

An entity bean represents a data object, such as a customer, an order, or a product. Entity beans may be stored in a relational database, where each instance of the bean corresponds to a row in a database table. Each entity bean has a unique identifier known as a primary key, which is used to find a specific instance of the bean within the database. For example, a customer entity bean may use the customer number as its primary key.
Unlike session beans, which are destroyed after use, entity beans are persistent. You can use an entity bean under the following conditions:
The following diagram shows the functional relationship between the scheduling manager, CA WA Agent for Application Services, and an entity bean residing on an application server:
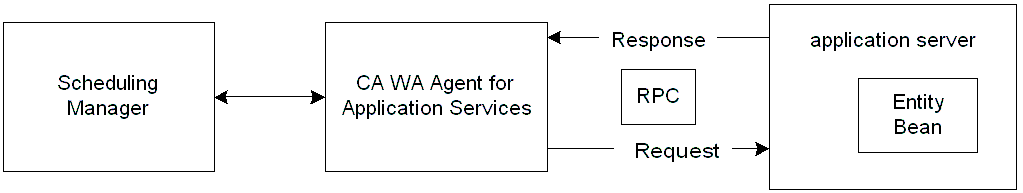
The Entity Bean job lets you create an entity bean, update the property values of an existing entity bean, or remove an entity bean from the database. To find the entity bean, the agent uses the bean's Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI) name along with its finder method.
Note: To run these jobs, your system requires CA WA Agent for UNIX, Linux, or Windows and CA WA Agent for Application Services.
To define an Entity Bean job, you require the following information:
|
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|