

The authentication context indicates how a user authenticated at an Identity Provider. The Identity Provider includes the authentication context in an assertion at the request of a Service Provider or based on configuration at the Identity Provider. A Service Provider can require information about the authentication process to establish a level of confidence in the assertion before granting access to resources.
When the Identity Provider receives a request, it compares the value of the <RequestedAuthnContext> element to the authentication context. The comparison is based on a comparison value sent in the request from the Service Provider. If the comparison is successful, the Identity Provider includes the authentication contexts in the assertion it returns to the Service Provider. If validation is configured, the Service Provider validates the incoming authentication context with the value it requested.
Verify that the policy administrators meet the following minimum knowledge requirements:
The following figure shows the configuration process for each partner. CA SiteMinder® Federation does not have to be installed at each site.
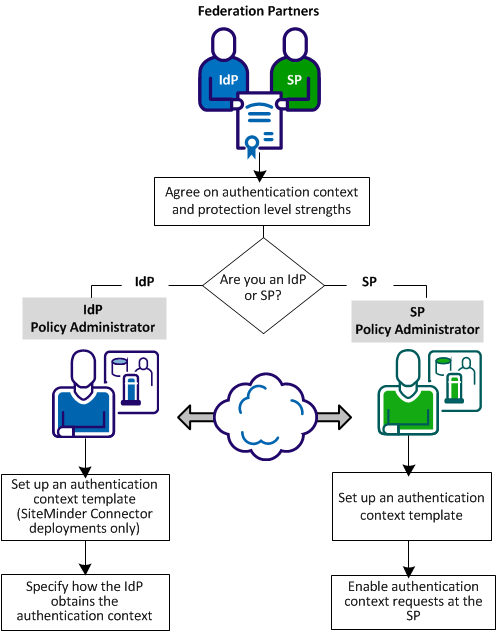
Complete the following steps to configure authentication context processing:
When single sign-on is initiated at the IdP, authentication context processing follows these steps:
Based on a configured authentication context template, the AuthnContext class is mapped to the protection level for the session.
The hard-coded URI you specify is added to the assertion.
When single sign-on is initiated at the SP, authentication context processing follows these steps:
Based on a configured authentication context template, the AuthnContext class is mapped to the protection level for the session.
The hard-coded URI you specify is added to the assertion.
If the SP includes multiple authentication context URIs in the request, the classes are compared one-by-one in sequential order against the context for the session. At the first successful comparison, the IdP adds the session authentication context to the assertion.
If the comparison is not successful, the transaction is terminated with a "noauthncontext" status response.
The following table shows examples of how an authentication context is processed depending on the comparison attribute sent in the authentication context request.
|
SP-requested Authentication Context |
Comparison Attribute Value |
IdP-configured Authentication Context |
Status Response |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Password |
exact |
InternetProtocol |
NoAuthnContext |
|
Password |
minimum |
InternetProtocol |
NoAuthnContext |
|
Password |
better |
InternetProtocol |
NoAuthnContext |
|
InternetProtocol |
exact |
InternetProtocol |
Success |
|
InternetProtocol |
minimum |
InternetProtocol |
Success |
|
InternetProtocol |
maximum |
InternetProtocol |
Success |
|
InternetProtocol |
maximum |
Password |
NoAuthnContext |
|
InternetProtocol |
better |
Password |
Success |
|
Copyright © 2013 CA.
All rights reserved.
|
|