


|
At a Glance |
|
|
Catalog |
System |
|
Category |
Database Appliances |
|
User volumes |
yes |
|
Min. memory |
160 MB |
|
OS |
Linux |
|
Constraints |
no |
|
Questions/Comments |
|
Important! MYSQL64 is not available in CA 3Tera AppLogic 2.8+; please use MYSQLR64 instead.
MYSQL is a database appliance based on the MySQL database engine (http://www.mysql.org). It provides an easy way to add a database to any application.
MYSQL stores the database on an application-defined volume that can be configured on each MYSQL instance. MYSQL automatically creates an empty database when it starts on an empty volume.
|
Name |
Latest Version |
OS |
MySQL |
Notes |
|
MYSQL5 |
2.0.3-1 |
CentOS 5.5 |
5.5.8 |
|
Resources
|
Resource |
Minimum |
Maximum |
Default |
|
CPU |
0.10 |
16 |
0.40 |
|
Memory |
160 MB |
32G |
512 MB |
|
Bandwidth |
1 Mbps |
2 Gbps |
250 Mbps |
Terminals
|
Name |
Dir |
Protocol |
Description |
|
in |
in |
MYSQL |
Receives MySQL database requests |
|
log |
out |
CIFS |
Network file system for storing error log. This terminal may be left unconnected if not used. |
|
mon |
out |
CCE |
Sends performance and resource usage statistics. This terminal may be left unconnected. |
The default interface is enabled. It is intended for diagnostics and troubleshooting (over SSH). Future versions of this appliance may disable SSH access.
User Volumes
|
Volume |
Description |
|
data |
Volume for the database data storage. |
The data volume can optionally contain a my.cnf file in its top directory, which includes MYSQL configuration options. See the Custom Configuration section for more details. This feature is available in MYSQL5/64 1.3.3 or later.
Important! The data volume must exclusively dedicated to the MYSQL instance (cannot be shared with other appliances).
Properties
|
Property name |
Type |
Description |
|
auto_create |
Integer |
Whether to create the database if it does not exist. Possible values are 1 to create it and 0 to prevent auto creation (to avoid accidental overwrite in case of corrupted volumes). If set to 0 and a database does not exist on the user volume, the appliance starts in maintenance mode (MySQL daemon not started). Default is 1. |
|
error_log_filename |
String |
Fully qualified file name for the error log file, relative to the log file system (for example, /mysql_logs/my.log). If empty, error logging is disabled. Default: (empty). |
|
error_log_level |
String |
Error logging level. Possible values are: error logs only errors, warn logs both warnings and errors. This property is not case sensitive. Default: error |
|
timezone |
String |
Specifies the time zone used in the appliance. If this property is empty, the timezone is not modified and left as-is. A list of supported time zones is available here. Default: empty |
Important!
The MYSQL appliance will fail to start if the error_log_filename is specified and the log terminal is not connected or the file system cannot be mounted.
Custom Configuration
This feature is available in MYSQLR 1.3.3 or later.
MYSQL5/64 allows the use of a custom MYSQL configuration file which can provide additional configuration options or overwrite existing configuration specified in /etc/my.cnf.
To use a custom configuration, create a file named my.cnf and place it in the top directory of the data volume. The format of the file should follow the MYSQL options file syntax as described on their website.
For example, the following can be used to tune MYSQL5/64 for better performance when using InnoDB (the default MYSQL5/64 configuration is optimized for MyISAM). The example is based on using 512M of memory (default for MYSQL5/64).
[mysqld] # Shrink down MyISAM buffers key_buffer = 512K myisam_sort_buffer_size = 512K # Make InnoDB the default storage engine (optional) default-storage-engine = INNODB # Set InnoDB buffer size innodb_buffer_pool_size=350M innodb_log_file_size=128M innodb_log_buffer_size=4M innodb_thread_concurrency=8 # If you do not have too many tables use this option, so you will not have uncontrolled innodb main tablespace growth which you cannot reclaim.
innodb_file_per_table=1
Custom Counters
The MYSQL appliance reports the following custom counters through the mon terminal.
The following counters belong to the MySql counter group:
|
Counter name |
Description |
|
Aborted Clients |
Number of clients aborted by the server |
|
Aborted Connections |
Number of connects aborted by the server |
|
Bytes Received |
Number of received bytes |
|
Bytes Sent |
Number of sent bytes |
|
Total Connections |
Number of connections |
|
Questions |
Total number of questions |
|
Slow Queries |
Number of slow queries |
|
Threads Created |
Number of threads created |
|
Threads Connected |
Number of threads connected |
|
Threads Running |
Number of threads running |
|
Max Used Connections |
Number of max connections used |
|
Open Files |
Number of open files |
|
Admin Commands |
Number of admin commands |
|
Alter Table Commands |
Number of alter table commands |
|
Analyze Commands |
Number of analyze commands |
|
Backup Table Commands |
Number of backup table commands |
|
Change DB Commands |
Number of change DB commands |
|
Change Master Commands |
Number of change master commands |
|
Check Commands |
Number of check commands |
|
Commit Commands |
Number of commit commands |
|
Create DB Commands |
Number of create DB commands |
|
Create Function Commands |
Number of create function commands |
|
Create Index Commands |
Number of create index commands |
|
Create Table Commands |
Number of create table commands |
|
Delete Commands |
Number of delete commands |
|
Drop DB Commands |
Number of drop DB commands |
|
Drop Function Commands |
Number of drop function commands |
|
Drop Index Commands |
Number of drop index commands |
|
Drop Table Commands |
Number of drop table commands |
|
Flush Commands |
Number of flush commands |
|
Grant Commands |
Number of grant commands |
|
Insert Commands |
Number of insert commands |
|
Insert Select Commands |
Number of insert select commands |
|
Kill Commands |
Number of kill commands |
|
Load Commands |
Number of load commands |
|
Load Master Table Commands |
Number of load master table commands |
|
Lock Tables Commands |
Number of lock tables commands |
|
Optimize Commands |
Number of optimize commands |
|
Purge Commands |
Number of purge commands |
|
Rename Table Commands |
Number of rename table commands |
|
Repair Commands |
Number of repair commands |
|
Replace Commands |
Number of replace commands |
|
Replace Select Commands |
Number of replace select commands |
|
Reset Commands |
Number of reset commands |
|
Restore Table Commands |
Number of restore table commands |
|
Revoke Commands |
Number of revoke commands |
|
Rollback Commands |
Number of rollback commands |
|
Select Commands |
Number of select commands |
|
Set Option Commands |
Number of set option commands |
|
Truncate Commands |
Number of truncate commands |
|
Unlock Tables Commands |
Number of unlock tables commands |
|
Update Commands |
Number of update commands |
Error Messages
The following messages may appear in either the appliance log file or the system log of the grid controller when the appliance fails to start:
Insufficient permissions for root@% in the mysql database.
Simple Two-tier Application
Appliances in use:
Client request arrive on the in1 gateway. The gateway forwards the requests to the web1 server, which serves the request. When scripts (for example, Perl or PHP) on web1 need to access persistent data, they use the db1 appliance through the out terminal of the web1 server. The db1 appliance is configured to store its log files within the root directory of the share exposed by logs.
Using a browser, administrators connect to the admin gateway to view the mysql log files. The admin gateway forwards the requests to the logs NAS appliance.
Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
auto_create |
1 |
Create the database if the volumes are empty. |
|
error_log_filename |
/my.log |
Name of error log file that is to be stored on the logs data volume. |
|
error_log_level |
error |
Error logging level |
Note: The data volume must also be configured on the db1 appliance and the logs appliance. To create application volumes that can be used here, see the Grid Users Guide.
Scalable Two-tier Application
The following diagram shows a typical usage of the mysql appliance in a two-tier web application in which the database is used to share state and data between multiple, load-balanced web servers. In addition, this example has a separate input for maintenance, through which an administrator can log in and access the database for maintenance and an input through which an administrator can log in and view the mysql error log.
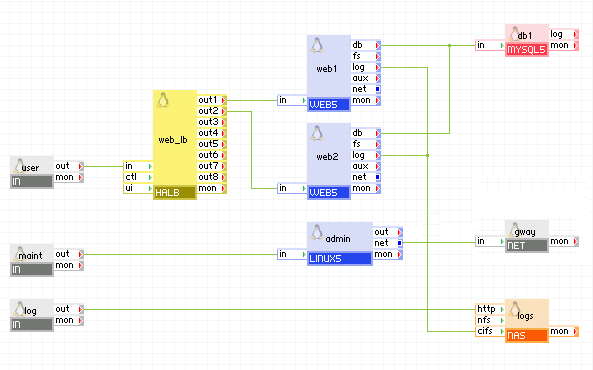
Appliances in use:
Client request arrive on the user gateway. The gateway forwards the requests to the web_lb load balancer, which directs the request to one of the web servers web1 and web2. The web servers access the db database.
The db database writes its error log to the logs appliance through the log terminal. In addition, an administrator can log in through the log gateway to the logs appliance and view the database error log files.
Additionally, an administrator can log in over SSH through the maint gateway to the admin server. From the admin server, the administrator can access the db database for statistics or changing the database schema. The admin server can access the Internet through the gway gateway, for example, to download a newer version of libraries or the database schema.
Example property configuration:
|
Property name |
Value |
Notes |
|
auto_create |
1 |
Create the database if the volumes are empty. |
|
error_log_filename |
/my.log |
Name of error log file that is to be stored on the logs data volume. |
|
error_log_level |
error |
Error logging level |
Note: The data volume must also be configured on the db appliance and the data volume must also be configured on the logs appliance.
The maint, admin, gway, and log appliances are not required for the operation of the two-tier application. If present, the admin server may have cron jobs for database scrubbing, sending e-mail, and so on.
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'monty'@'%'
-> IDENTIFIED BY 'some_pass' WITH GRANT OPTION;
MYSQL5 uses the following 3rd party open source packages in addition to the 3rd party open source packages used by its base class LUX5.
|
Software |
Version |
Modified |
License |
Notes |
|
libaio |
0.3.106-5 |
No |
LGPLv2.1 |
N/A |
|
MySQL-client |
5.5.8-1 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
MySQL-server |
5.5.8-1 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
MySQL-shared-compat |
5.5.8-1 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
perl |
5.12.2-1 |
No |
Artistic |
N/A |
|
perl-DBD-MySQL |
3.0007-2 |
No |
Artistic |
N/A |
|
perl-DBD-SQLite |
1.29-1 |
No |
Artistic |
N/A |
|
perl-DBI |
1.615-1 |
No |
Artistic |
N/A |
|
perl-DBIx-Simple |
1.32-1 |
No |
Artistic |
N/A |
|
samba-client |
3.0.33-3.29 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
samba-common |
3.0.33-3.29 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
libsmbclient |
3.0.33-3.29 |
No |
GPLv2 |
N/A |
|
Copyright © 2011 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|