

Access Data in Two Directions
In a bidirectional virtual relationship, access can go in both directions: from a logical child segment to its logical parent segment, and from the logical parent segment to its logical child segment.
A bidirectional virtual relationship requires that you define a virtual logical child segment, as well as a real logical child segment. The virtual logical child is a pointer to the real logical child. (Compare to the bidirectional physical relationship, described below, in which the virtual logical child is a physical duplicate of the real logical child.)
Unidirectional relationships involve three segments; bidirectional relationships always involve four segments.
Bidirectional Virtual Structure
The example below shows the bidirectional virtual relationship defined by the DBD source statements shown in Figure 9 earlier in this section. In this relationship, SEG6 is the real logical child, SEG5 is the physical parent, SEG1 is the logical parent, and SEG2 is the virtual logical child. Note that SEG5 and SEG6 are in DBD PHYSDB2, and SEG1 and SEG2 are in DBD PHYSDB1.
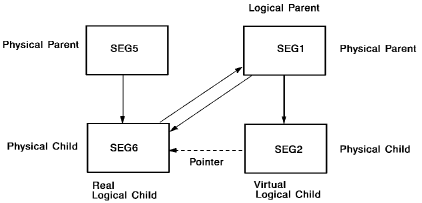
Figure 12. Bidirectional virtual structure
Defining the Virtual Logical Child
The physical parent, the physical child, the logical parent, and the real logical child are defined the same as for a unidirectional relationship (see Unidirectional Relationship). You define the virtual logical child in two places:
SEGM Statement for the Virtual Logical Child
The virtual logical child's SEGM statement must include the SOURCE parameter, which sets up a pointer to the real logical child and takes the following form:
Syntax
SOURCE=((segname,DATA,dbname))
Parameters
Identifies the name of the real logical child segment, as specified for the NAME parameter in the real logical child's SEGM statement.
Dbname is the name of the DBD that contains the real logical child's SEGM statement.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|