

Some authentication scheme types support Password Policies, while others do not. You can view whether a particular type of authentication scheme supports Password Policies by opening the Authentication Scheme Properties dialog in the Administrative UI. To view a particular authentication scheme type, select it from the drop-down list on the Scheme Common Setup group box and observe the Password Policies Enabled for this Authentication Scheme check box. If the authentication scheme does not support Password Policies, the check box description is dimmed and the check box is unavailable.
To view supported authentication scheme types and whether they support Password Policies without accessing the Administrative UI, see the following table:
|
Authentication Scheme Type |
Type Supports Password Policies? |
|
Anonymous |
No |
|
Basic |
Yes |
|
Basic over SSL |
Yes |
|
Custom |
Yes |
|
HTML Forms |
Yes |
|
Impersonation |
No |
|
MS Passport |
No |
|
RADIUS CHAP/PAP |
Yes |
|
RADIUS Server |
Yes |
|
SafeWord |
No |
|
SafeWord and HTML Forms |
No |
|
SecurID |
No |
|
SecurID and HTML Forms |
No |
|
X.509 Client Certificate |
No |
|
X.509 Client Certificate and Basic |
Yes |
|
X.509 Client Certificate or Basic |
Yes |
|
X.509 Client Certificate and HTML Forms |
Yes |
|
X.509 Client Certificate or HTML Forms |
Yes |
|
Windows Authentication |
Yes |
A single user can be stored in more than one user directory or database associated with a policy domain. This user has the same password in each user store. During authentication, if the Policy Server finds that the user is disabled in one user store, then by default, it continues searching for the user in all stores associated with the policy domain. The user fails authentication only if the Policy Server finds the user disabled in all associated user stores. The user is authenticated if it is enabled in any associated user store.
This default Policy Server behavior is configurable. To configure the Policy Server to stop searching when it first finds the user disabled in a user store, add the following registry key and set its value to one: ReturnOnDisabledUser.
To limit Policy Server search to one user store during authentication
Windows
Add the registry key ReturnOnDisabledUser to the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Netegrity\SiteMinder\CurrentVersion \PolicyServer
Solaris
Add the following lines to the sm.registry file:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Netegrity\SiteMinder\CurrentVersion \PolicyServer ReturnOnDisabledUser=0x1; REG_DWORD
When a user attempts to access a protected network resource, the Policy Server uses the authentication scheme associated with the resource’s realm to determine how to identify the user. The authentication scheme specifies the credentials that the user must supply for authentication, as well as the method used by the Policy Server to validate the user’s identity.
You can use the Administrative UI to configure authentication schemes and assign the schemes to realms. The following diagram illustrates how an authentication scheme is called when a user attempts to access a protected resource.
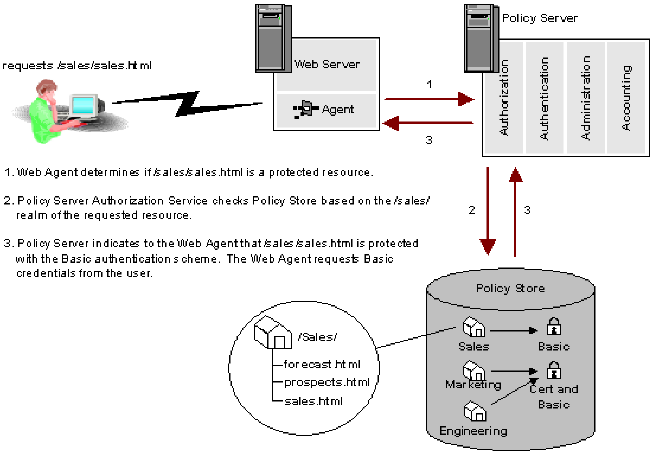
In the example above, the user requests the protected resource sales.html from the /Sales/ realm. This realm requires Basic authentication. The Policy Server informs the Web Agent that the resource is protected and requests Basic credentials from the user via the Web Agent, which prompts the user for a user name and password.
The Authentication Schemes supported by SiteMinder fall into a number of categories. These categories represent the general characteristics of available authentication methods. Details are provided in the sections of this chapter that discuss each specific authentication scheme.
Basic authentication identifies a user based on a user name and password. The user’s identity is stored in a user directory. With a basic authentication scheme, the Policy Server locates a user in a directory based on the user name, then verifies that the password matches the one saved in the user directory (binds the user to the directory). If the user name and password supplied by the user match the data in the user directory, SiteMinder authenticates the user.
The Administrative UI provides authentication scheme templates for the following basic schemes:
SiteMinder supports the use of customized HTML forms to collect authentication information. In a forms-based authentication scheme, a user can be required to enter additional information such as a Social Security Number, organization, account number, etc. The Policy Server verifies the additional information against user directory attributes before authenticating the user.
Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA) is a proprietary mechanism developed by Microsoft to validate users in pure Windows environments. IWA enforces Single Sign-On by allowing Windows to gather user credentials during the initial interactive desktop login process and subsequently transmitting that information to the security layer. SiteMinder, using the Windows Authentication scheme, secures resources by processing user credentials obtained by the Microsoft Integrated Windows Authentication infrastructure.
Previous versions of SiteMinder supported Windows authentication through the NTLM authentication scheme. However, this support was limited to environments with NT Domains or where the Active Directory service is configured to support legacy NT Domains in mixed mode.
The Windows authentication scheme allows SiteMinder to provide access control in deployments with Active Directories running in native mode, as well as Active Directories configured to support NTLM authentication. The Windows Authentication scheme replaces SiteMinder’s previous NTLM authentication scheme. Existing NTLM authentication schemes continue to be supported and can be configured using the new Windows Authentication scheme.
The NTLM authentication scheme can be used for resources that are protected by Web Agents on IIS Web servers, and whose users access resources via Internet Explorer Web browsers. This scheme relies on a properly-configured IIS Web server to acquire and verify a user’s credentials. The Policy Server bases authorization decisions on the user’s identity as asserted by the IIS server.
SiteMinder supports the use of X.509 V3 client certificates. Digital certificates act as cryptographic proof of a user’s identity. Once a certificate is installed on a client, that certificate can be used to verify the identity of a user who is accessing a resource. Certificate authentication uses SSL communication and can be combined with basic authentication to provide an even higher level of access security.
The Administrative UI provides authentication scheme templates for the following certificate-based authentication schemes:
Note: In the case of certificate-only authentication schemes, the web agent returns HTTP Error 403: Access Denied/Forbidden for any failed authentication or authorization attempt. This is because there is no way for the web agent to challenge the user for a new certificate.
Proxy authentication schemes are schemes that use the Policy Server as a proxy or substitute for the server required by a third party authentication product. With a proxy scheme, the Policy Server performs the authentication function of the third party server using scheme specific libraries.
SiteMinder supports the following proxy authentication schemes:
A digest authentication scheme reads an encrypted user attribute string stored in a directory, then compares the string to the encrypted string it receives from the user. If the encrypted strings match, the Policy Server authenticates the user. A digest scheme compares a string encrypted on a client workstation to an encrypted string on a server without using an encrypted transmission.
SiteMinder supports the following digest authentication schemes:
An anonymous authentication scheme allows non-registered users to access specific Web content. When a user accesses a resource that has anonymous authentication, SiteMinder assigns the user a Global User Identification (GUID). SiteMinder places this GUID in a persistent cookie on the user’s browser so that the user can access specific resources without being challenged to authenticate.
If SiteMinder does not provide a method of authentication that you want to use, you can use CA’s APIs to develop a custom authentication scheme.
Note: If you have installed the Software Development Kit, see the API Reference Guide for C or the API Reference Guide for Java for more information about creating custom authentication schemes.
Authentication can be configured to run over a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connection. SSL is a method of establishing an encrypted connection between a client and a server using digital certificates to initiate the connection, and to establish a proof of identity.
The following authentication scheme types are configured to use an SSL connection:
Note: An asterisk denotes that an SSL connection is optional.
|
Copyright © 2012 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|