

You can define an FTP job to automate FTP transfers. The output is directed to the spool file through an FTP server.
Note: To run these jobs, your system requires CA WA Agent for UNIX, Linux, Windows, or i5/OS.
Follow these steps:
The Application appears in the workspace.
The FTP icon appears on the Application workspace view.
The Basic page of the FTP dialog opens.
Defines the name of the job that you want to schedule.
Limits: 128 alphanumeric characters, plus the special characters commercial at (@), pound (#), dollar sign ($), underscore (_), square brackets ([]), brace brackets ({}), and percent sign (%) as a symbolic variable introducer character.
Specifies the name of the agent where the FTP transfer takes place.
Note: The drop-down list displays all the agents that are defined in the Topology for the specified job type.
Specifies the user ID of the user with the authority to download the file from the remote FTP server or upload the file to the remote FTP server. The user must be defined in the Topology. This field supports the use of a namespace for a user that has more than one password. Contact your administrator for the user name defined in the Topology.
Examples: Bob, Production:Bob
Note: The drop-down list displays all the user IDs that are defined in the Topology for the specified agent. You must have at least Read access to the ADMIN.Network Topology permission to view this list.
Specifies the DNS name or IP address of a remote server.
Example: 172.24.36.107 (IPv4) or 0:0:0:0:0:FFFF:192.168.00.00 (IPv6)
Specifies the file's source location (if downloading) or the file's destination (if uploading).
Note: You can specify multiple files. Separate each file name with a semi-colon. The number of files specified in the Local file name and Remote file name fields must match.
UNIX/Windows:
i5/OS:
/QSYS.LIB/libraryname.LIB/objectname.FILE/membername.MBR
Specifies the file's destination (if downloading) or the file's source location (if uploading).
Notes:
UNIX/Windows:
i5/OS:
/QSYS.LIB/libraryname.LIB/objectname.FILE/membername.MBR
Indicates the direction of transfer (Download or Upload).
Default: Download
Specifies the type of data you are transferring. Options are as follows:
Indicates a binary transfer.
Indicates an ASCII transfer.
i5/OS: If the ASCII file to be transferred already exists on the target computer, the file is written using the encoding of the existing file. If the file does not exist, the file is written using the ASCII CCSID (Coded Character Set Identifier) defined on the agent. The default is 819.
Indicates an EBCDIC transfer.
Note: EBCDIC applies to jobs running on System i5 only. If an EBCDIC file to be transferred already exists on the target computer, the file is written using the encoding of the existing file. If the file does not exist, the file is written using the EBCDIC CCSID (Coded Character Set Identifier) defined on the agent. The default is 37.
Default: Binary
Specifies the job class under which this job runs. The agent maintains a list of job classes and the number of initiators assigned to each job class. A job class with more initiators can process more jobs more quickly. For higher-priority jobs, assign a job class that contains more initiators.
Example: foo
Note: To find out which job classes exist and how many initiators are assigned, ask your agent administrator to check the initiators.class_n parameter in the agent parameter file (agentparm.txt).
Specifies the port number of the remote server.
Default: 22
Specifies a user ID on the UNIX or Linux computer where the agent is installed. This user ID determines the access permissions of a downloaded file on the agent computer and does not apply to uploads. When the file is downloaded, the file is created with this user as the file owner. To set the owner of a downloaded file, the agent must run as root.
Notes:
Defines the compression level (0 is no data compression, 9 is the best data compression).
Default: Default compression level set on the agent FTP client
Indicates whether to transfer the data using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) communication (True or False).
Default: Default FTP setting (regular FTP or SSL FTP) on the agent
Defines the commands that are to be executed prior to file transfer. You can use this section to send site-specific FTP commands to FTP servers.
Specifies the user ID that runs the job on behalf of the agent user. You can use this field to access remote resources that the agent user does not have access to. You are restricted to how you can access data on remote computers. To access restricted remote resources, you can run the job under a user ID that has access to those resources. The user must be defined in the Topology. This field supports the use of a namespace for a user that has more than one password. Contact your administrator for the user name defined in the Topology.
Examples: Bob, Production:Bob
Notes:
The FTP job is defined.
Example: Upload Multiple Files to a Directory Using a Wildcard
Suppose that you want to upload all the files in the C:\ca directory to the E:\ftp directory on a remote Windows server.
Follow these steps:
Example: Upload a File From a Local Computer to a Remote Windows Server Using SSL FTP
Suppose that the agent runs on a local computer as an FTP client and has SSL FTP configured, but not enabled. The remote Windows server has SSL FTP configured and enabled.
To securely upload a file from the agent FTP client to the remote Windows FTP server, set SSL connection to True in the FTP job definition. Although the agent FTP client does not have SSL FTP enabled, the file is uploaded using SSL FTP because the agent FTP client has SSL FTP configured and the FTP server has SSL FTP enabled.
The following diagram shows the scenario:
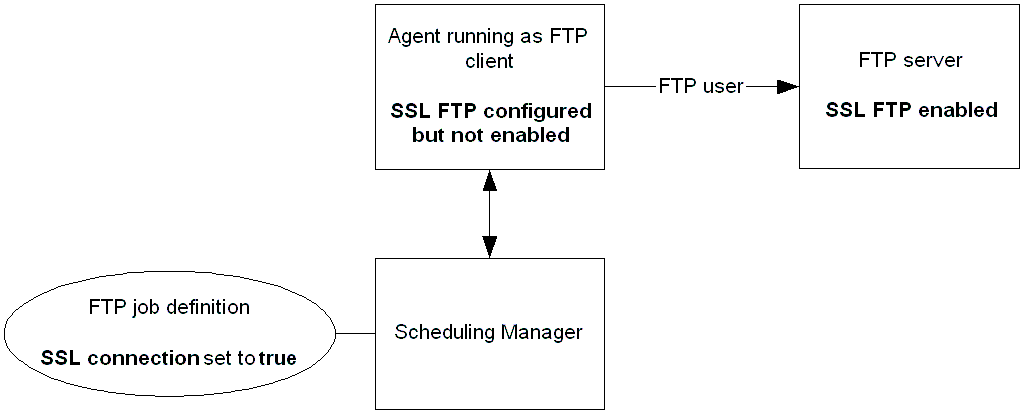
Suppose the FTP job FTP_UPLOAD uploads the file d:\files_to_upload\filename.txt from the agent FTP client to the c:\uploaded_files directory on a remote Windows server named winserver. The agent SYSAGENT logs into the remote Windows server using user user1. Because the FTP client has SSL configured but not enabled, SSL connection is set to True to transfer the file securely.
Follow these steps:
Example: Download a File from a Remote UNIX Server that Does Not Support SSL FTP to a Local Computer that Supports SSL FTP
Suppose that the agent runs on a local computer as an FTP client and has SSL FTP enabled (all FTP jobs on the agent computer run using SSL FTP). The remote UNIX server does not support SSL FTP.
The following diagram shows the scenario:
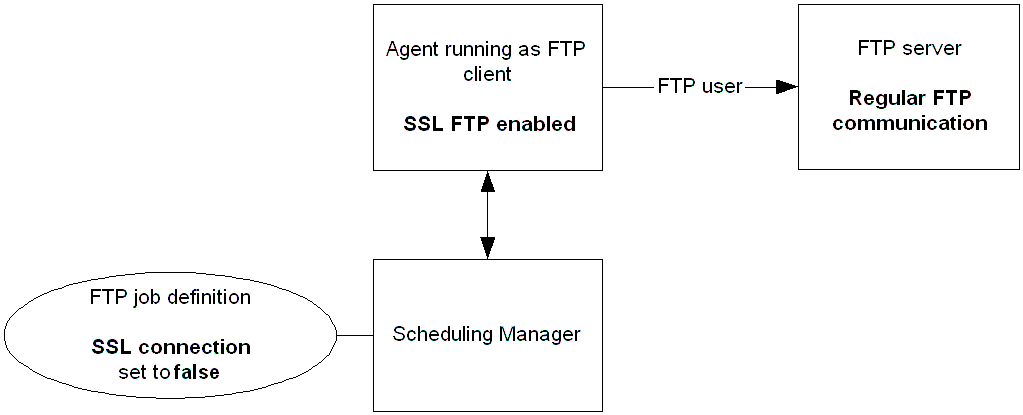
Suppose that the FTP job FTP_DOWNLOAD downloads the file /files_to_download/filename.txt from the remote UNIX server hpunix to the c:\downloaded_files directory on the local server. The agent SYSAGENT logs into the remote UNIX server using user user1. Because the FTP server does not support SSL FTP, SSL connection is set to False.
Follow these steps:
Note: To transfer FTP data, you must set SSL connection to False. Otherwise, the job will fail.
Example: Upload an ASCII-encoded File in the Root File System from an i5/OS System to a UNIX System
Suppose that the FTP job FTP_UPLOAD uploads a file named textfile in the root file system is uploaded from an i5/OS system to a UNIX system. Note that the two locations include a complete path statement.
Follow these steps:
Note: To transfer FTP data, you must set SSL connection to False. Otherwise, the job will fail.
Example: Download a QSYS.LIB EBCDIC-encoded File
Suppose that the FTP_DOWNLOAD job downloads an EBCDIC-encoded file named datafile in the QSYS.LIB file system from an i5/OS system to another i5/OS system. Note that the file names are specified in the path format.
Follow these steps:
Note: To transfer FTP data, you must set SSL connection to False. Otherwise, the job will fail.
Example: Upload and Convert an EBCDIC-encoded File to ASCII
Suppose that the FTP_CONVERT job uploads a file member named RESULT from an i5/OS system to a UNIX system. The job automatically detects that the RESULT file member is EBCDIC-encoded and that the target UNIX system accepts only ASCII-encoded files. The I5Agent agent is configured to automatically convert EBCDIC-encoded files to ASCII during an upload to an ASCII system, so the RESULT file member uploads successfully.
Follow these steps:
Note: To transfer FTP data, you must set SSL connection to False. Otherwise, the job will fail.
Example: Compress a File and Download it Using SSL
Suppose that the local server has an agent running as an FTP client. The remote server has the agent running as an FTP server. SSL FTP is enabled on both FTP client and FTP server. Both servers operate on a low bandwidth network.
Suppose that the FTP job FTPJOB downloads a large file named /files_to_download/largefile.txt from the remote server aixunix to the c:\downloaded_files directory on the FTP client. The agent SYSAGENT logs into the remote UNIX server using user user1. The servers are on a low bandwidth network, so the data is compressed at compression level 3. By default, the job runs using SSL FTP because SSL FTP is enabled on both FTP client and FTP server.
Follow these steps:
Example: Send Two FTP Commands to an FTP Server
Suppose that you want to send two FTP commands to the FTP server prior to transferring a file.
Follow these steps:
A new row is added to the Command table.
A new row is added to the Command table.
Example: Download a File from an FTP server to a Remote Location using Run as User
Suppose that you want to download a file (download_test.txt) from a remote FTP server to a remote location that the agent user does not have access to. An additional user (user2) that has access to the remote location is specified.
Follow these steps:
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|