

This scenario explains how and why a database administrator creates a batch reporting job.
As a DBA, you are involved in capacity planning. You are responsible for monitoring table spaces so that you know when more DASD is needed. The CA Chorus Investigator lets you easily search for all table spaces in a database and save the search query to a JCL batch job. This batch job, when executed, generates a report. After you create the JCL, you can run the report every week. You can also add the batch job to a job scheduler so that it executes at predetermined intervals, providing updated reports on the table space sizes.
The following illustration shows how a DBA creates and runs a job to monitor table space sizes:
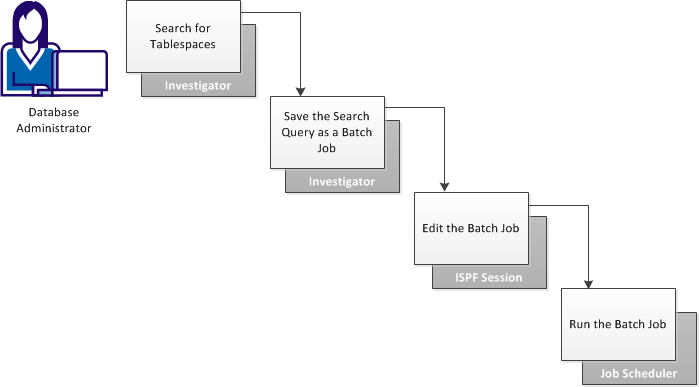
The DBA performs the following steps:
The Investigator displays all table spaces in the PAYROLL database.
In this scenario, the DBA removes all columns except DBNAME, NAME, PARTITIONS, NACTIVE, and SPACEF.
Click Save.
The column settings are saved for this view.
The column sorts in descending order, showing the largest table space at the top.
Click Save.
Note: You can also save the search query as an Investigator query by clicking the Save search queries icon and selecting Save Query. This feature saves you from creating the query each time you want to view the information in the Investigator. Also, you can export the list of table spaces that currently appear in Investigator by clicking the Export icon.
By using the Investigator to create batch jobs that can be run on a schedule, you can monitor table space sizes.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|