

Configuring CIA Real-Time Processing for CA Chorus › How CIA Real-Time Processing Works
How CIA Real-Time Processing Works
CIA real-time processing helps ensure that the information in the CIA repository is updated as changes occur to the security product database. When it is enabled, the CIA real-time feature performs the following actions:
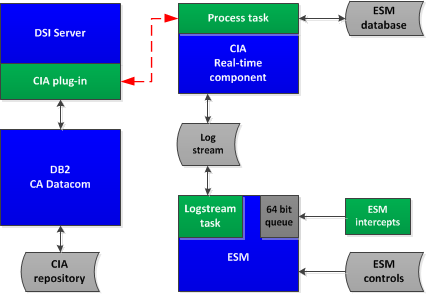
- A processing task in the security product address space removes the update requests from the request queue. The update request is written to a z/OS system logger logstream dedicated to the CIA real-time feature.
- A CIA real-time component reads the update requests from the CIA logstream. The component sends the request to a CA DSI Server running on the z/OS image where the CIA repository resides. When the CIA real-time feature is implemented, a CA DSI Server is required on the LPAR with the CIA repository. This CA DSI Server processes the CIA real-time requests, and updates the information in the CIA repository.
- A CIA real-time process in the CA DSI Server communicates the update requests to the DB2 or CA Datacom/AD subsystem where the CIA repository resides. The corresponding changes are made to the information in the CIA repository. The CA DSI Server communicates the results of the update request back to the CIA real-time component.
- If the update request was successfully processed into the CIA repository, the CIA real-time component deletes the update request from the CIA logstream.
- If the CIA real-time process was unable to complete due to a recoverable condition, the component stops processing, communicates the recoverable condition to the operator, and waits for resolution of the condition. The following are examples of these recoverable conditions:
- The CA DSI Server communication path through TCP/IP is unavailable
- The CA DSI Server is unavailable.
- The CA Datacom/AD MUF or DB2 subsystem in which the CIA repository resides is unavailable
- If a logical error was encountered trying to update the security information, the CIA real-time component records the error condition in a journal file (if one was supplied). The CIA real-time component then deletes the update request from the CIA logstream. These logical errors usually indicate that the request could not be processed because the security information in the CIA repository does not reflect the information in the security product database. Some examples of these logical errors are:
- The request is to add information that is already in the CIA repository.
- The request is to update information that does not exist in the CIA repository.
- The request is to delete information that does not exist in the CIA repository.
The following diagram illustrates the architecture of the CIA real-time process, and how the update requests flow from the security product to the CIA repository.
CIA Real-Time Implementation Checklist
The following checklist is available to assist as you implement and configure the CIA Real-Time component.
Implement the CIA Real-Time Feature
Perform the following steps to implement the CIA real-time feature.
- Define the CIA repository for CA Datacom or DB2.
- Configure CA DSI Server for CIA real-time
- Manually edit the dsi.conf configuration file using oedit or vi editor.
- For DB2 CIA Security Repository usage - Replace the ssid with the DB2 subsystem name or group attachment name that the CIA real-time plugin connects.
- For CA Datacom CIA Security Repository usage - Replace the ssid with the CA Datacom MUF that the CIA real-time plugin connects.
- Begin CIA real-time recording.
- Define the CIA real-time feature logstream.
- Modify the CA Top Secret control options to enable recording of update requests to the CIA logstream.
- Load the CIA repository.
- Unload the security product database information on a z/OS image containing the security product database.
- Load the security information into the CIA repository on the z/OS image that contains the CIA repository.
Configure the CIA Real-Time Component
Perform the following steps to configure the CIA real-time component.
- Define the CIA real-time component options. (Optional)
- Copy data set member CIAPARMS in CAI.CAKOJCL0 into the procedure or parameter library that is designated according to your installation standards.
- Edit data set member CIAPARMS to modify the CIA real-time component options to conform to your installation standards.
- Allocate the CIASTATS DD output data set. (Optional)
- Check if this data set already exists. If it does not, edit the CIARTALC job in CAI.CAKOJCL0 to conform to your installation standards.
- Submit the CIARTALC job.
- Verify that the CIASTATS DD was successfully created.
- Allocate the CIAJRNL DD output data set. (Optional)
- Check if this data set already exists. If it does not, edit the CIARTALC job in CAI.CAKOJCL0 to conform to your installation standards.
- Submit the CIARTALC job.
- Verify that the CIAJRNL DD data set was successfully created.
- Define the CIA Real-Time component.
- Copy the sample CIARTUPD procedure from the CAI.CAKOJCL0 installation data set to a procedure library in each z/OS system where the CIA real-time component will be executed.
- Edit the CIARTUPD procedure.
Create the CIA Real-time Component Security Definition
Create the CA Top Secret security environment required for the CIA real-time component. Modify and run the CIARTTSS sample job.
Start and Stop the CIA Real-Time Component
Perform the following steps to start and stop the CIA Real-Time component.
Control and Modify the CIA Real-Time Component
Perform the following step to control the execution of the CIA real-time component address space.
Copyright © 2013 CA Technologies.
All rights reserved.
 
|
|


