from extracting specific source components. You can specify as many as nine component types to be bypassed in a single execution.
,EXSOURCE=
Indicates source component types follow.
COMMENT
Indicates that all comments associated with entities are not to be extracted.
DATABASE
Indicates that all schema-related entities that exist in the source dictionary are not to be extracted. These include all schemas, schema records and elements, subschemas, and subschema records and elements.
DEFINITION
Indicates that definitions associated with entities are not to be extracted.
MESSAGE
Indicates messages that have codes embedded in maps and dialog module source are not to be extracted.
MAP
Indicates that all map-related entities are not to be extracted. These include maps and panels, tables and messages used by the map, and records and elements owned by the map.
RECORD
Indicates that all records and elements are not to be extracted.
MODULE
Indicates that the modules (other than process code) are not to be extracted.
PROCESS
Indicates that a process code is not to be extracted.
TABLE
Indicates that table source code is not to be extracted from the source dictionary.
SUBPROGRAM
Indicates that programs or dialogs referenced by dialogs found from the EXTRACT statement are not to be extracted.
ALL
Indicates that none of the source component types are to be extracted.
Default: All source component types are extracted.
EXLOADS (exclude loads) is an optional parameter that limits the load modules that CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator extracts from the DDLDCLOD (load) area of the source dictionary. You can enter up to four load module types in the same run.
/ / APPLICATION \ \ │ │ DIALOG │ │ │ │ MAP │ │ ,EXLOADS = < (< MODULE >...)> │ │ SUBSCHEMA │ │ │ \ TABLE / │ \ ALL / ,EXLOADS=
Indicates that a load module type follows.
APPLICATION
Indicates that load application modules are not extracted from source dictionary. The ADSA application cannot be updated unless the load module is migrated.
DIALOG
Indicates that dialog load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Consequently, you cannot regenerate the dialog if it does not already exist in the object dictionary.
MAP
Indicates that map load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Map load modules should not be extracted if map source is being extracted and the map will be regenerated.
MODULE
Indicates that the modules (other than process code) are not to be extracted.
SUBSCHEMA
Indicates that subschema load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Subschema load modules should not be extracted if subschema source is being extracted and the subschema will be regenerated on it if no database components are to be migrated
TABLE
Indicates that table load modules are not to be extracted from the source dictionary. Table load modules should not be extracted if table source is being extracted and the table will be regenerated.
ALL
Indicates that no load module types are to be extracted.
Default: All load modules are extracted.
,DATE=start-date
/ start-date \
,DATE = < (start-date,end date) >
Is an optional parameter that allows you to specify a time period in which an entity was updated. The DOMAIN parameter determines which entity occurrences will be tested.
,DATE=
Indicates that a date or date range follows.
start-date
Indicates the date, specified as mmddyy, which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to search for in the dictionary. Once the entity with the indicated date or a more recent date is located, the entities which will be extracted are determined by the domain parameter.
start-date,end-date
Indicates a date range with a starting date and ending date, specified as (mmddyy,mmddyy), which CA IDMS Dictionary Migrator is to search for in the source dictionary.
Default: All entities are extracted without regard to a date updated.
DOMAIN specifies where the date selection criteria will be applied.
EXTRACT
Indicates that the date range in the date parameter is tested on each entity name in an Extract Statement. If a test fails, the entity is not used as the starting point for extraction.
LEVEL
Indicates that the date range in the date parameter is tested on each entity serving as the top level of an extract path. This is dependent on the Level parameter. If the test fails neither the entity or any of its components will be migrated.
COMPONENT
Indicates that the date range in the date parameter is tested on each entity occurrence found in the extract path. If the test fails the entity is not extracted.
Default: Date range is tested on each entity named in an EXTRACT statement.
,VERSION=version-number
Is an optional parameter that allows you to locate an entity occurrence based on a specific version number. This parameter is used when an entity has multiple versions in the source dictionary. Entities often have more than one version when they are being used for application development.
The specified version number applies only to the entry point. You can specify values 0-9999.
Default: The default version number is 1.
CHANGE=(a,b)
The CHANGE statement is an optional statement which allows you to change the contents of the upload syntax files. Up to 50 change statements may be used. Each change is applied against every record in each of the upload syntax files. The changes are processed in the order in which they are entered.
a
Indicates the value which is to be changed and can have up to forty characters.
b
Indicates the value which is to replace value a and can be any string up to forty characters.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|