

Latest version: 3.0.2-1

|
At a Glance |
|
|
Catalog |
System |
|
Category |
Gateways |
|
User volumes |
no |
|
Min. memory |
96 MB |
|
OS |
Linux |
|
Constraints |
no |
|
Questions/Comments
|
|
IN is an input gateway that provides a firewalled entry point for network traffic into an application.
IN accepts all allowed incoming traffic on its external interface and passes it through its out terminal. IN forwards only the traffic explicitly allowed through configuration of its firewall properties; IN discards all disallowed traffic.
IN supports up to 4 incoming interfaces (protocol/pair combinations), such as http, ssh, and so on. By default, IN allows only tcp port 80 (http).
IN is used to accept all network traffic for applications. All external traffic must pass through an IN gateway to access any resources or services within an application.
Resources
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.05 |
4 |
0.05 |
|
Memory |
96 MB |
2 GB |
96 MB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
200 Mbps |
Terminals
|
Name |
Dir |
Protocol |
Description |
|
out |
out |
Any |
Sends all traffic out to the destination address and receives the responses |
|
mon |
out |
CCE |
Sends performance and resource usage statistics |
The external interface is enabled. It is used for incoming traffic. The external interface is configured through the properties listed in the following sections.
The default interface is enabled. It is used for maintenance (incoming SSH connections).
Properties
Base Configuration
The following property group defines the base network settings for the gateway.
|
Property name |
Type |
Description |
|
ip_addr |
ip_owned |
Defines the IP address of the external interface. This property is mandatory. |
|
netmask |
IP address |
Defines the network mask of the external interface. This property is mandatory. |
|
gateway |
IP address |
Defines the gateway for the external interface. Default is empty (no gateway). |
Firewall Configuration
The following property group defines the firewall settings for the gateway. There are two filters that can be used together: by source IP address (allowed_hosts and denied_hosts) and by protocol/port (ifaceX). Up to four protocol/port pairs (interfaces) can be configured.
If all parameters are left to their defaults, no traffic will be allowed. To allow traffic in, configure at least the iface1_protocol and iface1_port values.
|
Property name |
Type |
Description |
|
allowed_hosts |
String |
List of hosts and/or subnets allowed to connect. Separate multiple entries with spaces or commas. Supported format example: 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.0/24 192.168.2.0/255.255.255.0. Default: 0.0.0.0/0 (all allowed) |
|
denied_hosts |
String |
List of hosts and/or subnets to be denied connection. The format is the same as for allowed_hosts. Default: (empty) (none denied) |
|
iface1_protocol |
String |
Protocol to allow. Options: none, tcp (default), udp |
|
iface1_port |
String |
Port numbers or port ranges to allow. Accepts a string of comma or space-separated values. Port ranges must be specified as lower_port:higher_port with colon or dash as a separator (for example, 80,81,82:85 86-90). Default: 80 (http) |
|
iface2_protocol |
String |
Protocol to allow. Options: none (default), tcp, udp |
|
iface2_port |
String |
Port numbers or port ranges to allow. Accepts a string of comma or space-separated values. Port ranges must be specified as lower_port:higher_port with colon or dash as a separator (for example, 80,81,82:85 86-90). Default: 0 (disabled) |
|
iface3_protocol |
String |
Protocol to allow. Options: none (default), tcp, udp |
|
iface3_port |
String |
Port numbers or port ranges to allow. Accepts a string of comma or space-separated values. Port ranges must be specified as lower_port:higher_port with colon or dash as a separator (for example, 80,81,82:85 86-90). Default: 0 (disabled) |
|
iface4_protocol |
Integer |
IP Protocol number to allow (for example, 6 for TCP, 47 for GRE). See http://www.iana.org/assignments/protocol-numbers. Default: 0 (disabled) |
|
iface4_port |
String |
Port numbers or port ranges to allow. Accepts a string of comma or space-separated values. Port ranges must be specified as lower_port:higher_port with colon or dash as a separator (for example, 80,81,82:85 86-90). Used only if the selected IP protocol has port numbers (for example, udp and tcp); must be set to 0 for all other protocols. Setting this property to 0 for tcp or udp protocols will allow all ports. Default: 0 |
Notes:
The port number for iface4 has slightly different behavior from the other port numbers. Setting iface4_port to 0 means that the port number is not going to be checked (works both for protocols that simply don't have port numbers, like GRE, and for tcp and udp). Setting iface{1,2,3}_port disables the interface (equivalent to setting the protocol to none).
Error Messages
The following messages may appear in either the appliance log file or the system log of the grid controller when the appliance fails to start:
Failed to set up backup rule set (exit code code)
Simple Input Firewall
The following diagram shows a typical usage of IN for a simple web server application:
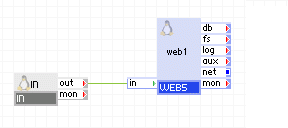
Summary of Parts
in1 accepts HTTP requests on its external interface and passes them to web1 through its out terminal.
Example:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
ip_addr |
192.168.1.1 |
IP address of the external interface |
|
netmask |
255.255.255.0 |
Network mask for the external interface |
|
gateway |
192.168.1.254 |
Gateway for the external interface |
|
iface1_protocol |
tcp |
Allow TCP traffic... |
|
iface1_port |
80 |
...only on port 80 (http) |
Advanced Firewall
In this example, the gateway is configured to allow the HTTP and HTTPS protocols, and the PPTP protocol (used by Microsoft Windows VPN).
Example:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
ip_addr |
192.168.1.1 |
IP address of the external interface |
|
netmask |
255.255.255.0 |
Network mask for the external interface |
|
gateway |
192.168.1.254 |
Gateway for the external interface |
|
iface1_protocol |
tcp |
Allow TCP traffic... |
|
iface1_port |
80 |
...on port 80 (http) |
|
iface2_protocol |
tcp |
Allow TCP traffic... |
|
iface2_port |
443 |
...on port 443 (https) |
|
iface3_protocol |
tcp |
Allow TCP traffic for the PPTP control connection... |
|
iface3_port |
1723 |
...on port 1723 (VPN) |
|
iface4_protocol |
47 |
Allow GRE traffic for the PPTP encapsulation |
|
iface4_port |
0 |
(not used) |
In this example, note the use of iface4 for the GRE protocol. It is OK to fill iface4 even if lower-numbered interfaces are not filled in.
If a host is present, directly or as part of a subnet, both in the allowed_hosts and in the denied_hosts lists, it will be denied access. IN first rejects all denied hosts and then allows only those in allowed hosts (standard security practice).
IN is not used for accessing external services by the application. Applications access external services (outgoing traffic) through OUT and NET gateways.
iface4_protocol has not been tested with protocols other than tcp and udp (due to lack of appliances supporting GRE or other non-tcp/udp protocol).
Open source and 3rd party software used inside of the appliance
IN uses the following 3rd party open source packages in addition to the 3rd party open source packages used by its base class LUX5.
|
Software |
Version |
Modified |
License |
Notes |
|
iptables |
1.3.5-1.2.1 |
No |
GPLv2 |
homepage |
|
Copyright © 2011 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|