

The SQL Database Execution step lets you connect to a database using JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) and make SQL queries on the database. Use this step when you have a JDBC connection asset defined.
Note: If you have a legacy SQL Database Execution (JDBC) step, you can export the connection information from the existing step instead of creating it manually. For more information see Create Assets from Test Steps.
Full SQL syntax is supported, but your SQL is not validated. The SQL is passed through to the database where it is validated. If you get an SQL error, it is captured in the response. You can assert on the error. Verify that the SQL is valid for the database manager you are using.
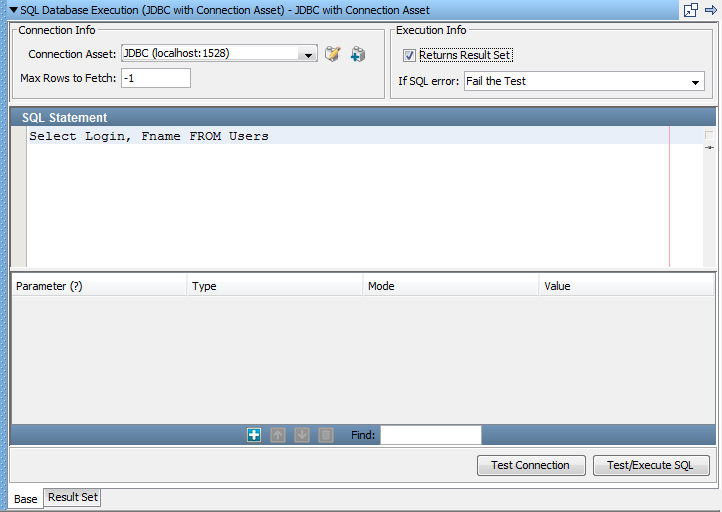
Select a connection asset that contains the connection parameters for the JDBC connection.
Enter the maximum number of rows you want returned in the result set. This field is required. Enter -1 for unlimited rows.
Select this check box if your query results in a Result Set being returned; that is, a SELECT type query. Leave cleared for an UPDATE, INSERT, or DELETE. If this check box is set incorrectly, your query causes an error.
Select the step to redirect to if an error occurs.
If the information is correct, a success message in a window appears. Otherwise an error message appears.
Properties can be used in your SQL. DevTest substitutes the parameter before passing the SQL string to the database.
The JDBC step supports stored procedure calls. Basic data types (strings, numbers, dates, Boolean) are supported as arguments that a stored procedure uses as input and returns. Click Add ![]() to add a parameter. You cannot edit the numbers in the Parameter column. As you add, delete, and move rows, the numbers in the Parameter column are automatically renumbered.
to add a parameter. You cannot edit the numbers in the Parameter column. As you add, delete, and move rows, the numbers in the Parameter column are automatically renumbered.
The JDBC step can also use JDBC prepared statements. You can use question marks in a SQL statement and can add named {{properties}}. This ability allows you to avoid being concerned about the type of the argument or escaping single quotation marks in parameter values. A statement "insert into MYTABLE(COL1,COL2) values (?, ?)" with a reference to {{col1}} and {{col2}} is easier to understand. The type and escape characters are automatically converted.
To include a null in your statement, use this syntax: {{<<NULL>>}}.
A message indicates the result status.
Your results display in the Result Set tab.
The three icons on the bottom of the Result Set tab provide easy access to the following filters and assertions:
You select a search field cell, a value field filter, and enter a property name. If the cell value in the search field is found, the value in the Value field in that row is set as the value of the property that is entered.
The value in the selected cell is set as the value of the property that is entered.
The value in the selected field (column) is compared to the regular expression that is entered.
For more information about these and other filters and assertions appropriate for result sets, see Filter Descriptions and Assertion Descriptions.
The SQL Database Execution step has a default name using this convention: JDBC with Connection Asset SQLfunction tablename. The supported functions in step name defaults are select, insert, delete, update, and perform. You can change step names at any time.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|