

Review the Hardware Requirements on the CA 3Tera AppLogic bookshelf to verify that you servers meet the minimum requirements and that you understand the required network topology. In addition, it is beneficial to read the BFC Control Node Requirements.
On the server you will be installing the BFC onto, install a "standard" package configuration of CentOS 5.5 32bit.
SELINUX=disabled
[iso] name=iso baseurl=file:///mnt/CentOS/5.5
rpm -import /mnt/CentOS/5.5/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-5
yum list (should list a pile of yum packages)
Note: Before you install the BFC, make sure that SSH password authentication is diabled on the BFC control node. To restrict SSH to key-based logins, do the following:
Note: Do not copy the files to /opt/bfc as that is the default directory for the installation of the BFC and is removed and recreated during the installation process).
mkdir -p /mnt/cdrom mount -r -o loop /<path to bfcinstall.iso> /mnt/cdrom
(for example, mount -r -o loop /tmp/BFC/bfcinstall.iso /mnt/cdrom)
/mnt/cdrom/fcinstall.sh -x /<path to bfcext.iso>
(for example, /mnt/cdrom/fcinstall.sh -x /tmp/BFC/bfcext.iso)
To install the BFC in a non-default location, use the following command:
/mnt/cdrom/fcinstall.sh -x /<path to bfcext.iso> -t <non-default-location-path>
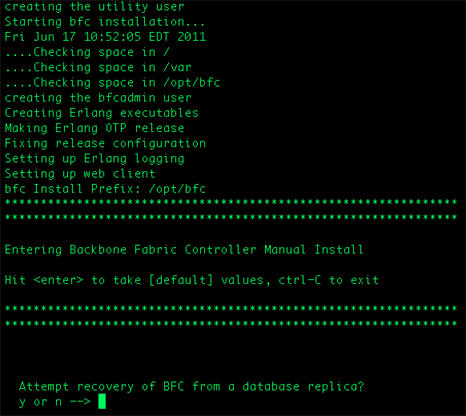
Database replication enables you to specify a location (preferably on a network storage device or on a network-mounted volume) where the BFC database will be replicated. If you need to restore a BFC (due to a hardware failure, disaster, or anything else), you simply run the installation program on the new BFC machine and specify the directory location of the replicated database. The new BFC will then be installed with the replicated database. Once the new BFC is installed, it will become aware of the existing grids and be able to control them as before.
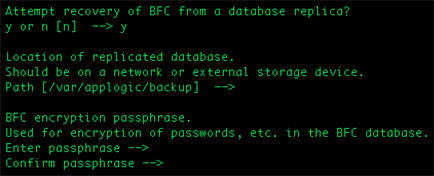
If you select Y, specify the values for the following parameters:
Location (preferably on a network storage device or on a network-mounted volume) where the BFC database will be replicated.
Note: The replica path should be writable by the bfcadmin account. You can run the chown or chmod commands to provide the required access to the replica path. For example:
chown bfcadmin <replica path> chmod 777 <replica path>
The passphrase to use for encryption of the replicated database.
You are prompted to enter a userid and password. When the credentials and License Agreement are accepted, you know the BFC component is working.
|
Copyright © 2011 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|