When a user request, such as a GET, PUT, or POST, is received by a Web Agent, the Web Agent forwards the request to the Policy Server. The Web Agent uses multiple threads to provide high performance processing of many requests. The Policy Server must provide enough sockets (one for each thread) to support communication with the Web Agent.
The Policy Service combines the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting functions in to one service that listens, by default, on port 44443 for Web Agent requests. By default, a Web Agent requires two sockets to communicate with the Policy Server on port 44443.
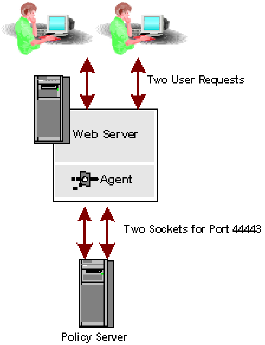
Note: The Policy Server Management Console lists the default ports of 44442, 44443, and 44441 for Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting, respectively, for 5.x Web Agent mixed-mode compatibility with the Policy Server. A 5.x Web Agent opens sockets across all three ports to communicate with a Policy Server service.
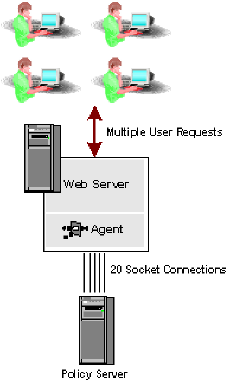
The total number of sockets used by the Web Agent is one factor you must consider when determining how many Web Agents a Policy Server can support. More information exists in How to Determine When to Add Policy Servers.
When the load requirements increase as more users attempt to access the resource protected by the Web Agent, the Web Agent uses more socket connections for each port. By default, the maximum number of socket connections that the Web Agent can sustain through port 44443 is 20.
| Copyright © 2010 CA. All rights reserved. | Email CA about this topic |