

Consider the elementary process Add New Customer, which has been used in the examples in this guide. Rather than combining Add New Customer and Delete Customer into a single Maintain Customer procedure, suppose that the designer opts to define Add New Customer in its own procedure.
Assume that the designer divides Add New Customer into two procedure steps as shown next:
Name
Street Address
City
State
Phone Number
Credit Limit
The elementary process Add New Customer should be implemented in two procedure steps. You should implement all update type entity actions, such as CREATE, UPDATE, and DELETE, in the final procedure step. This will avoid violating the integrity of the data base. By observing this guideline, the designer guarantees that the view of the business represented on the data base remains in a consistent state if the system fails between procedure steps.
Given this constraint, the sample Add Customer procedure can be implemented as shown in the following illustration, Dialog Flow Diagram With Two Procedure Steps.
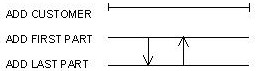
Assume the following details of the dialog flows shown in the illustration:
This division of procedures into steps requires no change to the views in the original Add Customer Process Action Diagram as shown in the following sample code.
Data Views for Add First Part
Procedure Step Definition Procedure Step ADD_FIRST_PART
Import Views
ViewIMPORT of entity CUSTOMER
Attributes:
NAME
STREET_ADDRESS
CITY
STATE
Export Views
ViewEXPORT of entity CUSTOMER
Attributes:
NAME
STREET_ADDRESS
CITY
STATE
End Of Report
The following notes will help clarify the example:
ADD_FIRST_PART
IMPORTS: Entity View import customer EXPORTS: Entity View export customer ENTITY ACTIONS: Entity View requested customer
EXIT STATE IS requested_operation_complete
READ requested customer WHERE DESIRED customer name IS EQUAL TO import customer name WHEN successful EXIT STATE IS customer_already_exists WHEN not found MOVE import customer TO export customer
Procedure Step ADD_LAST_PART Import Views
ViewIMPORT of entity CUSTOMER
Attributes:
NAME
STREET_ADDRESS
CITY
STATE
PHONE_NUMBER
CREDIT_LIMIT
DATE_ADDED
Export Views
ViewEXPORT of entity CUSTOMER
Attributes:
NAME
STREET_ADDRESS
CITY
STATE
PHONE_NUMBER
CREDIT_LIMIT
DATE_ADDED
ADD_LAST_PART
IMPORTS: Entity View import customer EXPORTS: Entity View export customer
EXIT STATE IS requested_operation_complete MOVE import customer TO export customer
USE add_new_customer
WHICH IMPORTS: Entity View import customer WHICH EXPORTS: Entity View export customer
This example satisfies the guidelines mentioned previously. The update takes place in Add Last Part using an unmodified Process Action Diagram, Add New Customer as shown in the following sample code.
Action Diagram for Add New Customer
ADD_NEW_CUSTOMER
IMPORTS: Entity View candidate_customer
EXPORTS: Entity View newly_created_customer
ENTITY ACTION: Entity View brand_new_customer
READ brand_new_customer
WHERE DESIRED customer name IS EQUAL TO candidate customer name
WHEN successful
EXIT STATE IS customer_already_exists
WHEN not found
CREATE brand_new_customer
SET name TO candidate_customer_name
SET number USING calculate_customer_number
WHICH IMPORTS: Entity View candidate customer
SET street address TO candidate customer street_address
SET city TO candidate customer city
SET state TO candidate customer state
SET zip TO candidate zip
SET phone_number TO candidate customer phone_number
SET credit_limit TO 0
SET date_added TO CURRENT DATE
MOVE brand_new_customer TO newly created customer
EXIT STATE IS requested_operation_complete
If, for any reason, you do not follow the guidelines, you should ensure that the business requirement is satisfied and that the integrity of the data is not compromised.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|