

As a Backbone Administrator, you want to configure networks with the BFC API. For example, you prefer using the API with a command line, or you prefer executing scripts for command sequences. Once you configure the networks, you can view and manipulate the networks through the BFC UI and other BFC API methods. You set up and configure networks configuration before you can create CA AppLogic grids, and you require a backbone and external network.
The following diagram shows how you can configure networks with the BFC API:
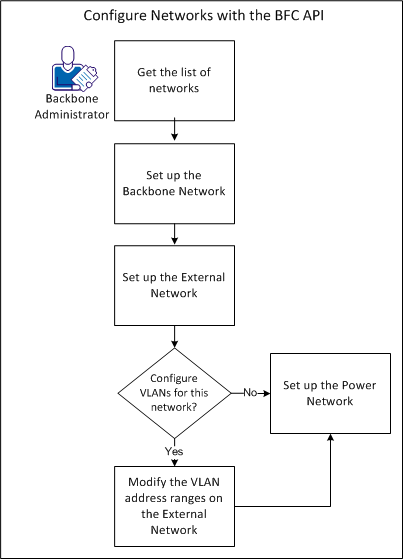
Your network configuration can have the following setup:
For example, you can configure the external network after you set up the backbone network.
You can then use the VLAN spaces as application IP capacity for a grid. For example, you want to add VLAN spaces to accommodate more applications on the grid.
Version 1.1 of the BFC API lets you view information about the networks in the BFC. In this example, your system does not contain any networks, but you want to confirm this information with the BFC API.
Follow these steps:
export BFC_Host=<IP Address of BFC Control Node>
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/1.1/login -X POST -d "{\"username\":\"core/admin\",\"password\":\"changeme\"}" -H "Content-Type:application/json"
export Session="Session_ID_Returned_from_Login"
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}"
The API displays the HTML return code 200 and indicates that your BFC does not contain any networks.
The backbone network hosts all traffic for BFC operations. CA AppLogic uses this internal network only for communications between servers on the grid.
Follow these steps:
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session" -d "{\"network\":{\"base_address\":\"127.0.x.x\",\"cidr\":\"24\",\"usages\":[\"bbc/applogic_backbone_network\"],\"gateway_addresses\":[\"127.0.x.x\"],\"address_space\":{\"ip_space\":{\"address_pools\":[{\"ip_pool\":{\"type\":\"hardware\",\"ranges\":[{\"ip_range\":{\"start_address\":\"127.0.x.x\",\"end_address\":\"127.0.x.x\"}}]}}]}}}}"
curl -k https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.0.x.x -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}" | python -mjson.tool
The following output appears:
{"network": {
"address_space": {
"ip_space": {
"address_pools": [
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 10,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}],
"num_addresses": 11,
"num_available": 10,
"num_used": 1,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 11,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}],
"type": "hardware",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 1,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}]}},
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [],
"num_addresses": 4,
"num_available": 0,
"num_used": 4,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}],
"type": "application",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}]}}],
"available_ranges": [[
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 137,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}},
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.0.x.x",
"size": 101,
"start_address": "127.0.x.x"}}],238]}},
"base_address": "127.0.x.x",
"cidr": 24,
"comp_id": 1450,
"gateway_addresses": [
"127.0.x.x"],
"ip_version": "ipv4",
"usages": [
"bbc/applogic_backbone_network"],
"vlan_address_spaces": []}}
The external network provides the available addresses for grids when you create virtual machines. This network lets servers communicate with other hosts outside the CA AppLogic grid.
Follow these steps:
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session" -d "{\"network\":{\"base_address\":\"127.50.x.x\",\"cidr\":\"24\",\"usages\":[\"bbc/applogic_external_network\"],\"gateway_addresses\":[\"127.50.x.x\"],\"address_space\":{\"ip_space\":{\"address_pools\":[{\"ip_pool\":{\"type\":\"hardware\",\"ranges\":[{\"ip_range\":{\"start_address\":\"127.50.x.x\",\"end_address\":\"127.50.x.x\"}}]}}]}},\"vlan_address_spaces\":[{\"vlan_ip_space\":{\"vlan\":\"150\"}}]}}"
curl -k https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.50.x.x -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}" | python -mjson.tool
In this example, you created the VLAN address space without associating any pools, ranges, or IP addresses.
The following output appears:
{"network": {
"address_space": {
"ip_space": {
"address_pools": [
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 10,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"num_addresses": 11,
"num_available": 10,
"num_used": 1,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 11,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"type": "hardware",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 1,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}]}},
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [],
"num_addresses": 4,
"num_available": 0,
"num_used": 4,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"type": "application",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}]}}],
"available_ranges": [[
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 137,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}},
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 101,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],238]}},
"base_address": "127.50.x.x",
"cidr": 24,
"comp_id": 1450,
"gateway_addresses": [
"127.50.x.x"],
"ip_version": "ipv4",
"usages": [
"bbc/applogic_external_network"],
"vlan_address_spaces": []}}
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.50.x.x/vlan_address_spaces/150/address_pools -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session" -d "{\"ip_pool\":{\"type\":\"application\",\"ranges\":[{\"ip_range\":{\"start_address\":\"127.50.x.x\",\"end_address\":\"127.50.x.x\"}}]}}"
curl -k https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.50.x.x -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}" | python -mjson.tool
The power network settings let the BFC intelligently controls the power management operations on grid nodes. These operations include power cycle and power off.
Note: If you enabled IPMI on your nodes, specify the Power IPs of those nodes in the power network.
Follow these steps:
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session" -d "{\"network\":{\"base_address\":\"127.50.x.x\",\"cidr\":\"24\",\"usages\":[\"core/power_network\"],\"gateway_addresses\":[\"127.50.x.x\"],\"address_space\":{\"ip_space\":{\"address_pools\":[{\"ip_pool\":{\"type\":\"power\",\"ranges\":[{\"ip_range\":{\"start_address\":\"127.50.x.x\",\"end_address\":\"127.50.x.x\"}}]}}]}}}}"
curl -k https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.50.x.x -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}" | python -mjson.tool
The following output appears:
{"network": {
"address_space": {
"ip_space": {
"address_pools": [
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 10,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"num_addresses": 11,
"num_available": 10,
"num_used": 1,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 11,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"type": "hardware",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 1,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}]}},
{"ip_pool": {
"available_ranges": [],
"num_addresses": 4,
"num_available": 0,
"num_used": 4,
"ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],
"type": "application",
"used_ranges": [
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 4,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}]}}],
"available_ranges": [[
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 137,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}},
{"ip_range": {
"end_address": "127.50.x.x",
"size": 101,
"start_address": "127.50.x.x"}}],238]}},
"base_address": "127.50.x.x",
"cidr": 24,
"comp_id": 1450,
"gateway_addresses": [
"127.50.x.x"],
"ip_version": "ipv4",
"usages": [
"bbc/applogic_power_network"],
"vlan_address_spaces": []}}
Modify the VLAN address range on the external network that is based on the needs of your BFC environment. For example, you can decrease the VLAN address space if you do not require your current amount. If you require more address space to run more applications on the grid, you can increase the address space on the external network.
Note: If you do not configure VLANs after creating the network, you can manage the VLANs through a POST or DELETE to the VLAN address space.
Follow these steps:
For example, you plan to use more applications in your grid. These added applications require an increased range.
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.x.x.0/vlan_address_spaces/150/address_pools/application/ranges -X POST -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session" -d "{\"ip_range\":{\"start_address\":\"127.x.x.51\",\"end_address\":\"127.x.x.150\"}}"
curl -k -v https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.x.x.0/vlan_address_spaces/150/address_pools/application/ranges/127.x.x.40-127.x.x.49 -X DELETE -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:$Session"
curl -k https://${BFC_Host}:8443/BFC/networks/127.x.x.1 -H "Content-Type:application/json" -H "Authorization:${Session}" | python -mjson.tool
The API displays HTML return code 200 and shows the ranges that you specified in Step 2.
You have successfully configured networks with the BFC API and can create and work with grids.
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|