

ACLs are applied to VLANs using an access map. An access map can contain multiple ACLs, each with an assigned priority number to specify the order in which it is processed. Each ACL is also assigned an action to take when the ACL is matched.
When a packet matches a permit ACL entry, it is forwarded along its intended path. The packet is not inspected against ACL lines or ACL maps. When a packet matches a deny ACL entry, it is verified against the next entries. If a permit exists for the next entries, the packet is forwarded into the network. A packet is dropped only when it does not match a permit ACL entry.
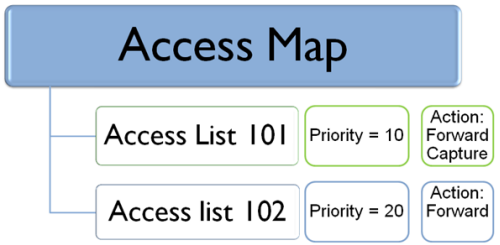
The preceding illustration depicts an access map that contains two ACLs. Each ACL is associated with a separate set of actions. The priority number determines which ACL is processed first (the lowest).
We recommend that you name ACLs numerically and that you name access maps in plain text. This strategy helps to prevent confusing the two. Add a description to each ACL to denote its purpose.
|
Copyright © 2015 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|