

Latest version: 2.0.2-1
|
At a Glance |
|
|
Catalog |
System |
|
Category |
Switches |
|
User volumes |
no |
|
Min. memory |
96M |
|
OS |
Linux |
|
Constraints |
no |
HALB is a switch for distributing workload to multiple Web servers of the same or different type. HALB is based on the HAProxy TCP/HTTP load balancing software package; which is designed to be extremely fast while consuming little resources.
HALB performs load-balancing functions using several algorithms. It performs simple round-robin balancing, equalizing the load for backend servers. It also supports persistent sessions, binding the client to a particular backend web server with session cookies or by using the request source IP address as a key. While using session cookies, any new sessions that do not have session cookies are distributed using the round-robin algorithm. HALB supports sessions with multiple cookies and modifies and/or tracks only the necessary ones, leaving others intact. Any particular session or client may be tied to particular backend web server or application using cookie association. Existing cookies may be transparently modified by HALB for clients that do not support requests with multiple cookies.
HALB constantly monitors the health state of all backend web servers. The health state checks conducted by HALB may include a simple TCP connect check or a more complex HTTP request (specified on HALB's boundary). In the case of a server failure detected by HALB using the parameterized health check method, HALB switches the traffic to an alternate server. If the failed server eventually recovers, HALB may switch the traffic back to the recovered server.
HALB exposes a web service interface on its ctl terminal. This interface allows a user to pragmatically enable/disable output terminals out1 - out8 and also to retrieve the state of all terminals. This is useful in cases when there is some kind of backend failure (that is, such as in a database or storage appliance) where the application itself can automatically disable traffic to a specific set of servers. In this case, HALB itself is unable to detect this type of failure; so it is up to the application to detect the failure and disable the corresponding set of backend servers.
HALB maintains detailed statistics including backend state, number of requests processed per server, number of errors occurred, and so on. The statistics are reported through the mon terminal and separate counters are also exposed through the ui terminal as a GUI accessible with a browser.
HALB is designed to be extremely fast using very few resources. Under regular conditions, HALB consumes about 25KB of memory for every session, or 1GB for 40000 simultaneous sessions, and processes up to 6000 requests per second.
Resources
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.1 |
16 |
0.4 |
|
Memory |
96 MB |
32 GB |
96 MB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
250 Mbps |
The amount of memory given to L3LB does not increase the throughput or response time. L3LB is a CPU/bandwidth bound appliance.
Terminals
|
name |
dir |
prot. |
description |
|
in |
in |
Any |
Common input. TCP requests sent to in are directed to one of the outputs, either using round-robin selection or source-based session information. |
|
ctl |
in |
HTTP |
Control terminal that is used for enabling/disabling the outputs and retrieving output terminal state |
|
out1-out8 |
out |
Any |
Balanced outputs. Any and all of these outputs can be left unconnected; traffic is distributed only to connected, enabled outputs. By default, all terminals are enabled. |
|
mon |
out |
CCE |
Used to send performance and resource usage statistics. |
Properties
General properties
|
name |
type |
description |
|
mode |
String |
Specifies the mode of operation and a way to use the named session cookie for session identification. Valid values are: |
|
cookie_name |
String |
The name of the cookie used to identify a session. For the passive modes ( passive and sync - see the mode property below), this is the name of the cookie used by the back-end servers connected to out1 - out8 to identify client sessions. For the insert mode, this is the name of the cookie that HALB should insert into HTTP responses in order to make each client 'stick' with a single server. If this property is set to the empty value, no session tracking is done and all requests are distributed in a simple round-robin fashion. Ignored for the source mode. |
|
cookie_check_length |
Int |
Defines how many bytes from the value of cookie are used as unique key in passive mode of operation to match session to backend web server. Default value of 10 is usually sufficient for all common PHP and java applications. This value must always be equal or less than the length of the cookie value. |
|
max_connections |
integer |
The maximum number of concurrently active connections that the load balancer handles. When this number is reached, new connections are still accepted, but their processing is delayed until another connection is closed. Upon start, HALB automatically determines the maximum number of connections based upon available memory, compares it to the value of this property and uses the lowest value. If this property equals 0 then the computed value is used. Note that neither the available memory nor an explicit setting of this property have a direct effect on the balancer's throughput or its maximum request rate - setting a low number (or having little memory) affects response only if the back-end servers are performing lengthy operations for each request (for example, database searches), causing many requests to remain open at the same time. |
|
backup_outputs |
String |
A space or comma delimited list of outputs ( out1 - out8 ) that are considered backups. Traffic is directed to the backup servers only if all backend servers are unavailable. The purpose of these backup servers is to notify clients that something is wrong or redirect them, instead of throwing errors from unavailable backend or timing out. |
Timeout properties
|
name |
type |
description |
|
timeout |
integer |
Timeout in seconds to expire inactive sessions. If set to zero, inactive sessions do not expire. If set to a non-zero value, inactive sessions resumed after timeout seconds are considered stale, and requests bearing the 'forgotten' cookie are treated as if they have no cookie at all and are directed to a random server, using the usual round-robin method. This property is only valid for passive mode and ignored for all other modes. |
|
client_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for waiting for a request from a client after establishing the connection. |
|
server_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for waiting for a reply from a backend web server after establishing the connection. |
|
conn_timeout |
Int |
Timeout in seconds for establishing any tcp connection. This includes the health checks. Extra attention must be paid to this setting, because if under high load the health checks time out because of insufficiently small value, HALB starts to disable outputs. It is not recommended to set it lower than 20 seconds. |
Health check properties
|
name |
type |
description |
|
healthcheck_url |
String |
The URL used to perform the health check of the backend web servers in http_get and http_head health check methods. May be specified as a complete URL (http://host.name/file/to/check/for.php) or as a relative path (/file/to/check/for.php). If specified as a URL, HALB uses the HTTP/1.1 protocol while performing the health checks using the hostname extracted from UR, in a Host: header. This allows usage of virtual hosts. If specified as a relative path, HALB uses the HTTP/1.0 protocol and checks for the document specified by this property. If this property is empty, HALB checks for the default root '/' using the HTTP/1.0 protocol. |
|
healthcheck_agent |
String |
The string used as an agent identifier for http_get and http_head health check methods. If empty, HALB-health-check is used. |
|
healthcheck_method |
String |
The method used for the health check of the backend web servers. |
|
healthcheck_regexp |
String |
A test string used with the http_get health check mode. Short or common values (eg. OK) will likely cause false positive matches. This string is a perl regular expression, more details about perl regular expressions are available here. |
|
healthcheck_interval |
Int |
Interval between health checks of the backend web servers (specified in seconds). |
UI/Web service interface properties
|
name |
type |
description |
|
username |
String |
Username for accessing the HALB GUI through the ui terminal. If empty, there is no authentication. |
|
password |
String |
Password for accessing the HALB GUI through the ui terminal. Password is ignored if username is empty. |
|
ctl_port |
Int |
Port that is used to access the web service control interface through the ctl terminal. |
|
ui_port |
Int |
Port that is used to access the HALB runtime statistics GUI through the ui terminal. |
Custom Counters
The HALB appliance reports the following custom counters through the mon terminal.
The following counters belong to the HALB counter group. X may have a value from 1 to 8.
|
Counter name |
Description |
|
outX_status |
State of output terminal outX: 0 - enabled and up, 1 - enabled and down, 100 - disconnected. |
|
outX_queue |
Number of queued requests for terminal outX. |
|
outX_queue_max |
Historical maximum of simultaneously queued requests for terminal outX. |
|
outX_sessions_active |
Number of active sessions for terminal outX. |
|
outX_sessions_max |
Maximal number of active simultaneous sessions for terminal outX. |
|
outX_sessions_total |
Number of completed sessions for terminal outX. |
|
outX_errors |
Number of failed health checks for terminal outX. |
|
queue |
Current queue length, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
|
queue_max |
Historical maximum of simultaneously queued requests, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
|
sessions_active |
Number of active sessions, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
|
sessions_max |
Historical maximal number of active sessions, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
|
sessions_total |
Number of completed sessions, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
|
errors |
Total number of health check failures, cumulative for out1 - out8. |
Performance
Request Rate
HALB routes no less than 6000 transactions (request/response pairs) per second, subject to document size and network bandwidth available.
Data Throughput
HALB routes no less than 15 MBytes/second
Concurrent Connections
HALB supports no less than 2000 concurrently pending requests. (A "pending request" being an open TCP connection from the client, on which there is one or more un-completed HTTP request in progress). Maximum amount of concurrent connections depends of available free memory and may be as high as 40000. HALB was tested to support more than 15000 of simultaneous active transfers.
Error Messages
In case of appliance startup failure, the following errors may be logged to the system log:
|
Error message |
Description |
|
Error: unable to determine appliance memory configuration, please contact CA Technologies support. |
HALB failed to detect amount of available memory, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: failed to create the HAProxy config file, please contact CA Technologies support. |
HALB failed to create the HAProxy config file, please contact CA support (possibly due to low diskspace). |
|
Error: failed to determine number of available CPUs, please contact CA Technologies support. |
HALB failed to detect amount of available CPUs, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: the healthcheck_url, when specified as an URL, must begin with http:// and contain a full path to the document ( ex: http://host.name.domain/file/to/check/for.html ). |
healthcheck_url property value is incorrect, it should begin with 'http://' and contain a full path, ex.: http://host.name.domain/file/to/check/for.html |
|
Error: unknown health check method healthcheck_method specified. |
healthcheck_method property value is incorrect, it should be one of tcp_connect, http_head or http_get |
|
Error: invalid operation mode specified |
Invalid mode specified, it should be one of passive, sync, insert or source |
|
Error: ui_port value must be between 1 and 65535. |
ui_port value must be more than 1 and less than 65535. |
|
Error: ctl_port value must be between 1 and 65535. |
ctl_port value must be more than 1 and less than 65535. |
|
Error: failed to start HALB, please see '/var/log/appliance/log' log file for details. |
A system error occurred while starting HALB, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: failed to initialize the control web service interface, please contact CA Technologies support. |
A system error occurred while initializing the control web service interface exposed on the ctl terminal, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: failed to initialize statistics reporting, please contact CA Technologies support. |
A system error occurred while initializing statistics reporting, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: failed to initialize the user interface terminal, please contact CA Technologies support. |
A system error occurred while initializing the graphical user interface exposed on the ui terminal, please contact CA support. |
|
Error: failed to initialize external health checker, please contact CA Technologies support. |
An error occurred while starting external health checker with support for regular expressions, please contact CA technical support. |
Overview
A control web service interface is exposed on the ctl terminal (on the configured port), allowing for the enabling and disabling of the output terminals (out1 - out8) and retrieving the current terminal state.
Protocol
The protocol only uses the GET HTTP method, as it only provides reading functionality. Thus, every supported type of protocol request can be defined by means of its URI and the output structure. Characters, that are considered special for the URI should be escaped via the standard %-encoding.
Below is a description of all supported URIs.
Control Calls
Disabling output terminals
There are two separate formats of the disable control call, based on how the output terminal is identified:
Request: /api/disable?channel=out3 (disables the output terminal out3)
Request: /api/disable?10.11.12.13 (disables the output terminal that is connected to the web server with the IP address of 10.11.12.13)
Response:
HALB returns the following structure with a status code and optional status message:
{
"status" :
{
"code": code_value,
"message": "status_message"
}
}
Possible status code values are listed below:
|
Code value |
Description |
|
0 |
Operation was successful, terminal was disabled. |
|
10 |
Operation was not successful, HALB configuration was not modified. The most probable causes are that the terminal is already disabled or the specified IP address is invalid. |
|
100 |
An error occurred while processing the request, more details are available in the status message. |
Enabling output terminals
There are two separate formats of the enable control call, based on how the output terminal is identified:
Request: /api/enable?channel=out3 (enables the output terminal out3)
Request: /api/enable?10.11.12.13 (enables the output terminal that is connected to the web server with IP address of 10.11.12.13)
Response:
HALB returns the following structure with a status code and optional status message:
{
"status" :
{
"code": code_value,
"message": "status_message"
}
}
Possible status code values are listed below:
|
Code value |
Description |
|
0 |
Operation was successful, terminal was enabled. |
|
10 |
Operation was not successful, HALB configuration was not modified. The most probable causes are that the terminal is already enabled or the specified IP address is invalid. |
|
100 |
An error occurred while processing the request, more details are available in the status message. |
Retrieving output terminal state
Request: /api/status (returns the state of all output terminals)
Response:
HALB returns the following structure with a status code and optional status message:
{
"status" :
{
"code": code_value,
"message": "status_message",
"terminal_id": "terminal_state",
"terminal_id": "terminal_state",
...
}
}
State is returned only for all connected terminals only, state for disabled and disconnected terminals is not reported.
Possible status code values are listed below:
|
Code value |
Description |
|
0 |
Operation was successful. |
|
100 |
An error occurred while processing the request, more details are available in the status message. |
Possible terminal values are out1 - out8.
Possible state values are:
|
State value |
Description |
|
up |
Terminal is connected and active. |
|
down |
Terminal is inactive. The web server that is connected to this terminal it is either down or failed the HALB health check. |
An example state output:
{
"status" :
{
"code": 0,
"message": "",
"out1": "up",
"out2": "up",
"out3": "down",
"out4": "up"
}
}
HALB exposes a statistics GUI through the ui terminal. Various runtime information is available through this GUI:
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
nbcproc |
Number of CPUs available for HALB. |
|
uptime |
HALB uptime. |
|
system limits |
Resource limits imposed on HALB by the operating system. |
|
memmax |
Maximum available memory for HALB. |
|
ulimit-n |
Maximum amount of simultaneously open files. Network sockets are considered files. |
|
maxsock |
Maximum amount of simultaneously open sockets. |
|
maxconn |
Maximum amount of simultaneous connections. Once reaching this number, all new connections are placed in wait queue. |
|
current conns |
Current number of active connections. |
|
Server Status |
State of a backend server. UP - server is functional, DOWN - server is not functional. |
|
Queue Curr. |
Current request queue length of the backend server. |
|
Queue Max. |
Maximum reached queue length of the backend server since HALB startup. |
|
Sessions Curr. |
Number of currently active sessions. |
|
Sessions Max. |
Maximum reached number of simultaneously active sessions. |
|
Sessions Cumul. |
Total number of completed sessions. |
|
Errors Conn. |
Number of errors occurred while connecting to backend server. |
|
Errors Resp. |
Number of 5xx errors reported by backend server. |
|
Errors Check |
Number of failed health checks for a backend server. |
|
Errors Down |
Number of times the backend server went from UP to DOWN state. |
Load-balancing Slow Dynamic-content Applications
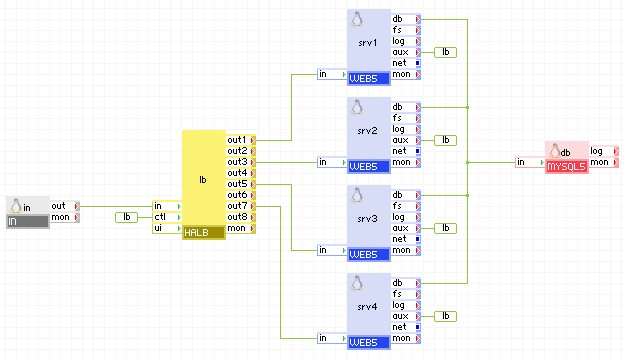
If your application requires a lot of computation to produce each page, it is naturally able to serve a limited amount of clients concurrently. However, if the data source is fast enough or can be replicated and served from multiple servers, HALB can be used to increase the number of connections that can be handled simultaneously. A typical example may be serving maps from a cartography database - the database is fast to read, but each pageload requires the map to be rendered as an image file.
The diagram below shows how HALB can be used to employ multiple CPUs to serve the same content, providing faster response under heavy load.
Configuration for a Server Keeping Sessions - Bugzilla
The configuration examples list only properties set to non-default values.
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
cookie_name |
Bugzilla_logincookie |
This is the name used by Bugzilla for its login cookie |
|
mode |
passive |
Bugzilla issues unique cookies for each username/IP address combination, therefore two bugzilla instances that are connected to the same database never returns the same cookie. It is thus safe to use the simplest passive mode. For other server types, the sync setting may be more appropriate. |
Sticky Load-balancing for Session-less Servers Using Cookies
For servers that do not have sessions, but keep some cached data and could benefit from a client being consistently directed to the same server, passive cookie monitoring does not work as there's no cookie to monitor. The insert mode is used in this case, as shown in the table:
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
cookie_name |
session_id |
Arbitrary name, but help ensure it does not match a name used by the servers for something else. |
|
mode |
insert |
HALB inserts a Set-Cookie: header |
Sticky Load-balancing for Session-less Servers Without Using Cookies with Session Persistence
Some clients do not support cookies, or disable them. In this case the example shown above is not the best solution, because the client ignores the cookie set. Much better solution is the source mode of HALB operation, that directs traffic to the web server based on request source IP address. Still, if the client uses multiple gateways simultaneously to access the Internet, it is possible for requests not to be directed to the same web server.
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
mode |
source |
HALB redirects the request to the web server using the request source IP address as a key. |
Load-balancing with Infrastructure Health Check
A successful health check of a backend web server does not guarantee that the data it returns is valid or the database that it depends on is still functional. One distinctive feature of HALB is the ability to use not only the conventional way of health checking (simply connect to port 80 of a web server), but also more advanced methods like http_head and http_get. Proper utilization of this ability helps ensure not only the availability of a backend web servers, but also their dependencies, database, application and storage servers. In this example two health check features of HALB are used. First, a special file health_check.php is created and its complete URL is specified in the healthcheck_url property. When this file is accessed, it evaluates the availability of the database, application or NAS servers and returns a status document with the text ALL_SERVICES_ARE_OK. This value is specified in the healthcheck_regexp property.
The HALB checks every output ( out1 - out8 ) with HTTP/1.1 GET requests, using site in the Host: HTTP header and /health_check.php as a document URL. These values are extracted from the healthcheck_url property (http://site/health_check.php). In the document, retrieved from each backend server, HALB searches for the value of healthcheck_regexp (ALL_SERVICES_ARE_OK). If this line is found, the server is considered to be functional/up, otherwise the output terminal is disabled. If the output is disabled and at a later time the HALB health check succeeds, the output is re-enabled.
When no virtual hosts are used, or backend server does not support HTTP/1.1 protocol, the healthcheck_url may be specified in a simple form (/health_check.php). In this case, HALB uses HTTP/1.0 protocol, and does not specify Host: HTTP header.
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
healthcheck_mode |
http_get |
HALB uses http_get mode of health check. |
|
healthcheck_url |
http://site/health_check.php |
the URL that HALB checks. |
|
healthcheck_regexp |
ALL_SERVICES_ARE_OK |
|
Using Backup Servers
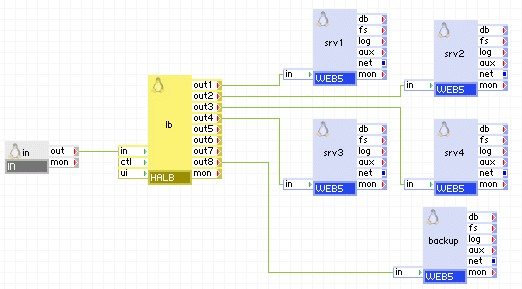
Backup servers are used when all back end servers are unavailable, and a conscious message or a redirection page must be delivered to client, instead of errors or timeouts. In the example below, server backup is configured as a last-resort server, serving only a static page telling clients that a technical maintenance is being performed. Once all four srv1 - srv4 servers go down, the content from server backup is served.
|
Property |
Value |
Notes |
|
backup_outputs |
out8 |
|
Using the Control Web Service Interface
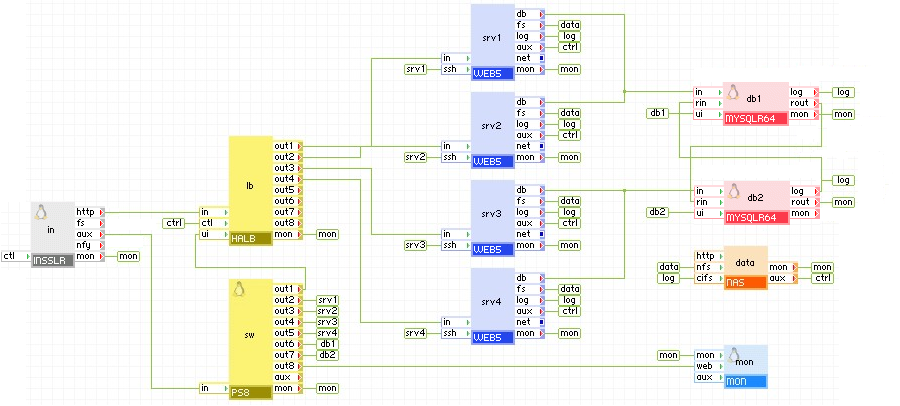
The control web service interface provides a way to dynamically and programmatically enable/disable output terminals of HALB. It can also be used to retrieve the current state of all of the output terminals. This interface is exposed through HALB's ctl terminal.
The diagram below shows a clustered environment with multiple web and database servers. Every web and database server has a feedback connection to the ctl terminal of HALB. If a web server detects a problem with database/connectivity/performance, it can disable the corresponding output terminal, thus ordering HALB to stop directing traffic to the web server. Similarly, any database server can disable the output terminals of HALB, thus disabling all incoming traffic. After the resolution of the problem, output terminals may be re-enabled.
Open source and 3rd party software used inside of the appliance
HALB uses the following 3rd party open source packages in addition to the 3rd party open source packages used by its base class LUX5.
|
Software |
Version |
Modified |
License |
Notes |
|
haproxy |
1.4.9 |
No |
GPLv2 |
homepage |
|
php-thttpd |
2.25b |
No |
BSD |
N/A |
|
Copyright © 2011 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|