

CA IDMS/DB Audit can detect, but not fix, seven other types of integrity errors in an integrated index.
1. Index entry db-key errors detected in integrated index records
When checking the db-keys of records in an integrated index set, CA IDMS/DB Audit either could not find the record pointed to by the db-key, or found errors within the record.
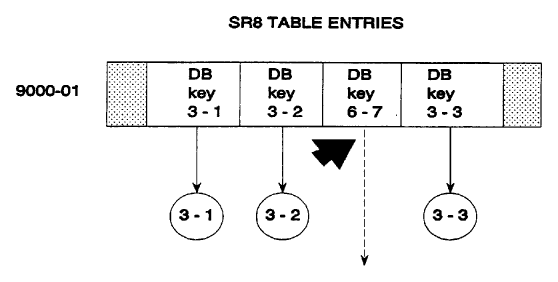
Figure 2.20: Integrated Index Entry Not Found
2. SR8 upper level pointer is not high values
In a top level SR8 record, the upper level pointer should be null (equal to HIGH-VALUES). If the upper level pointer in a top level SR8 is not null, CA IDMS/DB Audit lists the error under db-key errors and indicates that the upper level pointer is not HIGH-VALUES.
In the example in Figure 2.21 the upper level pointer in record 9000-07 points to a record in another set.
Figure 2.21: Integrated Index Invalid Upper Level Pointer
3. Level sequence errors detected in integrated indexes
The level number of an SR8 record in an integrated index set is in error. For example, in Figure 2.22 the level number in Level 1 should be 1, but the records contain Level 0 and 3.
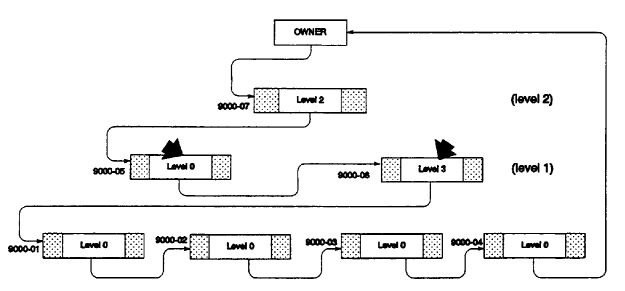
Figure 2.22: IIX Entry with Incorrect Level Numbers
4. Symbolic key errors detected in integrated index records in set
In a set sorted by symbolic key, an SR8 record points to a member record, but the symbolic key contained in the SR8 record does not match the symbolic key in the member record. In Figure 2.23 the db-key in the SR8 record points to the JONES member record, but the symbolic key in the SR8 record is WHITE.
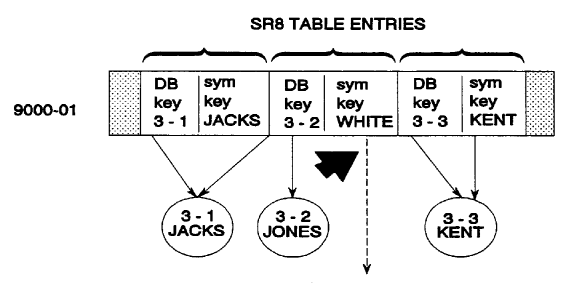
Figure 2.23: Incorrect Bottom Level Symbolic Key
5. Sort key sequence errors detected in integrated index records contained in set
Integrated index sets can be sorted either by db-key or by symbolic key, in ascending or descending order.
In a set sorted by db-key, the last db-key in an SR8 record should match the sort key in the upper level SR8 record just above. For example, in Figure 2.24, in the SR8 record on the right in the bottom level, the last db-key 3-6 does not match the sort key 4-8 in the SR8 record above it.
In a set sorted by symbolic key, the last symbolic key in an SR8 record should match the upper level symbolic key associated with the db-key. For example, in Figure 2.25, the symbolic key CLIFF does not match the symbolic key JONES in the top level SR8 record above.
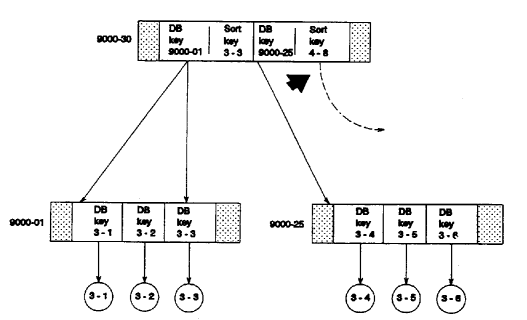
Figure 2.24: Incorrect Upper Level Db-key
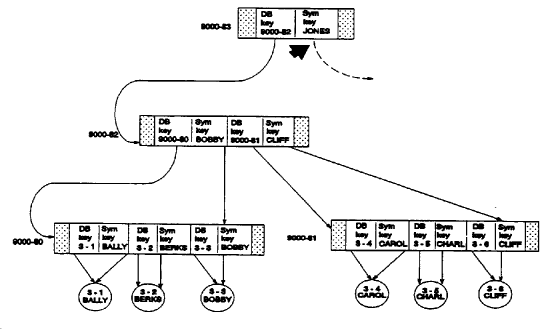
Figure 2.25: Incorrect Upper Level Symbolic Key
6. Sort flag inconsistent with symbolic sort flag in integrated index record
An SR8 record has flags that indicate whether the set is sorted and whether it is sorted by symbolic key. The sorted set flag ON and the symbolic key flag OFF indicates a set sorted by db-key. The sorted set flag ON and the symbolic key flag also ON indicates a set sorted by symbolic key. If the sorted set flag is OFF, the symbolic sort key flag should be OFF. Figure 2.26 shows the combinations of flag settings with their meanings.
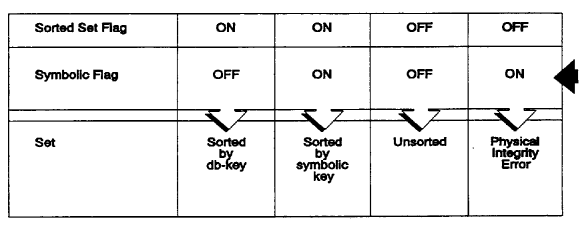
Figure 2.26: Integrated Index Sorted Flag Settings
7. Integrated index records disconnected from set
A member record is disconnected from an integrated index set. If INDEX is specified in the AUDIT statement, CA IDMS/DB Audit sweeps the area and creates a table of the db-keys of set member records. During index auditing, CA IDMS/DB Audit lists all the db-keys of member records of each mandatory-automatic integrated index set. Each member record should have a pair of entries--one obtained during sweep processing, and one obtained during the index auditing. If there is no pair, CA IDMS/DB Audit reports the member as disconnected.
In Figure 2.27, for example, three of the records in the SWEEP portion of the table are not paired with INDEX records, and two of the records in the INDEX portion of the table are not paired with SWEEP records. The five records are reported as disconnected.
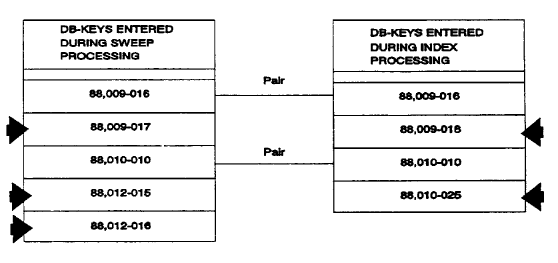
Figure 2.27: Integrated Index Disconnected Records
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|