

When a certificate name filter is defined, the information is stored in a CERTMAP record in the SDT on the security file. The filter definition specifies the significant portion of the issuer's or subject's distinguished name used to associate an ACID with a certificate.
Additional criteria can be specified to identify the ACID used. The system ID and application ID system variables can be used to select the ACID. Sites can define their own variable for selection criteria.
Criteria data is stored in a CRITMAP record in the SDT. CERTMAP and CRITMAP records are created with the TSS ADD command.
To understand how certificate name filtering works, it is important to know directory concepts and the models described by the X.500 standard. The subject's and issuer's distinguished names on a certificate identify the subject's or issuer's location in an X.500 directory information tree.
The following diagram is an example of a directory tree:
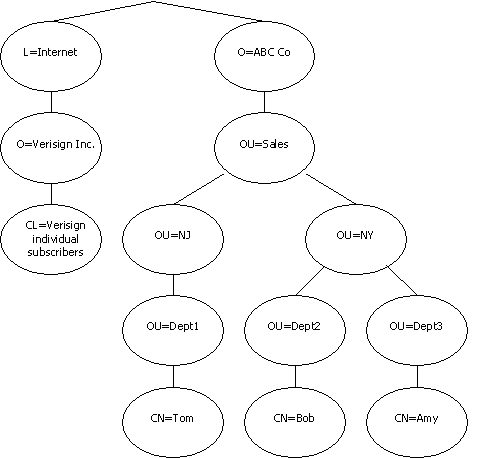
In this X.500 directory information tree, Amy's path name would be:
/O=ABC Co/OU=Sales/OU=NY/OU=Dept3/CN=Amy
Or, written in the address form used by CA Top Secret:
O=ABC Co.OU=Sales.OU=NY.OU=Dept3.CN=Amy
The nodes in this tree structure show that Amy works in department Dept3 in New York in the Sales division of the ABC Co company. A user's location in the hierarchy determines the access to resources that they have.
CA Top Secret supports this tree structure. ACIDs can be assigned to each level at which you want to group users or they can be assigned at just one level.
For example, node OU=Dept2 could be assigned to acid NYDEPT2 and OU=Dept3 could be assigned to NYDEPT3. When a user enters the system by presenting a certificate, CA Top Secret determines which ACID to assign by matching the subject's distinguished name to a node name.
If Amy entered the system with a certificate with a subject distinguished name, she would be assigned ACID NYDEPT3:
O=ABC Co.OU=Sales.OU=NY.OU=Dept3.CN=Amy
If ACID AMYUSR was assigned to node CN=Amy, she would be assigned ACID AMYUSR since that is a more specific match. Mapping is also done using the issuer name since two different certificate authorities can issue a certificate with the same subject name. ACID assignment can be based on a combination of subject name and issuer name, only a subject name or only an issuer name. Both full path names and partial path names can be defined.
You can use additional criteria (such as application ID or system ID) to select the ACID to be assigned to a certificate.
|
Copyright © 2014 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
|
|