

Each relationship reflects a reason for associating two entities. Sometimes, there are multiple reasons for joining two entities of the same two entity types. If so, the model should contain one relationship for each reason.
For example, consider the following illustration.
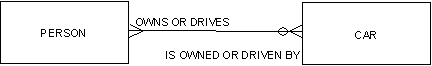
In this illustration, the M:N relationship between person and car has two distinct meanings:
The single M:N relationship fails to distinguish between two different reasons for associating person and car. It should be expanded into two relationships, as shown in the following illustration.
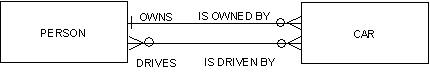
Two or more relationships that join the same entity types are called parallel relationships.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|