

The data flow within the system is in the form of Events. Where an Event is, an information message created by the Adapter based on source data and is in a format that can be used by CA Business Service Insight for its service level calculations. Raw data always consists of Events.
The focus of the design must therefore be on this Event flow within the system.
Before modeling the data requirements, both the Business Logic Expert and the Data Source Expert need to have a solid understanding of Events and their flow within the CA Business Service Insight system. The following diagram illustrates in high level this basic Event flow.
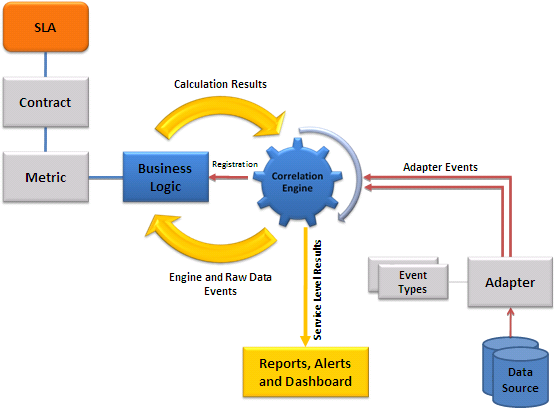
The previous diagram depicts how Events are retrieved from the data source by the Adapters and normalized into a standard Event structure defined as the Event Type. These Events are sent by the Adapters to CA Business Service Insight. These Events are referred as Raw Data Events.
The Business Logic calculations in each Metric are based on a subset of the Raw Data Events. The Business Logic therefore requests this subset by performing registration.
Based on the registration statement, the Correlation Engine sends only the Raw Data Events relevant for business logic calculations.
Additional types of Events sent to the business logic are the Engine Events. All concepts involved in this process are discussed in detail in this chapter.
This section focuses on the following parts of the diagram:
The CA Business Service Insight Data Model has been designed to maximize the efficiency of this stream of data within the system.
In general, CA Business Service Insight functions on two layers: The Infrastructure layer and the Business Model layer. As a simplistic breakdown, the infrastructure layer includes Adapters, Resources, and Event type objects, while the business layer includes Contracts, Metrics, and Services objects. Between the two layers there is a virtual shim layer, called the Correlation layer.
One Event identifier is the Event Type object. The Event type determines how Events are defined and how they are reported to CA Business Service Insight. It also defines the structure of the Event data field so that it can be interpreted by the Business Logic during processing.
Another Event identifier is the Resource which is the smallest entity used in calculations. For example, when calculating server availability, the logical definition of the smallest entity on which reporting is required might be a specific server, or it might be a customer when reporting on that customer's ticket handling. The Resource is a definition of an CA Business Service Insight entity that is derived from both the data source and the calculation requirement. Each Resource is given a Resource Type which is Resource identifier that determines exactly what 'type' of resource is defined. Each Resource must have a Resource Type associated, which also allows the addition of custom attributes to be associated with each resource. For more information about these attributes, see Resources and their Management.
The correlation occurs between incoming Adapter Events and Contract Metrics. The heart of this correlation process is the Resource allocation and Metrics registration.
Resource allocation and Metrics registration specify which resource event streams are measured and by which Metric.
Note here that with Metric registration, there may be a degree of re-use and co-dependency with other Metrics since it is possible to use the output of one Metric as the input to another one. Similarly, there are Interim events which are not used as the output of a Metric for service level measurement, but more as an intermediate calculation step which can then be used by other Metrics.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|