

How to Enable Web Services › How to Enable Web Services › Review Prerequisite Information › How Client Programs Access the API
How Client Programs Access the API
Web Services is a multithreaded application built with Java2 (the Apache Axis2/Java web services/SOAP/WSDL engine) and the Jersey framework (which serves as a JAX-RS reference implementation for RESTful web services). Web Services and client applications communicate using the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) or the direct RESTful approach. The client and Web Services communicate in a request-response fashion using the HTTP protocol.
The following graphic shows the flow of information between the client, Web Services, and the CA Endevor SCM API.
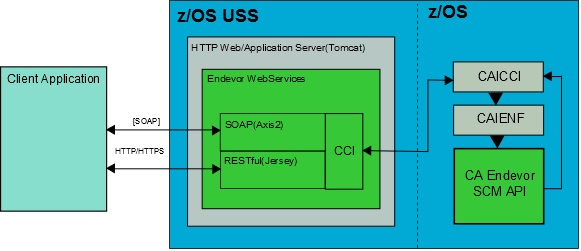
As shown in the graphic, client applications access the CA Endevor SCM API through Web Services. Details of this process follow:
- If the SOAP web service client model is used, then the client application formats and sends a SOAP message to the HTTP/Application server based on the definitions in the Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file. The request includes the name of the CA Endevor SCM data source that the client wants to access.
- With the RESTful model, the client creates an HTTP request that includes a specific URL and parameters. The request corresponds to a specific Endevor action and sets the appropriate HTTP method associated with the action.
- Web Services matches the name of the data source requested by the client call to a configuration file. One or more configuration files are stored on the HTTP web server and enable access to the CA Endevor SCM API. A configuration file identifies the name and number of API STCs (the STC pool) available to pass requests to CA Endevor SCM. The CA Common Services CAICCI Spawn facility spawns the specified number of API STCs.
- CA Endevor SCM processes the request and then the results are returned by CAICCI to Web Services where the data are processed and transformed into the appropriate response structure and then returned to the client.
To enable Web Services to process requests and communicate with the API, the z/OS environment where CA Endevor SCM is installed requires certain CA Common Services components, including the following:
- CAICCI provides a common communications software layer that enables communication between Web Services and the API.
- CAIENF must be configured to enable the CAICCI Spawn facility that lets CA Endevor SCM schedule, execute, and monitor a pool of STCs for Web Services requests.
This process uses the following standard technologies:
- XML language – The data format used by web service components. Communications between web service applications are written in XML format.
- Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) – An XML-based messaging protocol and encoding format for inter-application communication. SOAP messages are XML messages sent between applications. A SOAP message is a text file written in standard XML format that is enclosed in a SOAP structure. SOAP enables applications to know how to send and interpret the XML data.
- Web Services Description Language (WSDL) – A service description protocol. A web service's WSDL file is a dynamic XML file that serves as the interface between a SOAP-based client program and the web service. The Web Service WSDL file describes what CA Endevor SCM operations are available to the client program and the SOAP protocol bindings and message formats required to enable the client to interact with the web service.
If you are using Web Services for a user-written client application, your web developer must create a client stub from the WSDL file. The client stub is responsible for conversion of parameters used in a function call and deconversion of results passed from the server after execution of the function. The client stub interacts with the web service stub. For more information see, CA Endevor SCM SOAP Web Services.
- Web Application Description Language (WADL)— Jersey supports WADL. WADL is an XML description of the deployed RESTful web application. It contains the model of the resources, structure, supported media types, HTTP methods, and so on. It is similar to the WSDL, which is used for the SOAP-based Web Services model. WADL can be used for generating a client-side stub, however this feature is not as sophisticated as the stubs generated using the WSDL.
- HTTP Protocol— The Hyper Text Transfer protocol (HTTP) is an application protocol for distributed, collaborative information systems, and is the foundation for data communication on the World Wide Web.
- JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)— JSON is an open standard, language independent, data format used to transmit data objects as structured attribute-value pairs in human-readable text. It is considered an alternative to XML.
- JAX-RS— Java API for RESTful Services (JAX-RS) is a Java programing language API that provides support for the Representational State Transfer (REST) type of web services.
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


